
电子科发女学光电科学与工程学院 SCHOOL OF OPTOELECTRONIC SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING OF UESTC 4.Fourier Transform of Functions of One Continuous Variable Representation of Fourier transform in polar coordinates F(n)=|F(e四 Power spectrum P()=F()=R()+I2(u)
( ) ( ) j ( ) F F e = ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 2 2 P F R I = = + 4. Fourier Transform of Functions of One Continuous Variable ◼ Representation of Fourier transform in polar coordinates ◼ Power spectrum
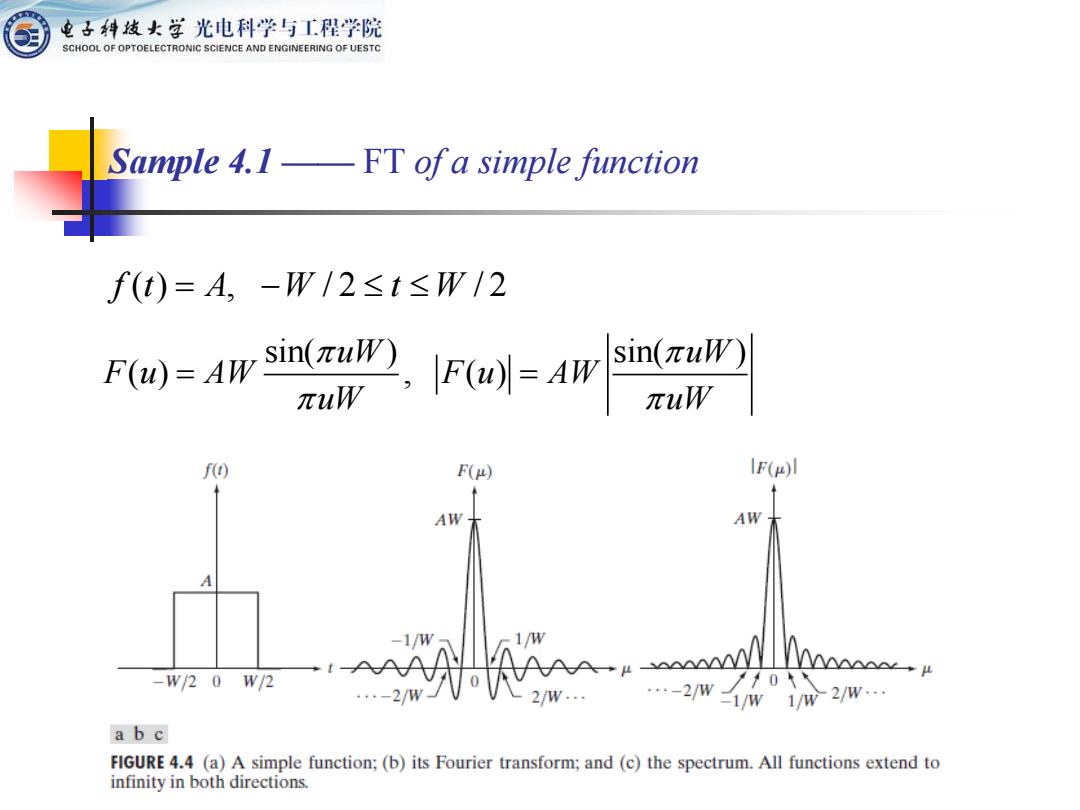
电子科发女学光电科学与工程学院 SCHOOL OF OPTOELECTRONIC SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING OF UESTC Sample 4.1-FT of a simple function f(t)=A,-W/2≤t≤W/2 F(u)=AWS w.a-4 πu f(t) F() IF() AW AW 7 -1/W -w/20w/2 -2m02w ab c FIGURE 4.4 (a)A simple function;(b)its Fourier transform;and(c)the spectrum.All functions extend to infinity in both directions
Sample 4.1 —— FT of a simple function f t A W t W ( ) , / 2 / 2 = − sin( ) sin( ) ( ) , ( ) uW uW F u AW F u AW uW uW = =
电子科发女学光电科学与工程学院 SCHOOL OF OPTOELECTRONIC SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING OF UESTC Sample 4.2-FT of impulse and impulse train t-0,impulse F(u)=6)e2di=∫re2wδ(0)dt=e20=e°=l t-to impulse F(u)=(t-t)e pudi=e(t-to)di=e cos(2mt)-jsin(2t)
Sample 4.2 —— FT of impulse and impulse train ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 2 0 2 0 1 j t j t j F t e dt e t dt e e + + − − − − − = = = = = ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 0 0 0 2 2 2 0 0 cos 2 sin 2 j t j t j t F t t e dt e t t dt t j t e + + − − − − − = − = − = = − ◼ t=0, impulse ◼ t=t0 , impulse

电子科发女学光电科学与工程学院 SCHOOL OF OPTOELECTRONIC SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING OF UESTC Sample 4.2-FT of impulse and impulse train impulse train w=2ce品 2πn 2πn 502e0 s例-收w-s位合-点合2品
Sample 4.2 —— FT of impulse and impulse train ◼ impulse train ( ) ( ) 2 2 1 1 1 n n j t j t T T T n n n n S s t e e T T T T =− =− =− = = = = − ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 2 2 2 2 0 2 2 2 , 1 1 1 1 1 n j t T T n n n n T T j t j t T T n T T T n j t T T n s t c e c s t e dt t e dt e T T T T s t e T =− − − − − =− = = = = = =

电子科发女学光电科学与工程学院 SCHOOL OF OPTOELECTRONIC SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING OF UESTC 5.Convolution Definition f(t)*h()=f()h(t-z)dr and FT 3()h(()h(-)drnd =∫fh-)e2h: =f(lH(We2rr=H(四F(四 Convolution theorem f(t)*h(t)台F()H() f(t)h(t)台F()*H()
f t h t f h t d ( ) * ( ) ( ) ( ) + − = − ◼ Definition and FT ◼ Convolution theorem 5. Convolution ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 2 2 * j t j t j f t h t f h t d e dt f h t e dt d f H e d H F − − − − − − − − = − = − = =