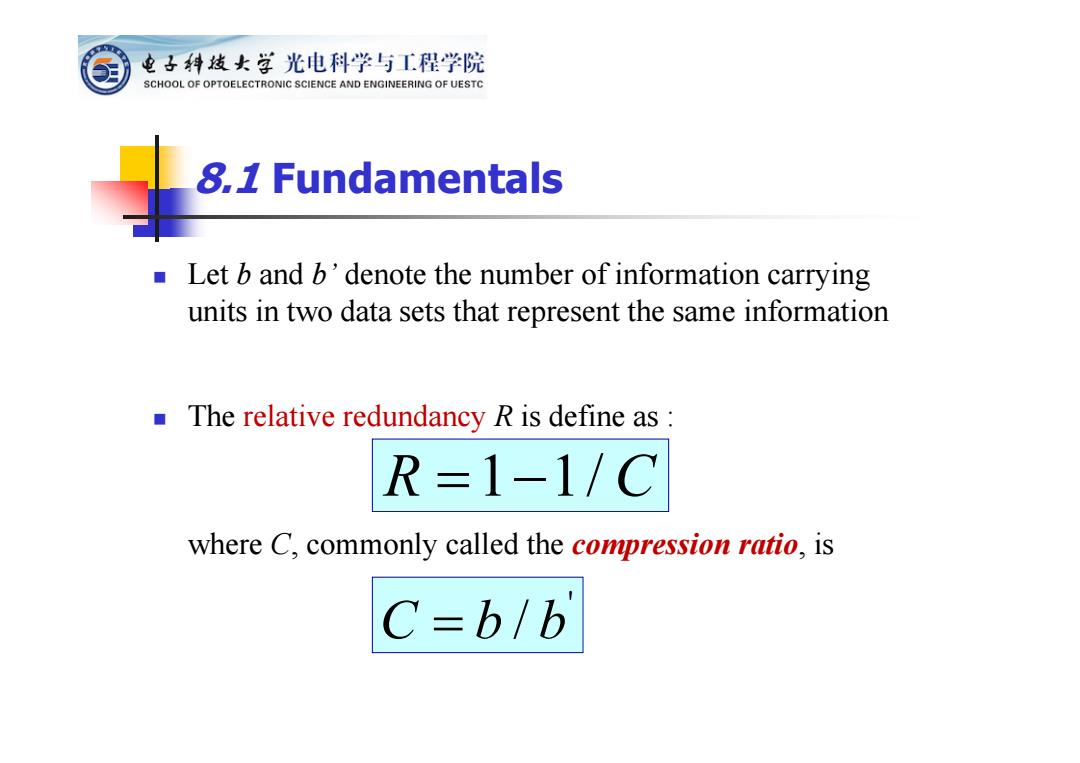
电子科技女学光电科学与工程学院 SCHOOL OF OPTOELECTRONIC SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING OF UESTC 8,1 Fundamentals ■ Let b and b'denote the number of information carrying units in two data sets that represent the same information The relative redundancy R is define as: R=1-1/C where C,commonly called the compression ratio,is C=b/b
Let b and b’ denote the number of information carrying units in two data sets that represent the same information The relative redundancy R is define as : where C, commonly called the compression ratio, is R 1 1/ C 8.1 Fundamentals ' C bb /

电子科发女学光电科学与工程学院 SCHOOL OF OPTOELECTRONIC SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING OF UESTC 8,1 Fundamentals ■Ifb=b'C=1andR=0 no redundancy ■Ifb>b'C→and R→1 high redundancy ■Ifb<b'C→0andR→-oo> undesirable In Image compression,3 basic redundancy can be identified 。Coding redundancy Spatial and Temporal Redundancy Irrelevant Information
If b = b’ , C = 1 and R = 0 no redundancy If b >> b’ , C and R high redundancy If b << b’ , C and R undesirable In Image compression , 3 basic redundancy can be identified Coding Redundancy Spatial and Temporal Redundancy Irrelevant Information 1 0 8.1 Fundamentals

电子科发女学光电科学与工程学院 SCHOOL OF OPTOELECTRONIC SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING OF UESTC 8,1 Fundamentals ab c FIGURE 8.1 Computer generated 256 X 256 X 8 bit images with(a)coding redundancy,(b)spatial redundancy, and (c)irrelevant information.(Each was designed to demonstrate one principal redundancy but may exhibit others as well.) Coding Redundancy Spatial and Temporal Redundancy Irrelevant Information
Coding Redundancy Spatial and Temporal Redundancy Irrelevant Information 8.1 Fundamentals
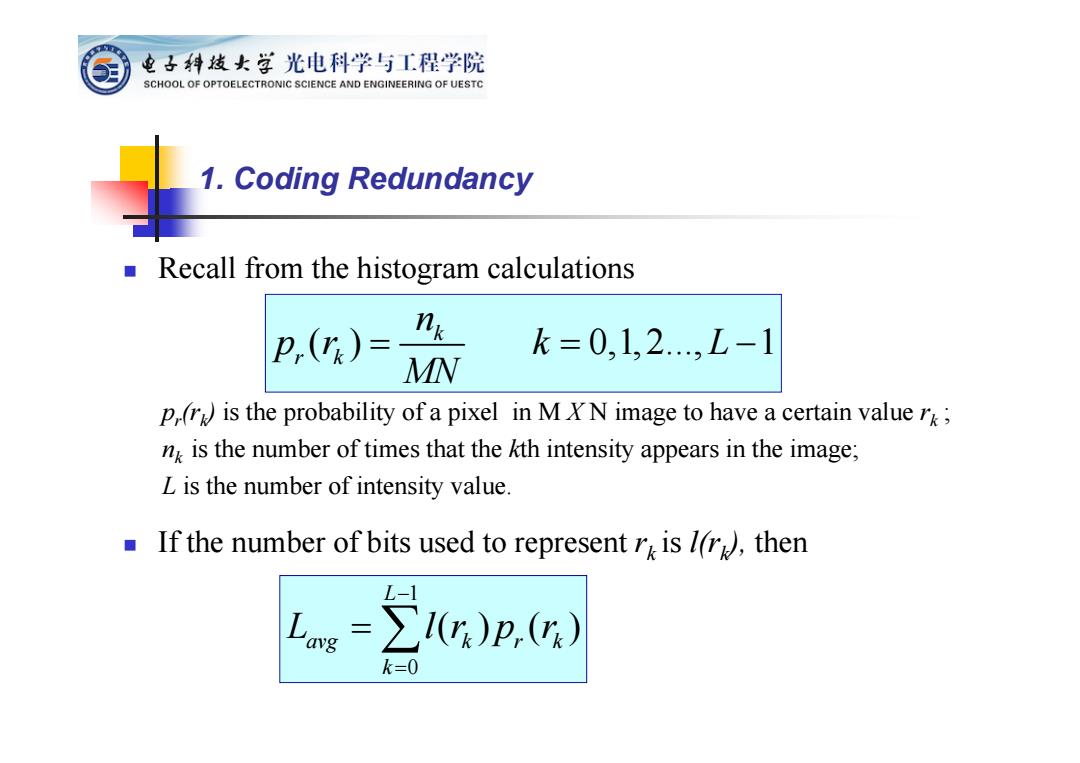
电子科技女学光电科学与工程学院 SCHOOL OF OPTOELECTRONIC SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING OF UESTC 1.Coding Redundancy Recall from the histogram calculations 卫() k=0,1,2,L-1 MN p,(r)is the probability of a pixel in M XN image to have a certain value rk; nk is the number of times that the kth intensity appears in the image; L is the number of intensity value. If the number of bits used to represent r is I(r),then L = ∑1)p,) k=0
Recall from the histogram calculations pr(rk) is the probability of a pixel in M X N image to have a certain value rk ; nk is the number of times that the kth intensity appears in the image; L is the number of intensity value. If the number of bits used to represent rk is l(rk), then ( ) 0,1, 2..., 1 k r k n pr k L MN 1. Coding Redundancy 1 0 () () L avg k r k k L lr p r
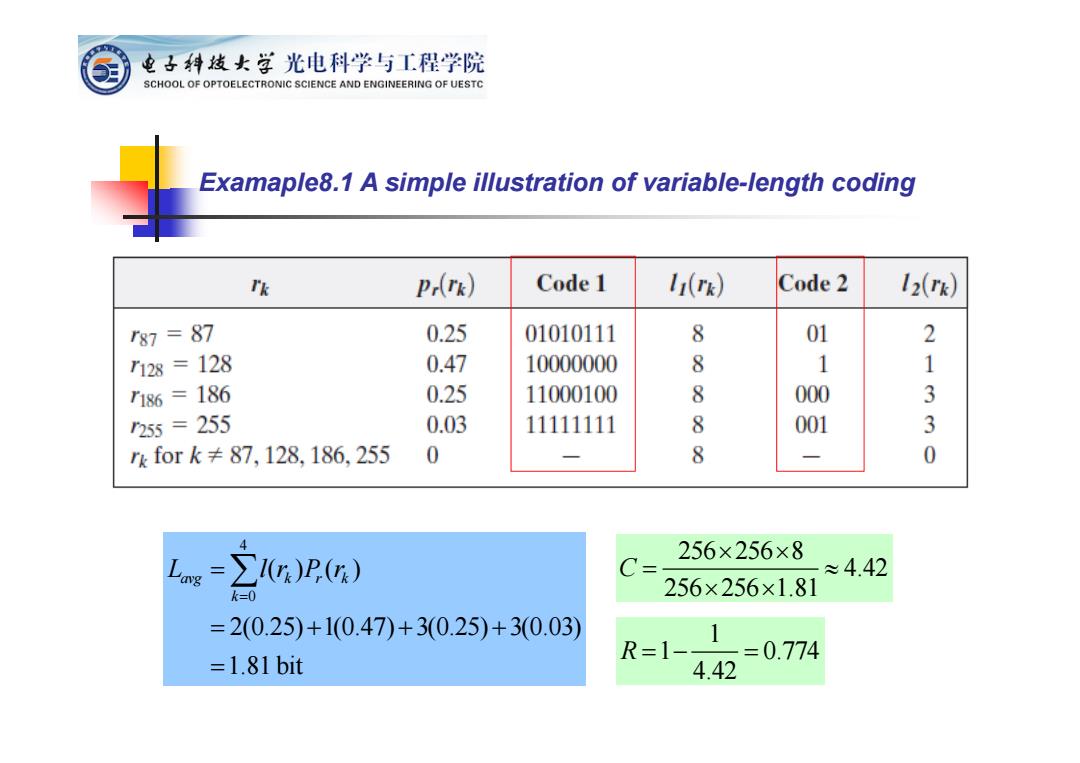
电子科技女学光电科学与工程学院 SCHOOL OF OPTOELECTRONIC SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING OF UESTC Examaple8.1 A simple illustration of variable-length coding Tk p() Code 1 1i(rk) Code 2 12(k) r87=87 0.25 01010111 8 01 2 128=128 0.47 10000000 8 1 1 186=186 0.25 11000100 8 000 3 255=255 0.03 11111111 8 001 3 rk for k≠87,128,186,255 0 8 0 4 256×256×8 1)P) C= ≈4.42 k=0 256×256×1.81 =2(0.25)+1(0.47)+3(0.25)+3(0.03) =1.81bit R=11 =0.774 4.42
4 0 () () 2(0.25) 1(0.47) 3(0.25) 3(0.03) 1.81 bit avg k r k k L lr P r 1 1 0.774 4.42 R Examaple8.1 A simple illustration of variable-length coding 256 256 8 4.42 256 256 1.81 C