
H Electron Affinity He -73 >0 Li Be B C N F Ne -60 >0 -27 -122 >0 -141 -328 >0 Na Mg Al Si P S CI Ar -53 0 -43 -134 -72 -200 -349 >0 K Ca Ga Ge As Se Br Kr -48 -2 -30 -119 -78 -195 -325 >0 Rb Sr In Sn Sb Te I Xe -47 -5 -30 -107 -103 -190 -295 >0 1A 2A 3A 4A 5A 6A 7A 8A Copyright 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc Electron affinities for the s-and p-block elements in the first five rows of the periodic table. The more negative the electron affinity,the greater the attraction of the atom for an electron
Electron Affinity EEA<0 Electron affinities for the s- and p-block elements in the first five rows of the periodic table. The more negative the electron affinity, the greater the attraction of the atom for an electron

Periodic Table The highest electron affinity The lowest ionization energy
The highest electron affinity Periodic Table The lowest ionization energy
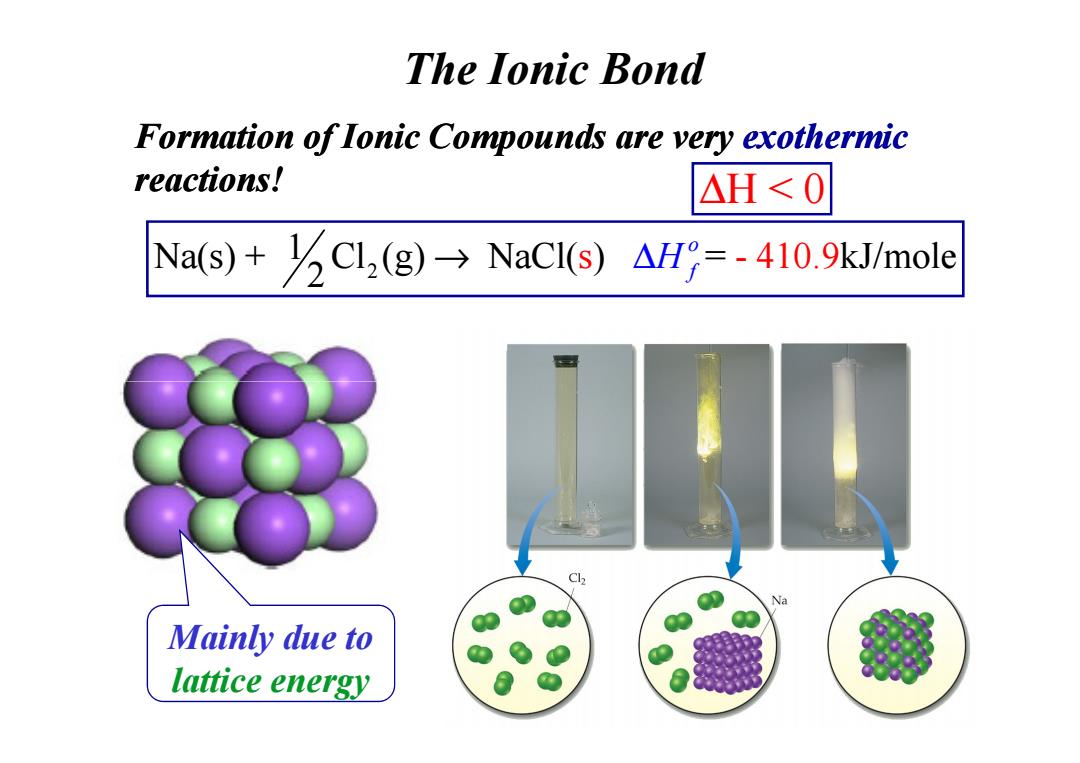
The lonic Bond Formation of lonic Compounds are very exothermic reactions! △H<0 Na(s)+Cl(g)NaCI(s)AH=-410.9kJ/mole Cl Na Mainly due to lattice energy
Formation of Ionic Compounds are very exothermic reactions! The Ionic Bond ∆H < 0 2 Na(s) + Cl (g) NaCl( ) = 1 s - 410.9kJ/mole 2 o → ∆H f Mainly due to lattice energy
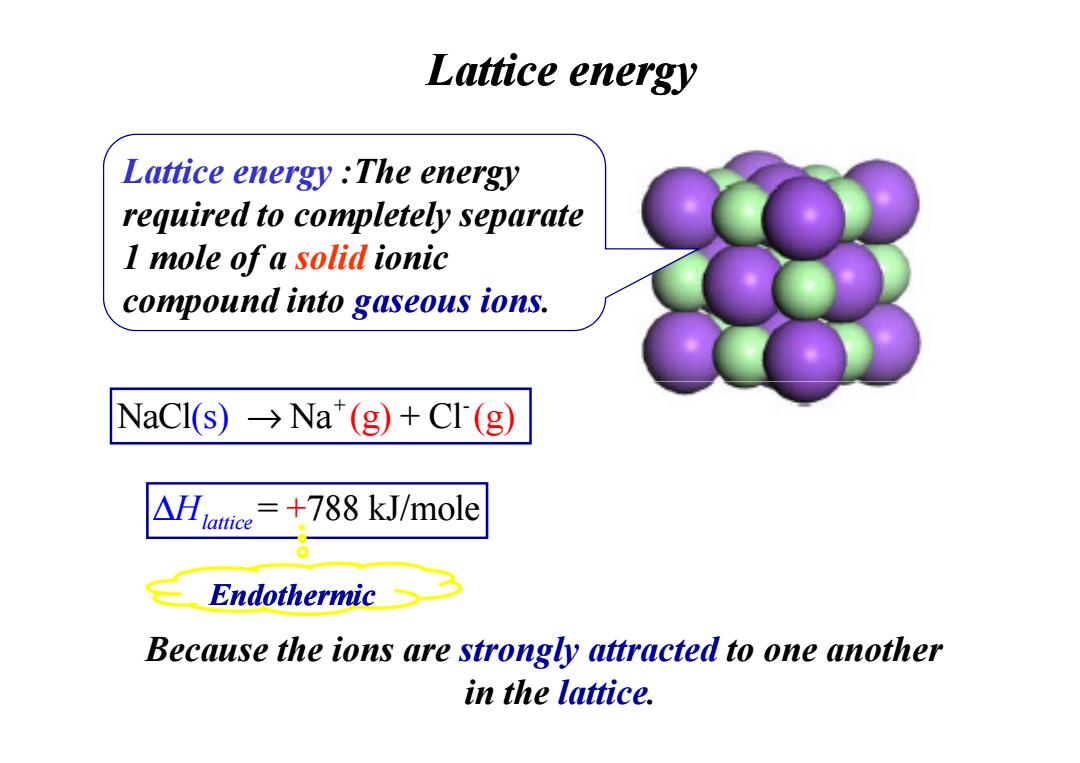
Lattice energy Lattice energy The energy required to completely separate I mole of a solid ionic compound into gaseous ions. NaCl(s)→Na(g)+CI(g) △lace =+788 kJ/mole Endothermic Because the ions are strongly attracted to one another in the lattice
Lattice energy Lattice energy :The energy required to completely separate 1 mole of a solid ionic compound into gaseous ions. + - NaCl Na + Cl ( )s → (g) (g) Because the ions are strongly attracted to one another in the lattice. ∆Hlattice= 788 kJ/mole + Endothermic

Lattice Energy (Electrostatic Attraction) Lattice energy (E):much depends on the charges of ions,the sizes of ions and their arrangement in solid. O:the charge on the cation E=k O.the charge on the anion r the distance between the ions Compound lattice energy MgF2 2957 Q=+2,-1 Lattice energy (E) MgO 3938 Q=+2,-2 increases as O increases LiF 1036 increases as r decreases LiCI r(F)<r(CI) 853
Lattice Energy (Electrostatic Attraction) Q+ : the charge on the cation Q- : the charge on the anion r : the distance between the ions Lattice energy (E): much depends on the charges of ions, the sizes of ions and their arrangement in solid. Q Q E k r + − ⋅ = Lattice energy (E) increases as Q increases increases as r decreases lattice energy MgF2 MgO LiF LiCl 2957 3938 1036 853 Q= +2,-1 Q= +2,-2 r(F) < r(Cl) r : the distance between the ions Compound r