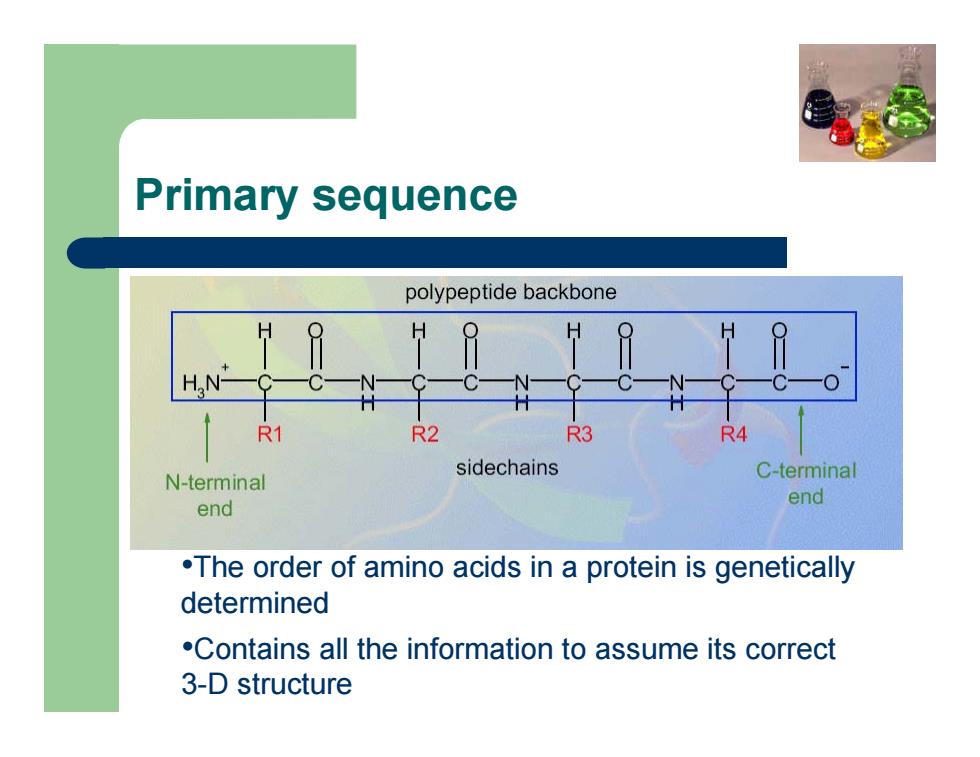
Primary sequence •The order of amino acids in a protein is genetically determined •Contains all the information to assume its correct 3-D structure
Primary sequence •The order of amino acids in a protein is genetically determined •Contains all the information to assume its correct 3-D structure
Peptides
Peptides
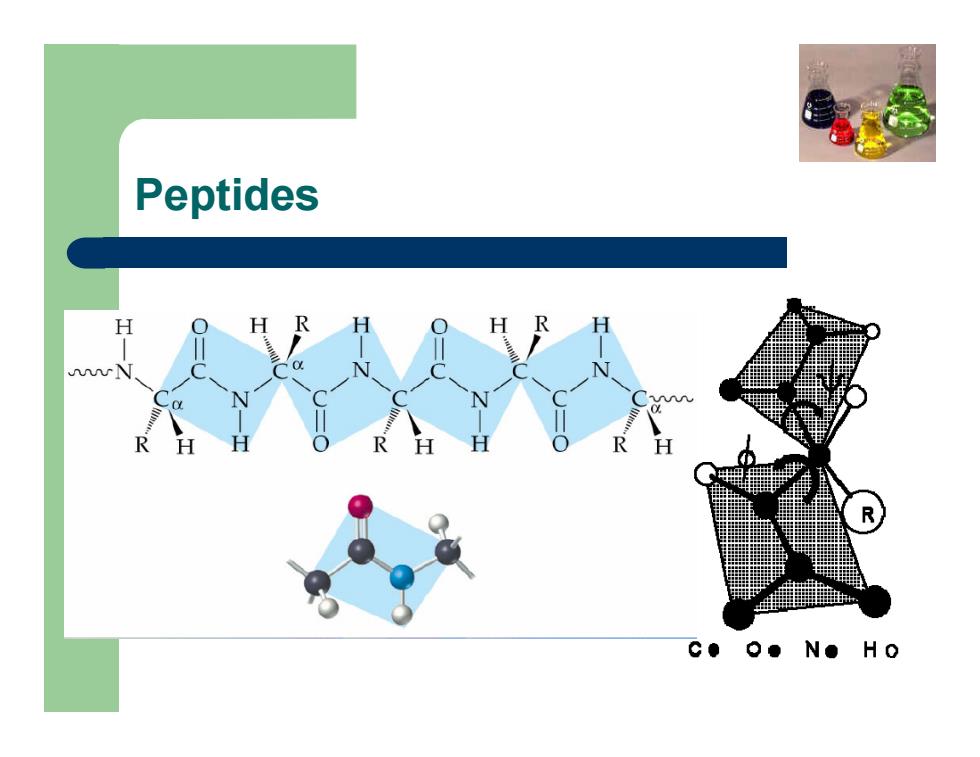
Primary structure z The oxygen and hydrogen of the CO-NH group are in the trans position as consequence of the stabilization resonance z α-carbon atoms are the only ones that may rotate freely z -NH- group does not protonate z Polypetidic chain may be presented by a series of rigid planes separated by HCR- groups
Primary structure z The oxygen and hydrogen of the CO-NH group are in the trans position as consequence of the stabilization resonance z α-carbon atoms are the only ones that may rotate freely z -NH- group does not protonate z Polypetidic chain may be presented by a series of rigid planes separated by HCR- groups
Protein Folding z Balance between Chain entropy and Solvent Entropy z Non-covalent interactions – Steric restraints: bulky side chains – Hydrogen bonding – Interchain electrostatic interactions – Hydrophobic interactions – Disulfide bonds
Protein Folding z Balance between Chain entropy and Solvent Entropy z Non-covalent interactions – Steric restraints: bulky side chains – Hydrogen bonding – Interchain electrostatic interactions – Hydrophobic interactions – Disulfide bonds
Secondary Structure z Spatial structure the polypeptide chain assumes exclusively along the axis z Native conformation – Minimal free energy z Main structures: – helix – β-structures
Secondary Structure z Spatial structure the polypeptide chain assumes exclusively along the axis z Native conformation – Minimal free energy z Main structures: – helix – β-structures