
Anti hypertensive Drugs
Anti hypertensive Drugs

OVERVIEW Hypertension is defined as a sustained diastolic blood pressure greater than 90 mm Hg accompanied by an elevated systolic blood pressure (>140 mm Hg)
OVERVIEW ◼ Hypertension is defined as a sustained diastolic blood pressure greater than 90 mm Hg accompanied by an elevated systolic blood pressure (>140 mm Hg)
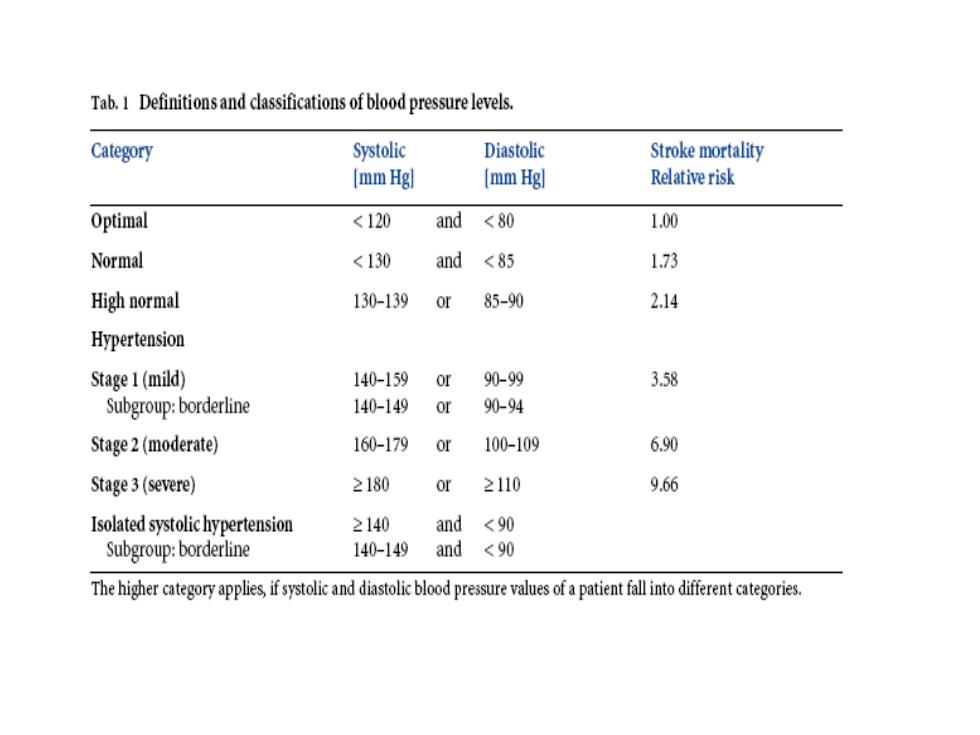
Tab.1 Definitions and classifications of blood pressure levels. Category Systolic Diastolic Stroke mortality [mm Hgl (mm Hg] Relative risk Optimal <120 and <80 1.00 Normal <130 and <85 1,73 High normal 130-1390r 85-90 2.14 Hypertension Stage 1(mild) 140-1590r 90-99 3.58 Subgroup:borderline 140-149 90-94 Stage2(moderate) 160-1790r 100-109 6.90 Stage3(severe) 2180 or 2110 9.66 Isolated systolichypertension ≥140and<90 Subgroup:borderline 140-149 and <90 The higher cateory appies if systoliand diastolicblood presurevalues ofa patient fallintoifferentcatris

can lead to congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction,renal damage, and cerebrovascular accidents
◼ can lead to congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction, renal damage, and cerebrovascular accidents

ETIOLOGY OF HYPERTENSION more than 90%of patients have essential hypertension,a disorder of unknown origin affecting the blood pressure-regulating mechanism. ■Inheritance factors Environmental factors such as a stressful lifestyle,high dietary intake of sodium,obesity
ETIOLOGY OF HYPERTENSION ◼ more than 90% of patients have essential hypertension, a disorder of unknown origin affecting the blood pressure-regulating mechanism. ◼ Inheritance factors ◼ Environmental factors such as a stressful lifestyle, high dietary intake of sodium, obesity