
·Reacts with X, Cu+Cl,t>V Ag+Cl2->proceed slowly at r.t. Au+Cl2—→proceed only at high temp Chemical reactivity order CuAg-Au ·reacts with acids DCu,Ag,Au can't displace H+ions in dilute acid (poor reduction ability);
• Reacts with X2 C u C l2 r. t. Chemical reactivity order :Cu>Ag>Au proceed only at high temp. Au Cl2 proceed slowly at r.t. Ag Cl2 • reacts with acids ①Cu, Ag, Au can’t displace H+ ions in dilute acid (poor reduction ability);
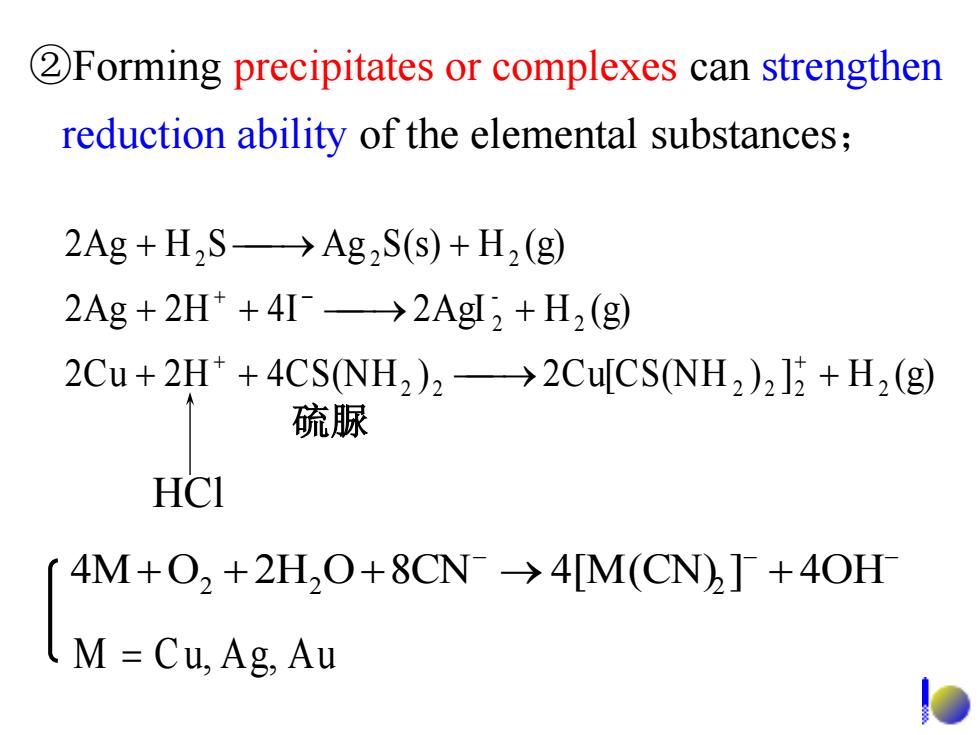
2Forming precipitates or complexes can strengthen reduction ability of the elemental substances; 2Ag+H2S->Ag2S(s)+H2(g) 2Ag 2H*+4I->2AgI,+H2 (g) 2Cu+2H*+4CS(NH2)2->2Cu[CS(NH2)2]2+H2(g) 硫脲 HCI 4M+O,+2H,O+8CN->4[M(CN)]+40H M=Cu,Ag,Au
2Cu 2 H 4CS(NH ) 2Cu[CS(NH ) ] H (g) 2Ag 2 H 4 I 2AgI H (g) 2Ag H S Ag S(s) H (g) 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 - 2 2 2 2 HCl 硫脲 ②Forming precipitates or complexes can strengthen reduction ability of the elemental substances; 4MO2 2H2 O8CN 4[M(CN)2 ] 4OH M C u, Ag, A u
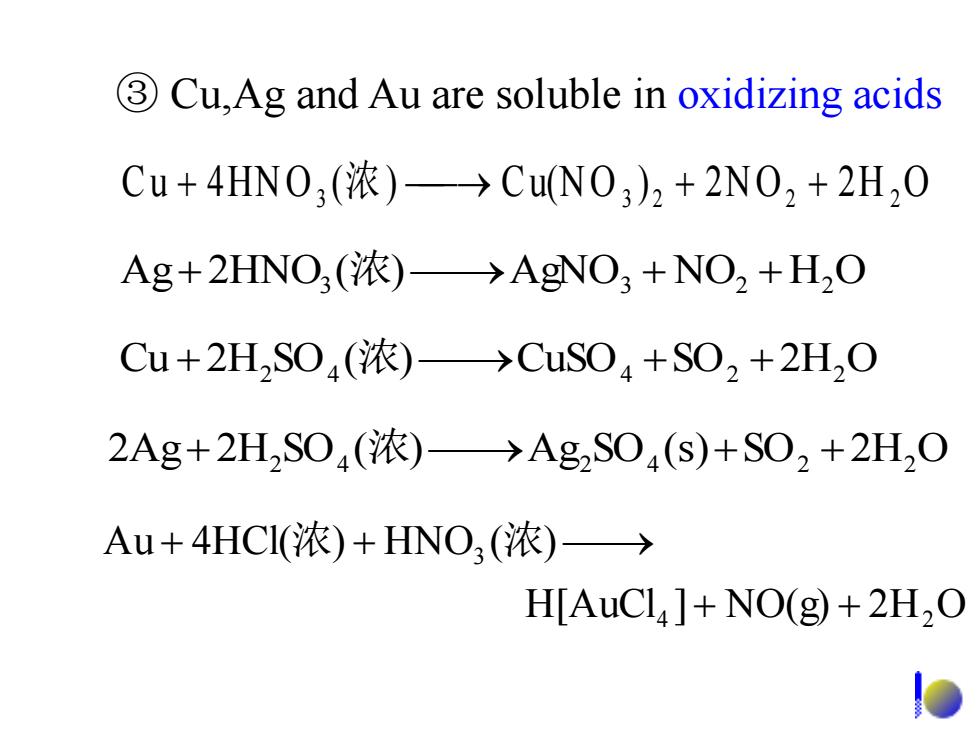
3 Cu,Ag and Au are soluble in oxidizing acids Cu+4HN0,(浓)→CuN0,)2+2N02+2H20 Ag+2HNO,(浓)→AgNO3+NO2+HO Cu+2HS04(浓)→CuS04+S02+2H20 2Ag+2H2S04(浓)→Ag2S04(s)+S02+2H2O Au+4HCI(浓)+HNO3(浓)→ H[AuCl]+NO(g)+2H2O
③ Cu,Ag and Au are soluble in oxidizing acids C u 4HN O3 (浓) Cu(N O 3 ) 2 2N O2 2 H 2 O H[AuCl ] NO(g) 2H O Au 4HCl( ) HNO ( ) 4 2 3 浓 浓 2Ag 2H2 SO4 (浓) Ag2 SO4 (s)SO2 2H2 O Cu 2H2 SO4 (浓) CuSO4 SO2 2H2 O Ag 2HNO3 (浓) AgNO3 NO2 H2 O

19.1.2 The compounds of copper 1.The compounds of copper Cu:3d104s1 Cu(D):d10,Compounds of Cu(I)are white or colorless, no d-d transition Cu(ID:d9,Compounds of Cu(ID)have colors, d-d transition Cu(IID):ds,K3CuF(light green),strong oxidizing agent d-d transition
1.The compounds of copper 19.1.2 The compounds of copper Cu(I): d 10, Compounds of Cu(I) are white or colorless, no d-d transition Cu(II): d9 , Compounds of Cu(II) have colors, d-d transition Cu(III): d8 , K3CuF6 (light green), strong oxidizing agent d-d transition Cu: 3d104s1
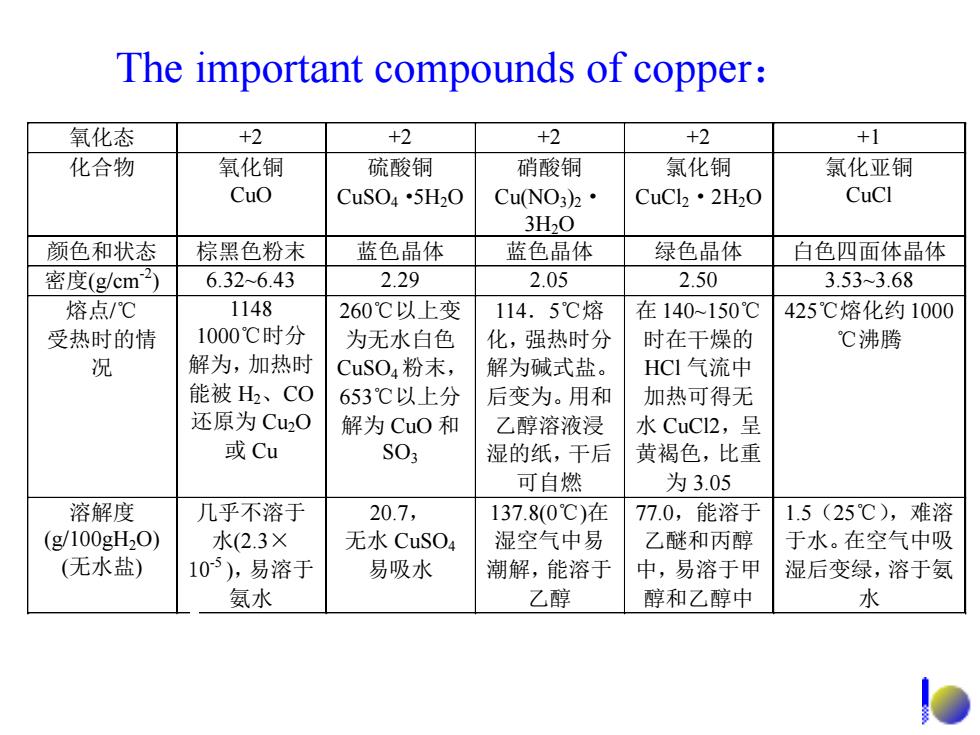
The important compounds of copper: 氧化态 +2 +2 +2 +2 +1 化合物 氧化铜 硫酸铜 硝酸铜 氯化铜 氯化亚铜 Cuo CuSO4·5H20 CuNO3)2· CuCl2·2H2O CuCl 3H20 颜色和状态 棕黑色粉末 蓝色晶体 蓝色晶体 绿色晶体 白色四面体晶体 密度(g/cm2) 6.32-6.43 2.29 2.05 2.50 3.533.68 熔点/℃ 1148 260℃以上变 114.5℃熔 在140~150℃ 425℃熔化约1000 受热时的情 1000℃时分 为无水白色 化,强热时分 时在干燥的 ℃沸腾 况 解为,加热时 CuSO4粉末, 解为碱式盐。 HCI气流中 能被H、CO 653℃以上分 后变为。用和 加热可得无 还原为Cu20 解为CuO和 乙醇溶液浸 水CuC2,呈 或Cu S03 湿的纸,干后 黄褐色,比重 可自燃 为3.05 溶解度 几乎不溶于 20.7, 137.8(0℃)在 77.0,能溶于 1.5(25℃),难溶 (g100gH20) 水(2.3× 无水CuSO4 湿空气中易 乙醚和丙醇 于水。在空气中吸 (无水盐) 105),易溶于 易吸水 潮解,能溶于 中,易溶于甲 湿后变绿,溶于氨 氨水 乙醇 醇和乙醇中 水
The important compounds of copper: 氧化态 +2 +2 +2 +2 +1 化合物 氧化铜 CuO 硫酸铜 CuSO4·5H2O 硝酸铜 Cu(NO3)2· 3H2O 氯化铜 CuCl2·2H2O 氯化亚铜 CuCl 颜色和状态 棕黑色粉末 蓝色晶体 蓝色晶体 绿色晶体 白色四面体晶体 密度(g/cm-2 ) 6.32~6.43 2.29 2.05 2.50 3.53~3.68 熔点/℃ 受热时的情 况 1148 1000℃时分 解为,加热时 能被 H2、CO 还原为 Cu2O 或 Cu 260℃以上变 为无水白色 CuSO4 粉末, 653℃以上分 解为 CuO 和 SO3 114.5℃熔 化,强热时分 解为碱式盐。 后变为。用和 乙醇溶液浸 湿的纸,干后 可自燃 在 140~150℃ 时在干燥的 HCl 气流中 加热可得无 水 CuCl2,呈 黄褐色,比重 为 3.05 425℃熔化约 1000 ℃沸腾 溶解度 (g/100gH2O) (无水盐) 几乎不溶于 水(2.3× 10-5 ),易溶于 氨水 20.7, 无水 CuSO4 易吸水 137.8(0℃)在 湿空气中易 潮解,能溶于 乙醇 77.0,能溶于 乙醚和丙醇 中,易溶于甲 醇和乙醇中 1.5(25℃),难溶 于水。在空气中吸 湿后变绿,溶于氨 水