
Water Activity l Relationship between water and perishability l Various foods with the same water content differ significantly in perishability – Water content alone is not reliable l Importance of water associations with non-aqueous constituents to support deteriorative activities l Rates of deteriorative changes and microbial growth at normal food storage conditions often depend on water content and aw
Water Activity l Relationship between water and perishability l Various foods with the same water content differ significantly in perishability – Water content alone is not reliable l Importance of water associations with non-aqueous constituents to support deteriorative activities l Rates of deteriorative changes and microbial growth at normal food storage conditions often depend on water content and aw

Water Activity l Water activity is defined as the ratio of the vapor pressure of water in a material (p) to the vapor pressure of pure water (po) at the same temperature. l The water activity (aw) represents the ratio of the water vapor pressure of the food to the water vapor pressure of pure water under the same conditions l aw = p/po = ERH (%) / 100
Water Activity l Water activity is defined as the ratio of the vapor pressure of water in a material (p) to the vapor pressure of pure water (po) at the same temperature. l The water activity (aw) represents the ratio of the water vapor pressure of the food to the water vapor pressure of pure water under the same conditions l aw = p/po = ERH (%) / 100
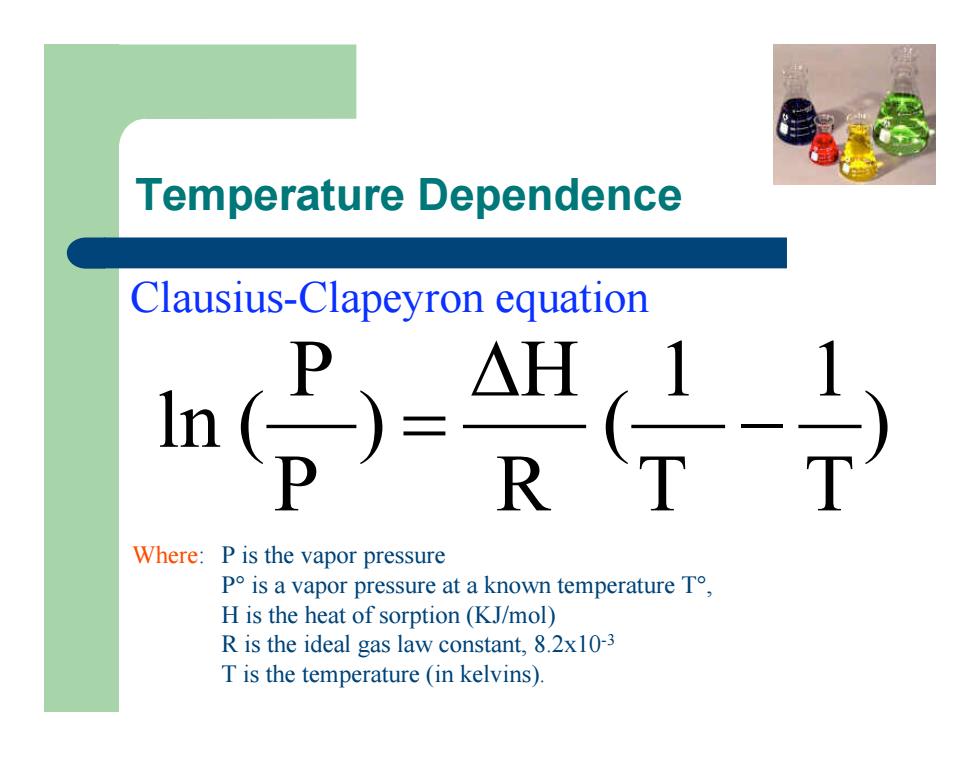
Temperature Dependence ) T 1 T 1 ( R H ) P P ln ( - D = Clausius-Clapeyron equation Where: P is the vapor pressure P° is a vapor pressure at a known temperature T°, H is the heat of sorption (KJ/mol) R is the ideal gas law constant, 8.2x10-3 T is the temperature (in kelvins)
Temperature Dependence ) T 1 T 1 ( R H ) P P ln ( - D = Clausius-Clapeyron equation Where: P is the vapor pressure P° is a vapor pressure at a known temperature T°, H is the heat of sorption (KJ/mol) R is the ideal gas law constant, 8.2x10-3 T is the temperature (in kelvins)
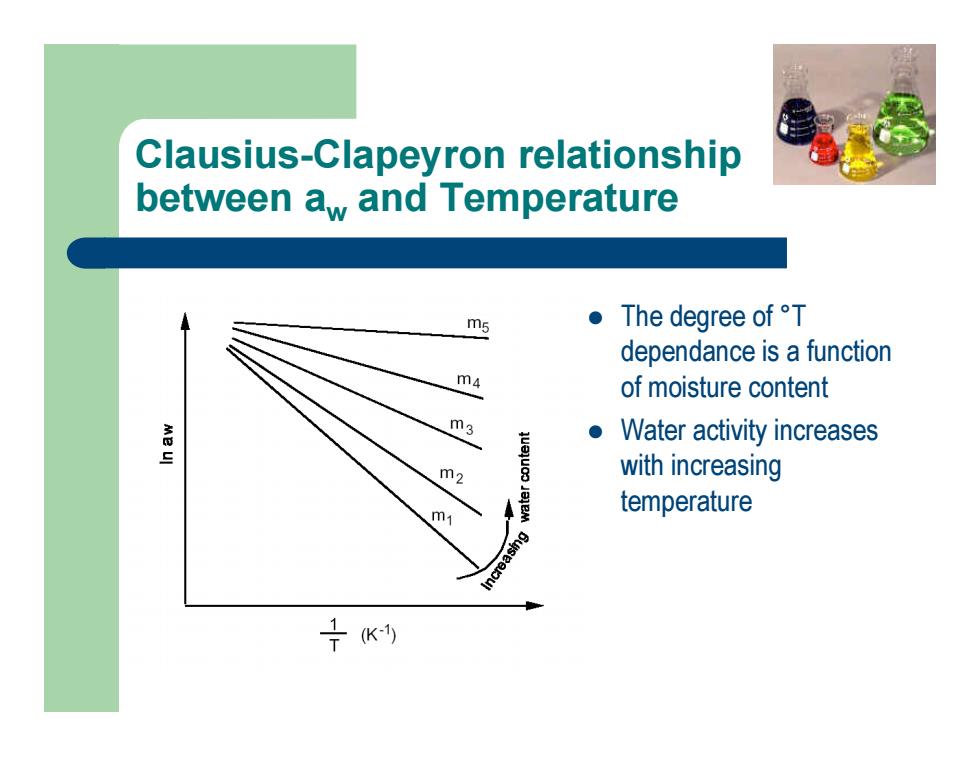
Clausius-Clapeyron relationship between aw and Temperature l The degree of °T dependance is a function of moisture content l Water activity increases with increasing temperature
Clausius-Clapeyron relationship between aw and Temperature l The degree of °T dependance is a function of moisture content l Water activity increases with increasing temperature