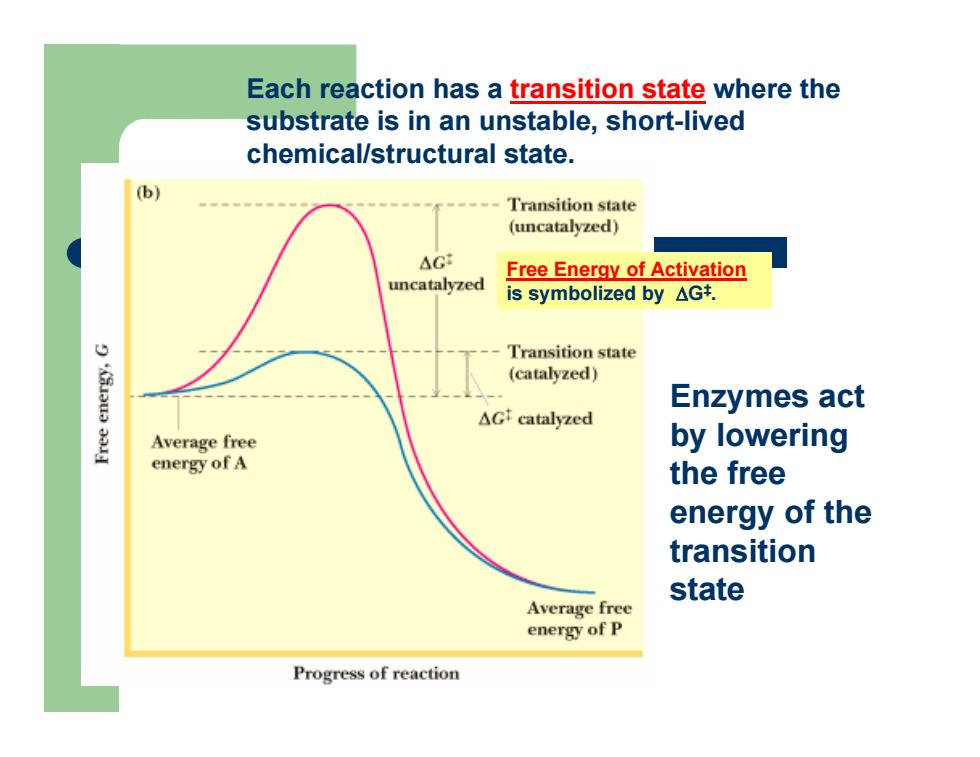
Each reaction has a transition state where the substrate is in an unstable, short-lived chemical/structural state. Free Energy of Activation is symbolized by ΔG‡. Enzymes act by lowering the free energy of the transition state
Each reaction has a transition state where the substrate is in an unstable, short-lived chemical/structural state. Free Energy of Activation is symbolized by ΔG‡. Enzymes act by lowering the free energy of the transition state
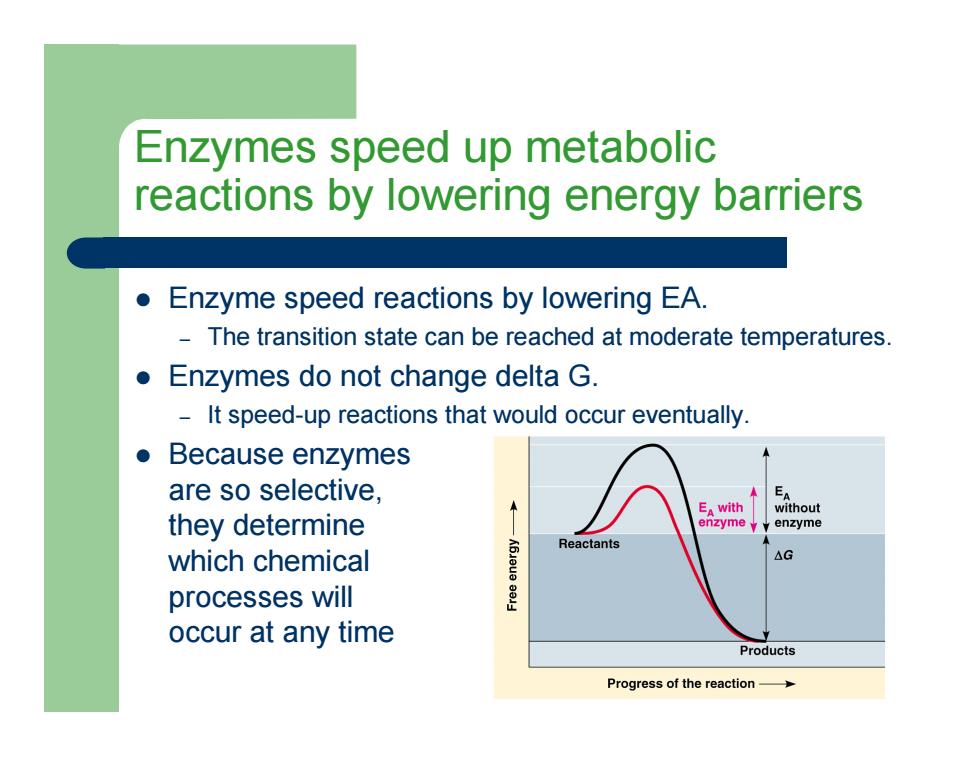
Enzymes speed up metabolic reactions by lowering energy barriers z Enzyme speed reactions by lowering EA. – The transition state can be reached at moderate temperatures. z Enzymes do not change delta G. – It speed-up reactions that would occur eventually. z Because enzymes are so selective, they determine which chemical processes will occur at any time
Enzymes speed up metabolic reactions by lowering energy barriers z Enzyme speed reactions by lowering EA. – The transition state can be reached at moderate temperatures. z Enzymes do not change delta G. – It speed-up reactions that would occur eventually. z Because enzymes are so selective, they determine which chemical processes will occur at any time
z Enzymes lower the free energy of activation by binding the transition state of the reaction better than the substrate z The enzyme must bind the substrate in the correct orientation otherwise there would be no reaction z Not a lock & key but induced fit – the enzyme and/or the substrate distort towards the transition state
z Enzymes lower the free energy of activation by binding the transition state of the reaction better than the substrate z The enzyme must bind the substrate in the correct orientation otherwise there would be no reaction z Not a lock & key but induced fit – the enzyme and/or the substrate distort towards the transition state