Principle errorClassification oforiginal erronAdjustmenterrorSetup errorBeforeMachinetoolerrormachiningStaticerrorFixture errorCutting tool manu errorOrigianlDeformationunderforceerror(原Thermaldeformation始误差In machiningDynamic errorCutting tool wearDeformationbyinnerstressAftermachiningInspection error
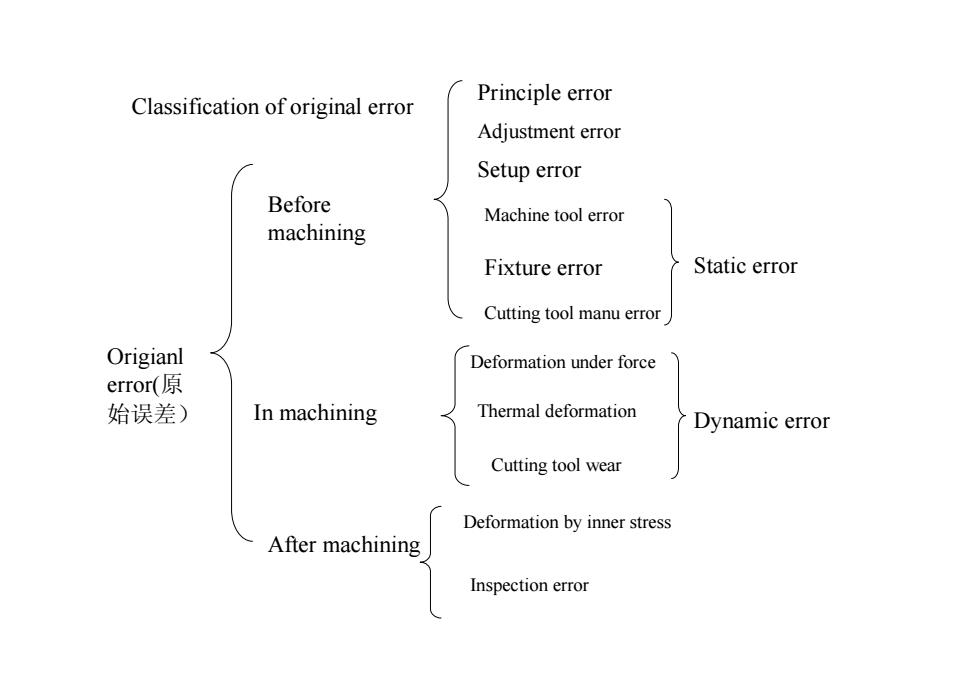
Classification of original error Origianl error(原 始误差) Before machining In machining After machining Principle error Adjustment error Setup error Machine tool error Fixture error Cutting tool manu error Deformation under force Thermal deformation Cutting tool wear Deformation by inner stress Inspection error Dynamic error Static error
WeightdeformationDeformationGeometricunderaccuracyofthecuttingforcemachinetoolThermaldeformationControl system accuracyWorkpieceTool wearaccuracyandLocationclampingaccuracy
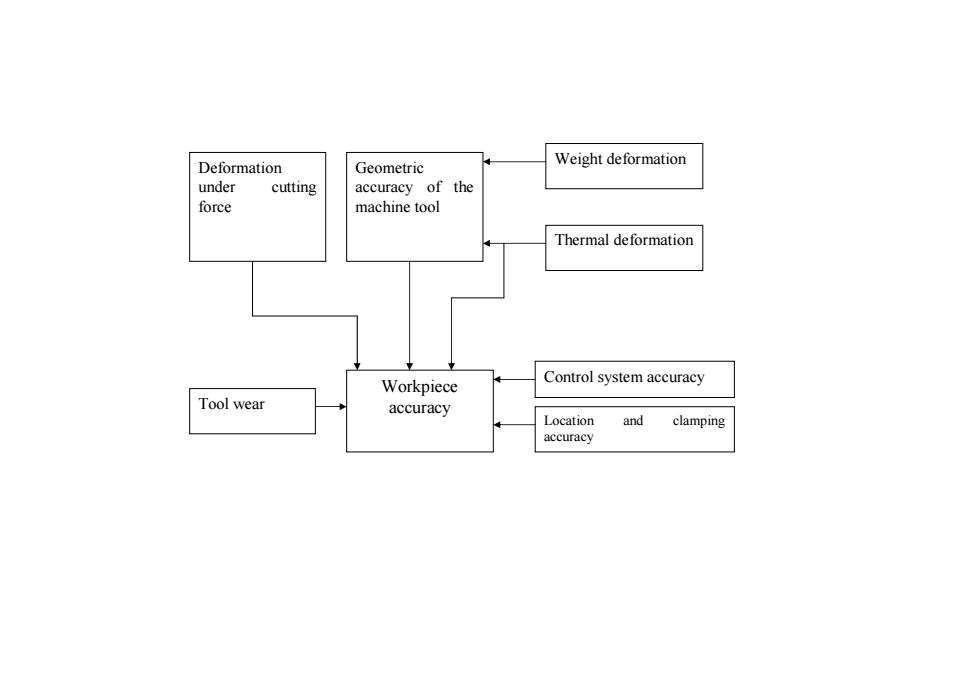
Deformation under cutting force Geometric accuracy of the machine tool Tool wear Workpiece accuracy Control system accuracy Location and clamping accuracy Weight deformation Thermal deformation

3.2.1 Error of machining principleMachining principle refers to the forming principle of the surface on theworkpiece. The error of machining principle is caused by similar cuttingmotion of forming or similar cutting edge geometry. The purpose is tosimplify the design and manufacturing of the machine tool and cuttingtool, reduce the manufacturing cost, raise the production efficiency andfacilitatetheuse
3.2.1 Error of machining principle Machining principle refers to the forming principle of the surface on the workpiece. The error of machining principle is caused by similar cutting motion of forming or similar cutting edge geometry. The purpose is to simplify the design and manufacturing of the machine tool and cutting tool, reduce the manufacturing cost, raise the production efficiency and facilitate the use

3.2.2 Error of the machine toolErrorofthemachinetoolreferstothemanufactureerror,setuperrorandwearcomefromthemachinetoolwithoutcuttingforce.3.2.2.1 spindlerotational error(1)conceptof spindlerotational errorTheoretically,thepositionoftherotational axisofthespindleinthespace is fixed, or in another word, the instant speed is zero. But inpractice,there are a lot of factors influence the position of the spindle andmakethe spindleposition changeinstantly.Wecallthemaximumfloatingvalueinthesensitivedirectionoftheerrortherotationalerrorofthespindle
3.2.2 Error of the machine tool Error of the machine tool refers to the manufacture error, setup error and wear come from the machine tool without cutting force. 3.2.2.1 spindle rotational error (1)concept of spindle rotational error Theoretically,the position of the rotational axis of the spindle in the space is fixed, or in another word, the instant speed is zero. But in practice,there are a lot of factors influence the position of the spindle and make the spindle position change instantly. We call the maximum floating value in the sensitive direction of the error the rotational error of the spindle
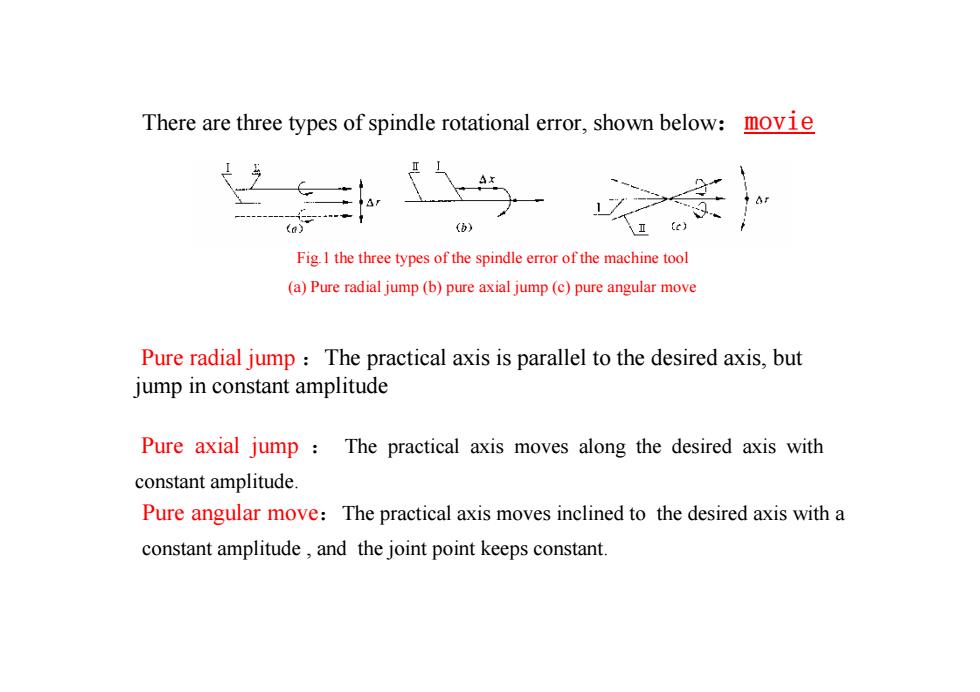
movieTherearethreetypes ofspindlerotational error,shown below:()Fig.1 the threetypes of the spindle error of themachinetool(a)Pureradial jump (b)pureaxial jump(c)pureangularmovePure radial jump :Thepractical axis is parallel to the desired axis, butjumpinconstantamplitudePure axial jump :The practical axis moves along the desired axis withconstantamplitude.Pure angular move:The practical axis moves inclined to the desired axis with aconstant amplitude,and the jointpoint keeps constant
Pure angular move:The practical axis moves inclined to the desired axis with a constant amplitude , and the joint point keeps constant. Pure radial jump :The practical axis is parallel to the desired axis, but jump in constant amplitude Pure axial jump : The practical axis moves along the desired axis with constant amplitude. There are three types of spindle rotational error, shown below:movie Fig.1 the three types of the spindle error of the machine tool (a) Pure radial jump (b) pure axial jump (c) pure angular move