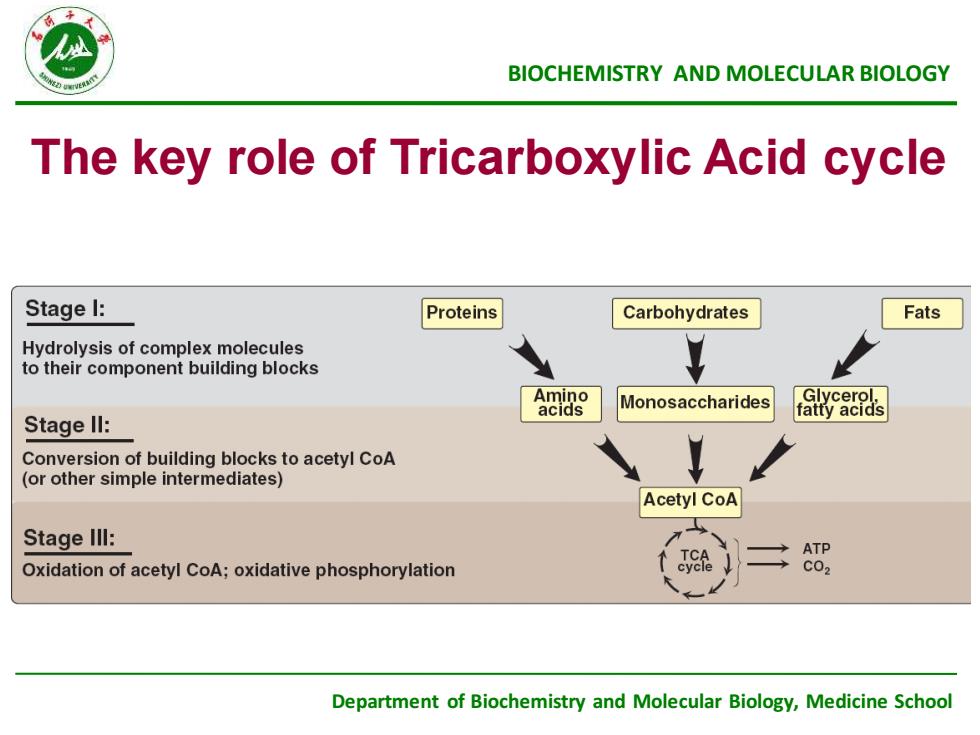
BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYThe key role of Tricarboxylic Acid cycleStage l:ProteinsCarbohydratesFatsYHydrolysisofcomplexmoleculestotheircomponentbuildingblocksAminoGlvcerolMonosaccharidesacidsfatty acidsStage ll:IConversion of building blocksto acetyl CoA(orothersimpleintermediates)AcetylCoAStage IllI:ATPCTCTeCO2Oxidationof acetyl CoA;oxidativephosphorylationDepartment of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY The key role of Tricarboxylic Acid cycle

BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYTheTricarboxylicAcidCycle1.OverviewThe tricarboxylic acid cycle (also called the Krebs cycle orthe citric acid cycle) plays several roles in metabolism. Itscentral function is the oxidation of acetyl CoA to CO, andH20.Department of Biochemistryand Molecular Biology,MedicineSchool
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY The Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle 1.Overview The tricarboxylic acid cycle (also called the Krebs cycle or the citric acid cycle) plays several roles in metabolism. Its central function is the oxidation of acetyl CoA to CO2 and H2O
BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYThe significance of Citricacid cycle> It's the final oxidative metabolic pathway wherecarbohydrates, amino acids and fatty acids converge.> This cycle provides the majority of ATP in mostanimals, including humansDepartment of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY The significance of Citric acid cycle ➢ It’s the final oxidative metabolic pathway where carbohydrates, amino acids and fatty acids converge. ➢ This cycle provides the majority of ATP in most animals, including humans
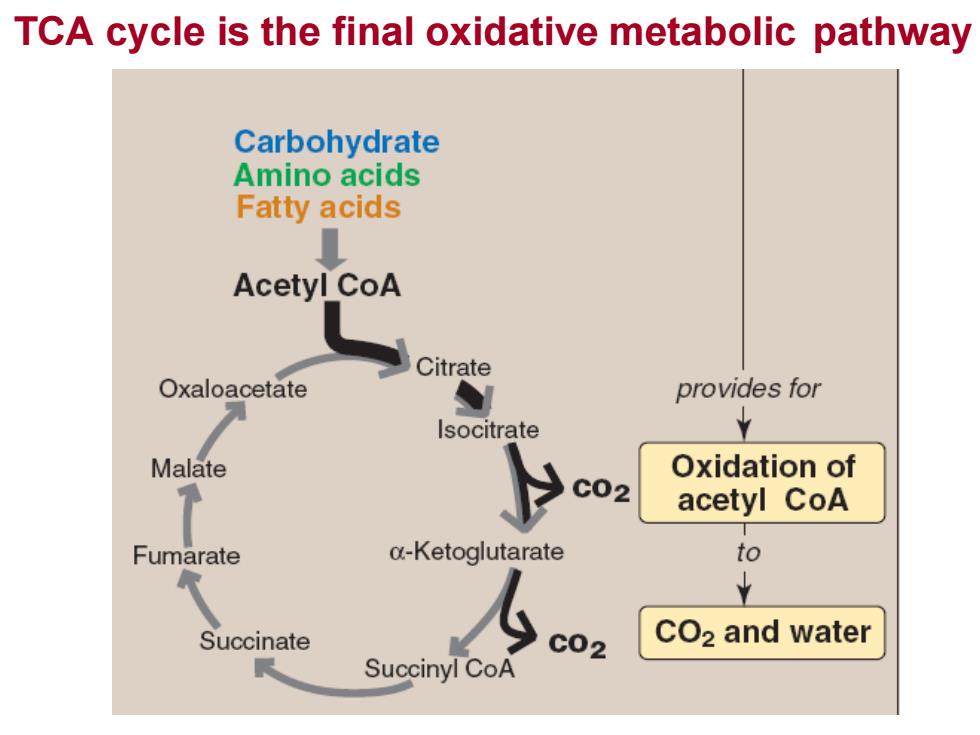
TCA cycle is the final oxidative metabolic pathwayCarbohydrateAminoacidsFatty acidsAcetylCoACitrateOxaloacetateprovidesforYIsocitrateOxidationofMalateCO2acetyl CoAtoα-KetoglutarateFumarate+LcO2andwaterSuccinateCO2Succinyl CoA
TCA cycle is the final oxidative metabolic pathway
BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYThe significance of Citricacid cycle> It's the final oxidative metabolic pathway wherecarbohydrates, amino acids and fatty acids converge> This cycle provides the majority of ATPin mostanimals, including humans.Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY The significance of Citric acid cycle ➢ It’s the final oxidative metabolic pathway where carbohydrates, amino acids and fatty acids converge. ➢ This cycle provides the majority of ATP in most animals, including humans