BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYEssential amino acids: Includingphenylalaninevaline,tryptophan,threonine, isoleucine, methioninehistidine, arginine, leucine, lysine.PVTTIMHALLDepartmentofBiochemistryandMolecularBiology,MedicineSchool
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Essential amino acids: Including phenylalanine , valine, tryptophan , threonine, isoleucine, methionine, histidine, arginine, leucine, lysine. PVT TIM HALL
Essential amino acidsBeans(richGrains Crich ininlysine)methionine)MilkPastaefagioli (pasta andbeans,ahealthyItaliansouptiff13.mov
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYl. Catabolism of the carbonskeletonsof aminoacidsA. Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acidsKetogenic: amino acids whose catabolism yieldseither acetoacetate or one of its precursors, acetylCoA or acetoacetyl CoA(ketone bodies), are termedketogenic.Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenicamino acids found in proteinDepartment ofBiochemistryandMolecularBiology,MedicineSchool
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY A. Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids 1. Catabolism of the carbon skeletons of amino acids Ketogenic: amino acids whose catabolism yields either acetoacetate or one of its precursors, acetyl CoA or acetoacetyl CoA(ketone bodies), are termed ketogenic. Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids found in protein
BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYl. Catabolism of the carbonskeletonsof aminoacidsA.Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acidsGlucogenic: amino acids whose catabolism yieldspyruvate or one of the intermediates of the citric acidcycle are termed glucogenic or glycogenic.forTheseintermediatessubstratesaregluconeogenesis and therefore can give rise to the netformation of glycogen in liver and muscle.Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,MedicineSchool
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY A. Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids 1. Catabolism of the carbon skeletons of amino acids Glucogenic: amino acids whose catabolism yields pyruvate or one of the intermediates of the citric acid cycle are termed glucogenic or glycogenic. These intermediates are substrates for gluconeogenesis and therefore can give rise to the net formation of glycogen in liver and muscle
ABIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYl. Catabolism of the carbonskeletonsofaminoacidsB.Amino acids that form oxaloacetateAsparagineandaspartateAminotransferase Asparaginase Aspartate-AsparagineoxaloacetateDepartment ofBiochemistryandMolecularBiology,MedicineSchool
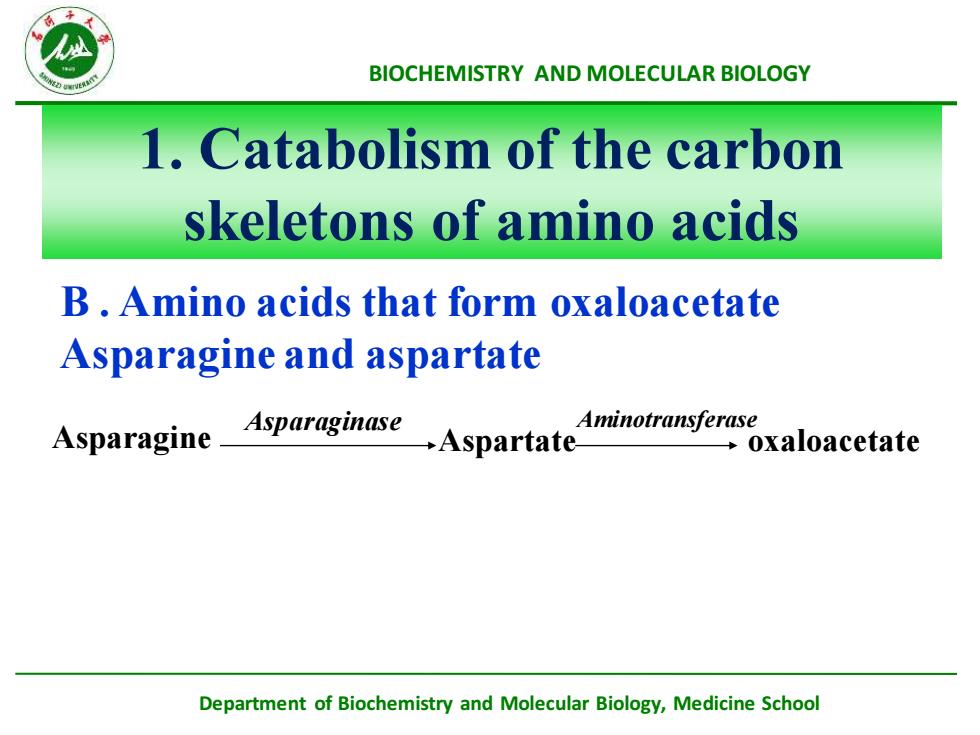
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY B . Amino acids that form oxaloacetate Asparagine and aspartate 1. Catabolism of the carbon skeletons of amino acids Asparagine Aspartate oxaloacetate Asparaginase Aminotransferase