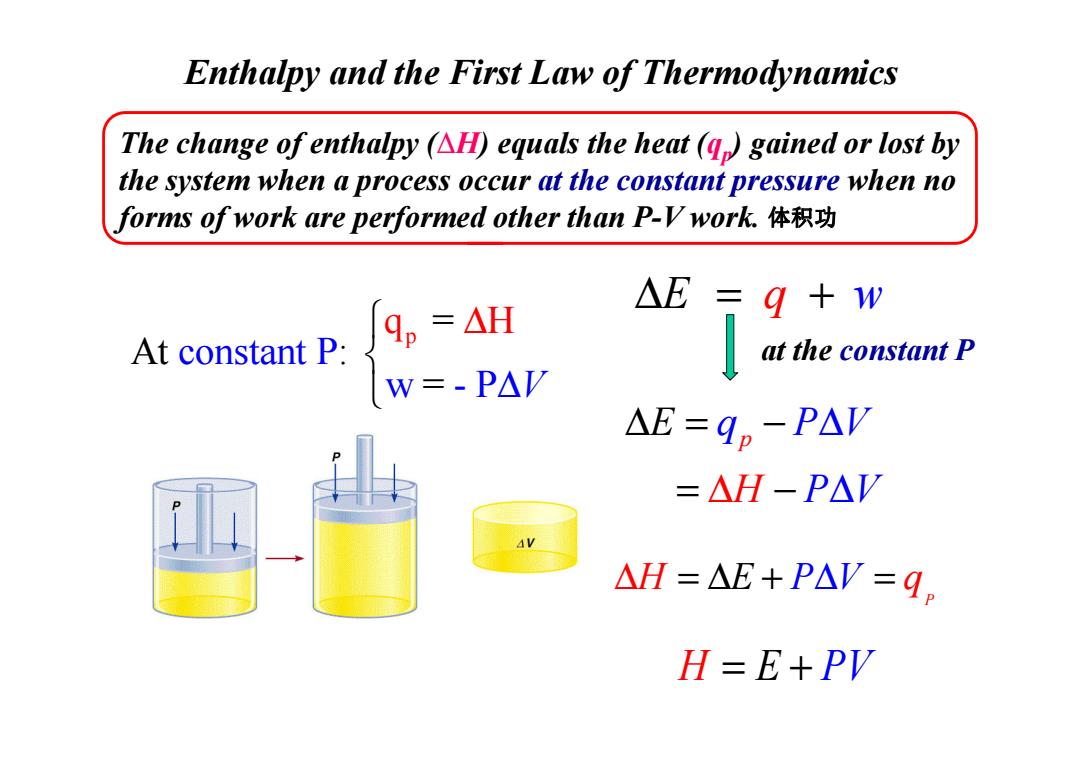
Enthalpy and the First Law of Thermodynamics The change of enthalpy (AH)equals the heat(q)gained or lost by the system when a process occur at the constant pressure when no forms of work are performed other than P-V work.体积功 △E= 9+w At constant P: qp=△H at the constant P w=-P△V AE=9p-PAV =△H-P△V AV △H=△E+PAV=q。 H=E+PV
Enthalpy and the First Law of Thermodynamics ∆ = + E q w p q = constant H At : P w = - P V ∆ ∆ The change of enthalpy (∆H) equals the heat (qp) gained or lost by the system when a process occur at the constant pressure when no forms of work are performed other than P-V work. at the constant P 体积功 w = - P ∆ V p q P V H E P V ∆ = = − ∆ ∆ ∆ − P ∆H = ∆ + = E P V∆ q H = + E P V
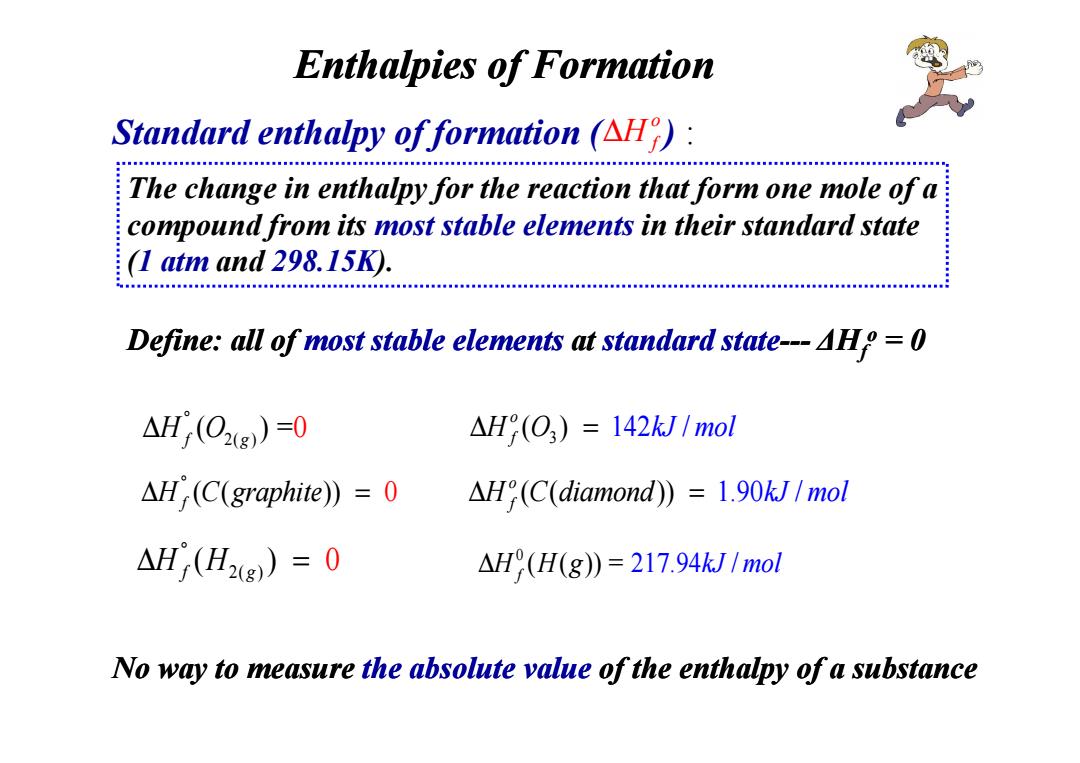
Enthalpies of Formation Standard enthalpy of formation (AH): The change in enthalpy for the reaction that form one mole of a compound from its most stable elements in their standard state (I atm and 298.15K) Define:all of most stable elements at standard state---AHp =0 △H(02g)-0 △H9(O3)=142kJ1mol △Hr(C(graphite)=0 AH(C(diamond))=1.90kJ/mol △H(H2g))=0 AH(H(g))=217.94kJ/mol No way to measure the absolute value of the enthalpy of a substance
Standard enthalpy of formation ( ) : Enthalpies of Formation o ∆H f The change in enthalpy for the reaction that form one mole of a compound from its most stable elements in their standard state (1 atm and 298.15K). Define: all of most stable most stable elements elements at standard state--- ∆Hf o = 0 No way to measure the absolute value of the enthalpy of a substance 2( ) ( ) = 0 H Of g ° ∆ ( ( )) 0 H C graphite f ° ∆ = 3 ( ) 142 / o f ∆ = H O kJ m l o ( ( )) 1.90 / o H C dia f ∆ = mo n d kJ mol 0 ( ( )) = 217.94 / f ∆H H g kJ mo l 2( ) ( ) 0 H Hf g ° ∆ =
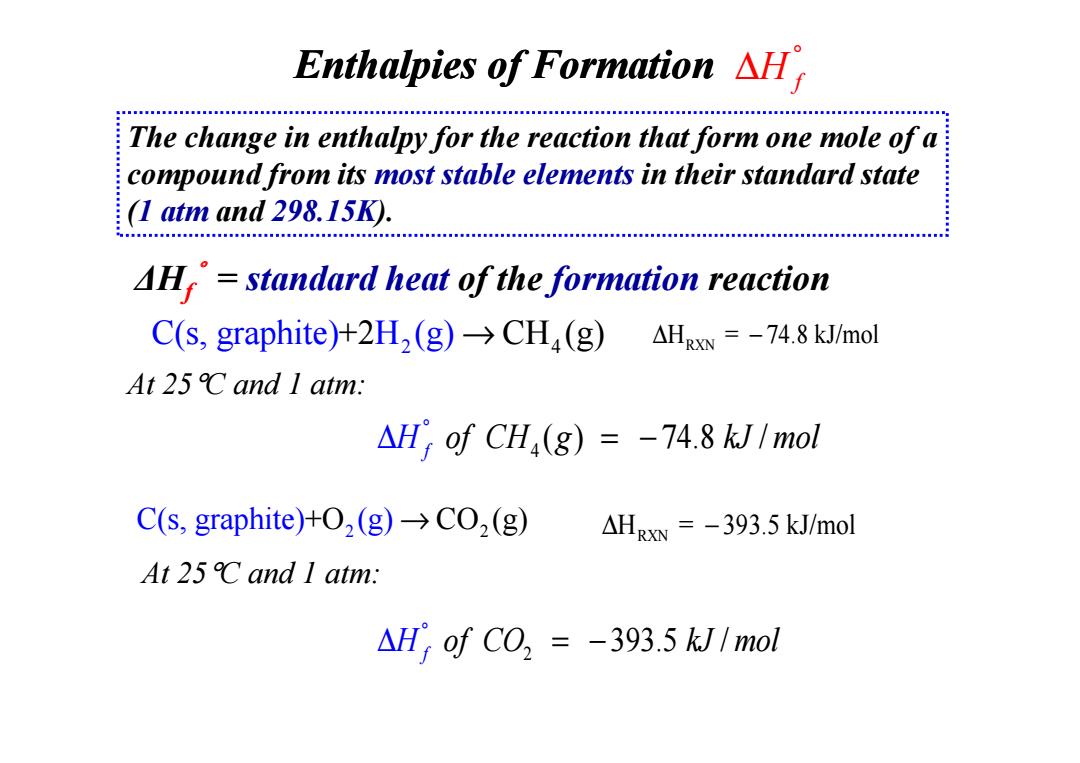
Enthalpies of Formation AH The change in enthalpy for the reaction that form one mole of a compound from its most stable elements in their standard state (1 atm and 298.15K). AH=standard heat of the formation reaction C(s,graphite)+2H2(g)>CHa(g)AHRxN =-74.8 kJ/mol At25℃and1atm.: △H)ofCH,(g)=-74.8kJ1mol C(s,graphite)+2(g)>CO2 (g) △HR=-393.5kJ/mol At25℃and1atm.: AH;of CO =-393.5 kJ/mol
C(s, graphite) H + 2 4 2 CH (g) → (g) At 25°C and 1 atm: ∆ − H = 74.8 kJ/mol RXN ∆Hf°= standard heat of the formation reaction Enthalpies of Formation The change in enthalpy for the reaction that form one mole of a compound from its most stable elements in their standard state (1 atm and 298.15K). H f ° ∆ At 25°C and 1 atm: 4 ( ) 74.8 / f H of CH g kJ mol ° ∆ = − C(s, graphite) (g +O2 CO 2 ) → (g) ∆ − H = 393.5 kJ/mol RXN 2 393.5 / f H of C mol O kJ ° ∆ = − At 25°C and 1 atm: