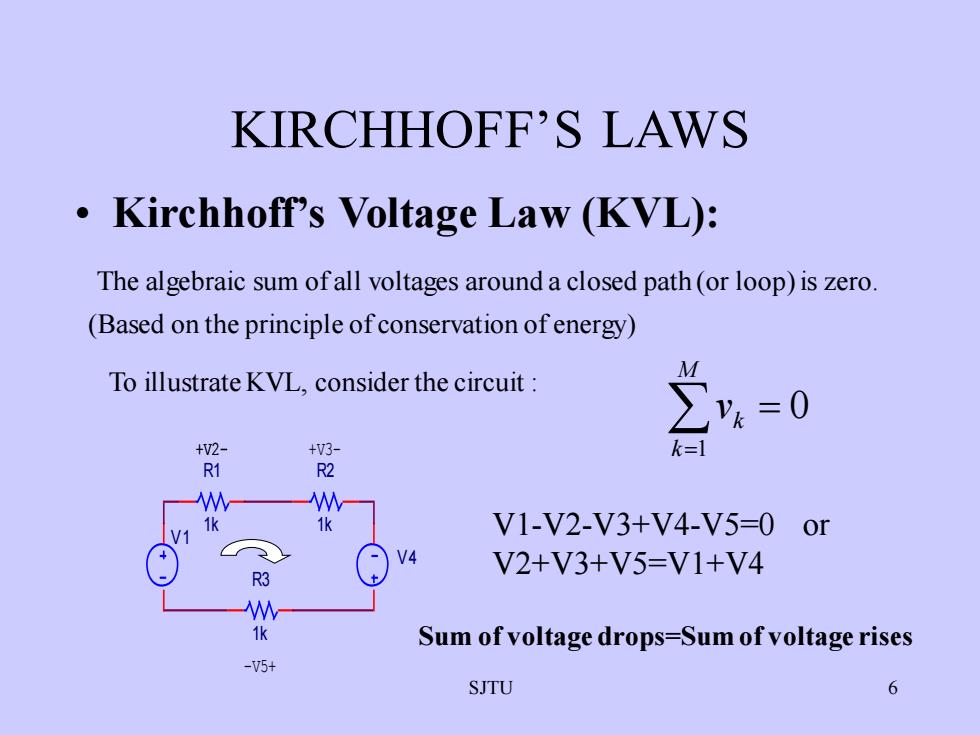
KIRCHHOFF'SLAWS.Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL):The algebraic sum of all voltages around a closed path (or loop)is zero(Based on the principle of conservation of energy)MTo illustrateKVL,considerthecircuit :Z=0Vkk=l+V2+V3-R1R2W1k1kV1-V2-V3+V4-V5-0orV1+V4V2+V3+V5=V1+V4R3W1kSum of voltagedrops=Sumofvoltagerises-V5+6SJTU
SJTU 6 KIRCHHOFF’S LAWS • Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL): The algebraic sum of all voltages around a closed path (or loop)is zero. (Based on the principle of conservation of energy) To illustrate KVL, consider the circuit : +V2- R1 1k V 4 -V5+ R3 1k V 1 R2 1k +V3- V1-V2-V3+V4-V5=0 or V2+V3+V5=V1+V4 Sum of voltage drops=Sum of voltage rises = = M k k v 1 0

TWOSORTS OE CONSTRAINTS1.Topological constraintsDetermined by the way of connection among the elements.(Such asKCL KVL)2.Elementconstraints(VAR)Determined bythe elements.Using two sorts of constraints, we can analysis anylumped circuit (solve out all the voltages and currents)SJTU7
SJTU 7 TWO SORTS OF CONSTRAINTS • 1. Topological constraints Determined by the way of connection among the elements. (Such as KCL KVL) 2. Element constraints Determined by the elements. (VAR) Using two sorts of constraints, we can analysis any lumped circuit (solve out all the voltages and currents)