
1 Special Matrices 1 Special Matrices 1/60
1 Special Matrices 1 Special Matrices 1 / 60
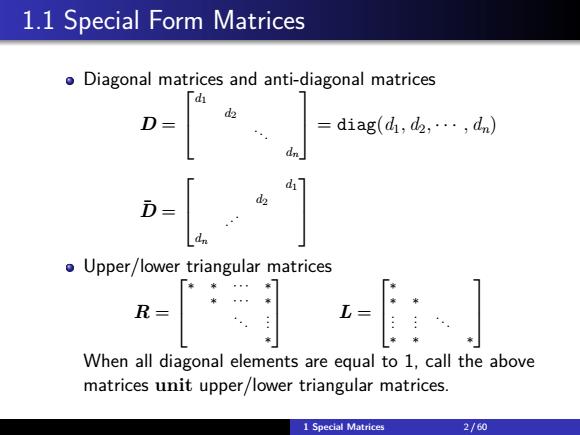
1.1 Special Form Matrices oDiagonal matrices and anti-diagonal matrices 、 = diag(d,d2,…,dn) D- Upper/lower triangular matrices R-t When all diagonal elements are equal to 1,call the above matrices unit upper/lower triangular matrices. 1 Special Matrices 2/60
1.1 Special Form Matrices Diagonal matrices and anti-diagonal matrices D = d1 d2 . . . dn = diag(d1, d2, · · · , dn) D¯ = d1 d2 . . . dn Upper/lower triangular matrices R = ∗ ∗ · · · ∗ ∗ · · · ∗ . . . . . . ∗ L = ∗ ∗ ∗ . . . . . . . . . ∗ ∗ ∗ When all diagonal elements are equal to 1, call the above matrices unit upper/lower triangular matrices. 1 Special Matrices 2 / 60
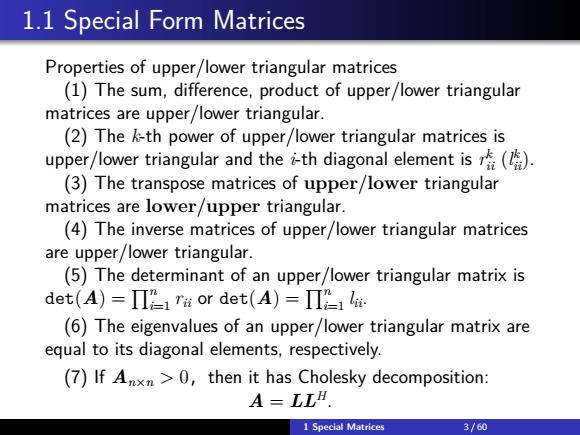
1.1 Special Form Matrices Properties of upper/lower triangular matrices (1)The sum,difference,product of upper/lower triangular matrices are upper/lower triangular. (2)The k-th power of upper/lower triangular matrices is upper/lower triangular and the i-th diagonal element is(). (3)The transpose matrices of upper/lower triangular matrices are lower/upper triangular. (4)The inverse matrices of upper/lower triangular matrices are upper/lower triangular. (5)The determinant of an upper/lower triangular matrix is det(A)=II21 T#or det(A)=IIP14. (6)The eigenvalues of an upper/lower triangular matrix are equal to its diagonal elements,respectively. (7)If Anxn>0,then it has Cholesky decomposition: A=LLH. 1 Special Matrices 3/60
1.1 Special Form Matrices Properties of upper/lower triangular matrices (1) The sum, difference, product of upper/lower triangular matrices are upper/lower triangular. (2) The k-th power of upper/lower triangular matrices is upper/lower triangular and the i-th diagonal element is r k ii (l k ii). (3) The transpose matrices of upper/lower triangular matrices are lower/upper triangular. (4) The inverse matrices of upper/lower triangular matrices are upper/lower triangular. (5) The determinant of an upper/lower triangular matrix is det(A) = Qn i=1 rii or det(A) = Qn i=1 lii. (6) The eigenvalues of an upper/lower triangular matrix are equal to its diagonal elements, respectively. (7) If An×n > 0,then it has Cholesky decomposition: A = LLH . 1 Special Matrices 3 / 60
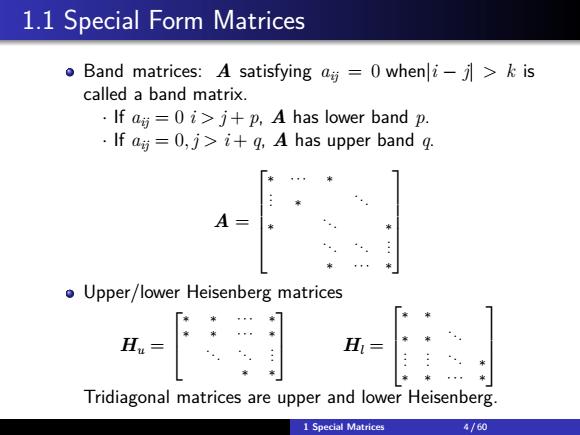
1.1 Special Form Matrices Band matrices:A satisfying ag =0 wheni->is called a band matrix. If a=0i>j+p,A has lower band p. ·lfa时=0,j>i+g,A has upper band g. A= o Upper/lower Heisenberg matrices H.- Hu= Tridiagonal matrices are upper and lower Heisenberg. 1 Special Matrices 4/60
1.1 Special Form Matrices Band matrices: A satisfying aij = 0 when|i − j| > k is called a band matrix. · If aij = 0 i > j + p, A has lower band p. · If aij = 0, j > i + q, A has upper band q. A = ∗ · · · ∗ . . . ∗ . . . ∗ . . . ∗ . . . . . . . . . ∗ · · · ∗ Upper/lower Heisenberg matrices Hu = ∗ ∗ · · · ∗ ∗ ∗ · · · ∗ . . . . . . . . . ∗ ∗ Hl = ∗ ∗ ∗ ∗ . . . . . . . . . . . . ∗ ∗ ∗ · · · ∗ Tridiagonal matrices are upper and lower Heisenberg. 1 Special Matrices 4 / 60

1.1 Special Form Matrices o Basic matrices:defined by the outer product of an m x 1 basic vector and an n x 1 basic vector: xn)em(e7 Properties: ()写mxx=Emx (2)(E写x)T=Exm网 m n )4=盆 amx列 (4)E$xmAX”=aEX (5)det(x=0, (m=n>1) 1 Special Matrices 5/60
1.1 Special Form Matrices Basic matrices: defined by the outer product of an m × 1 basic vector and an n × 1 basic vector: E (m×n) ij = e (m) i (e (n) j ) T . Properties: (1) E (m×n) ij E (n×r) kl = δjkE (m×r) il (2) (E (m×n) ij ) T = E (n×m) ji (3) A = Pm i=1 Pn j=1 aijE (m×n) ij (4) E (s×m) ij AE(n×r) kl = ajkE (s×r) il (5) det(E (m×n) ij ) = 0, (m = n > 1) 1 Special Matrices 5 / 60