
Unsupervised Learning: Principle Component Analysis
Unsupervised Learning: Principle Component Analysis

Unsupervised Learning ● Dimension Reduction ·Generation(無中生有) (化繁為簡) only having function input function only having function output function Random numbers
Unsupervised Learning • Dimension Reduction (化繁為簡) • Generation (無中生有) function function Random numbers only having function input only having function output
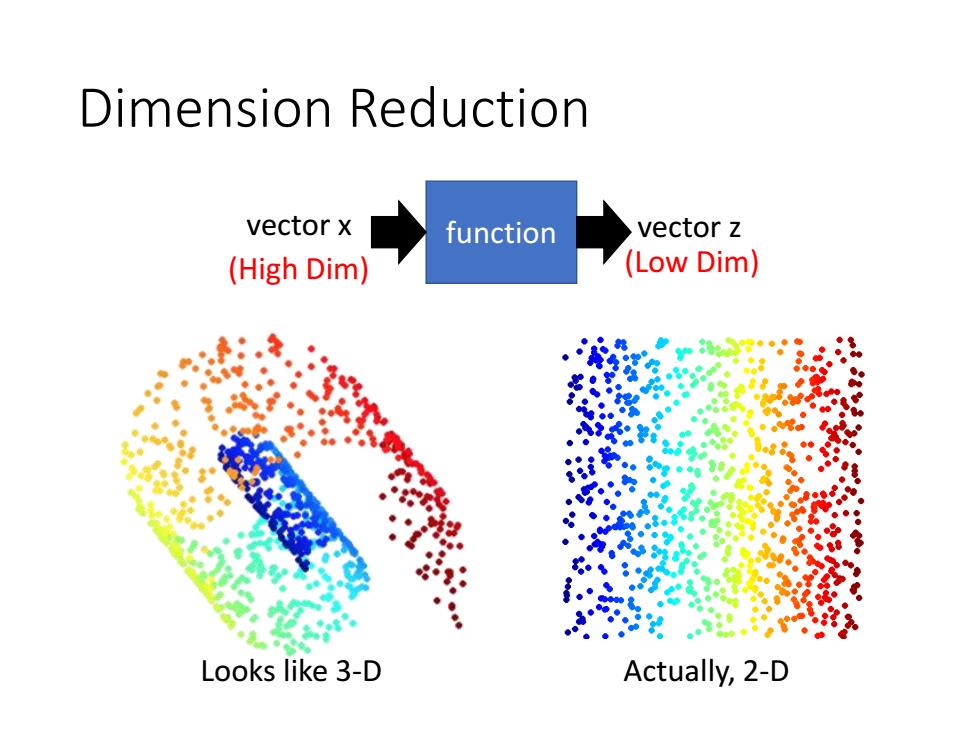
Dimension Reduction vector x function vector z (High Dim) (Low Dim) Looks like 3-D Actually,2-D
Dimension Reduction Looks like 3-D Actually, 2-D function vector x vector z (High Dim) (Low Dim)
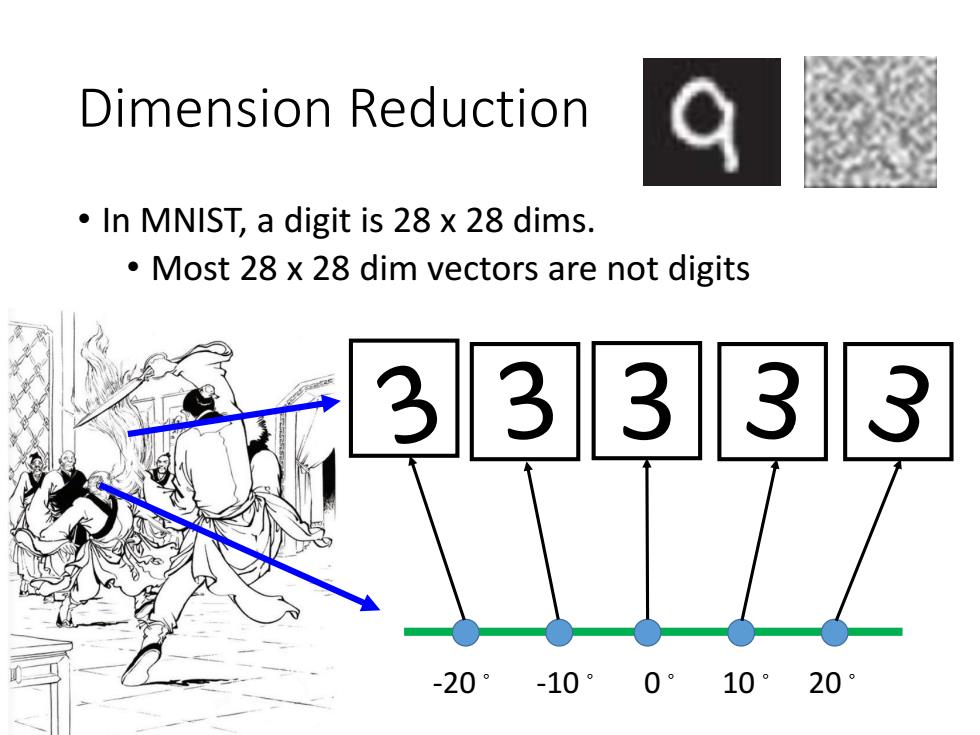
Dimension Reduction In MNIST,a digit is 28 x 28 dims. Most 28 x 28 dim vectors are not digits 3 333 -20°-10° 0°10°20°
Dimension Reduction • In MNIST, a digit is 28 x 28 dims. • Most 28 x 28 dim vectors are not digits 3 -20。 -10。 0。 10。 20
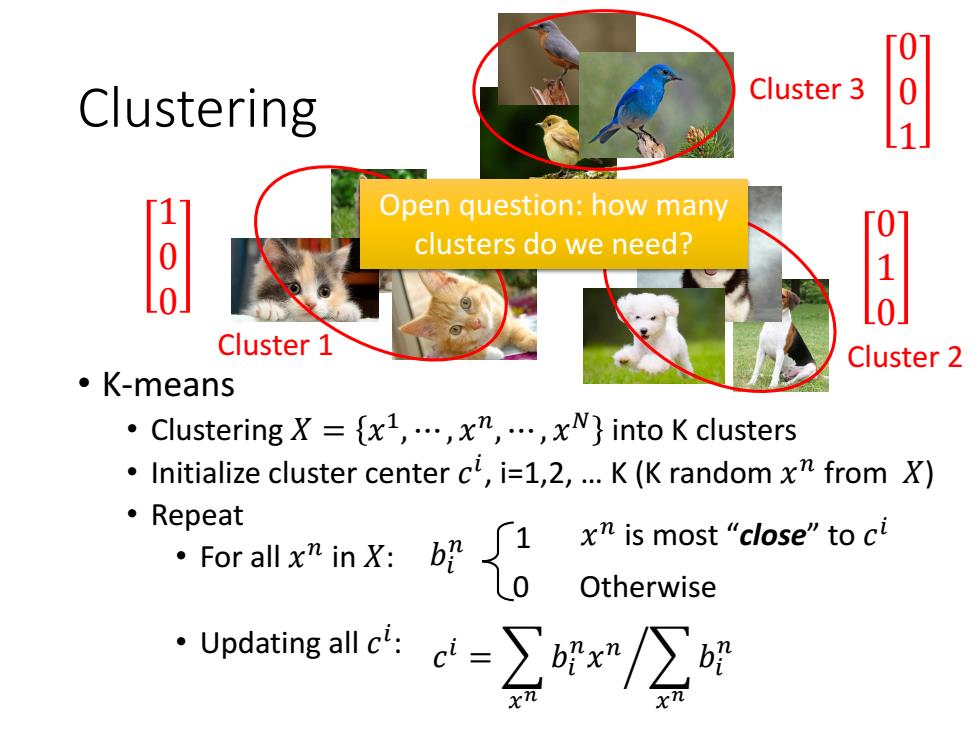
0 Clustering Cluster 3 0 1 Open question:how many 8 clusters do we need? Cluster 1 Cluster 2 。K-means ·Clustering X={xl,…,xn,,xN}into K clusters Initialize cluster center cl,i=1,2,...K (K random x from X) 。Repeat nX好0 x is most "close"to ci Otherwise ·Updating4c=∑oix/∑时
Clustering • K-means • Clustering 𝑋 = 𝑥 1 , ⋯ , 𝑥 𝑛 , ⋯ , 𝑥 𝑁 into K clusters • Initialize cluster center 𝑐 𝑖 , i=1,2, … K (K random 𝑥 𝑛 from 𝑋) • Repeat • For all 𝑥 𝑛 in 𝑋: • Updating all 𝑐 𝑖 : Cluster 1 Cluster 2 Cluster 3 Open question: how many clusters do we need? 𝑏𝑖 𝑛 0 1 𝑐 𝑖 = ൘ 𝑥 𝑛 𝑏𝑖 𝑛 𝑥 𝑛 𝑥 𝑛 𝑏𝑖 𝑛 Otherwise 𝑥 𝑛 is most “close” to 𝑐 𝑖 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1