
上海交通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Chapter 11.Surface and Interface Surface energy surface tension Effect of surface curvature ·Vapor pressure ·Solubility of small particles ·Wetting of surfaces 1
Chapter 11. Surface and Interface 1
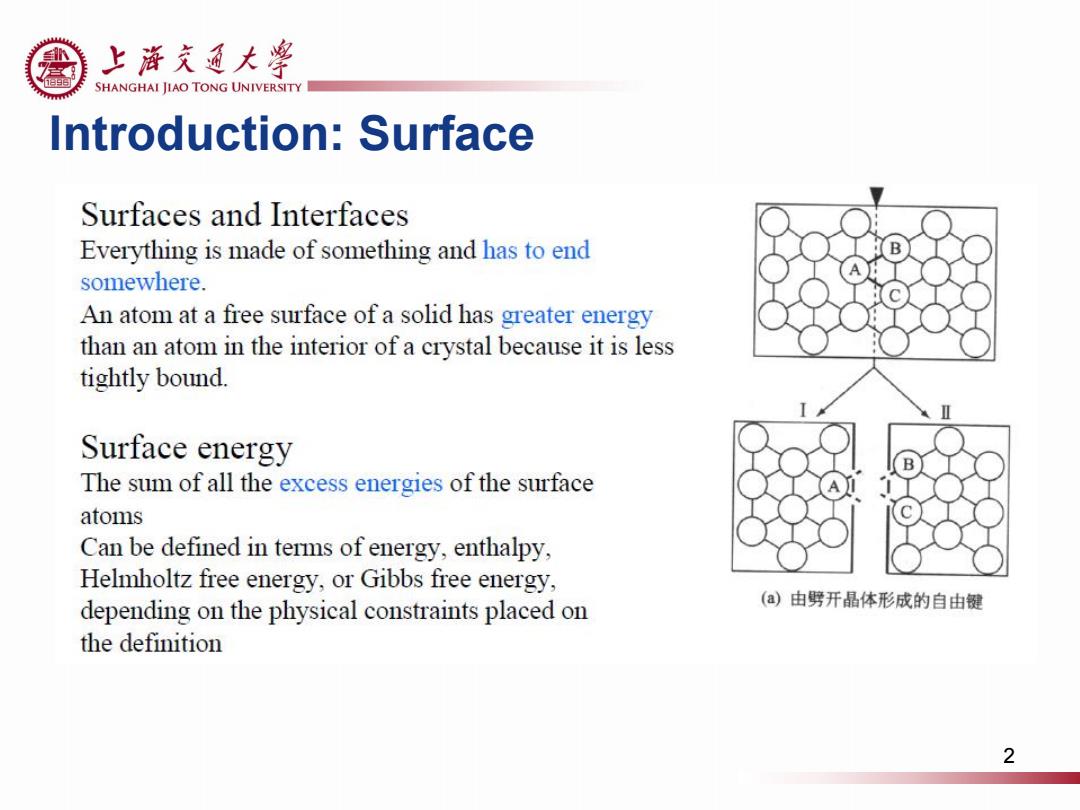
上游充通大粤 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Introduction:Surface Surfaces and Interfaces Everything is made of something and has to end somewhere. An atom at a free surface of a solid has greater energy than an atom in the interior of a crystal because it is less tightly bound. Surface energy The sum of all the excess energies of the surface atoms Can be defined in terms of energy,enthalpy, Helmholtz free energy,or Gibbs free energy, depending on the physical constraints placed on (a)由劈开晶体形成的自由键 the definition 2
Introduction: Surface 2

上游充通大粤 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Introduction:Surface energy Surface energy based on Gibbs free energy dG=-SdT+VaP+ydA OH OF 6A T.P Water droplets try to minimize its Small particles of metals will melt free energy by agglomerating into or sinter into spherical particles arger spherical particles. ro
Introduction: Surface energy 3 Water droplets try to minimize its free energy by agglomerating into larger spherical particles. Small particles of metals will melt or sinter into spherical particles
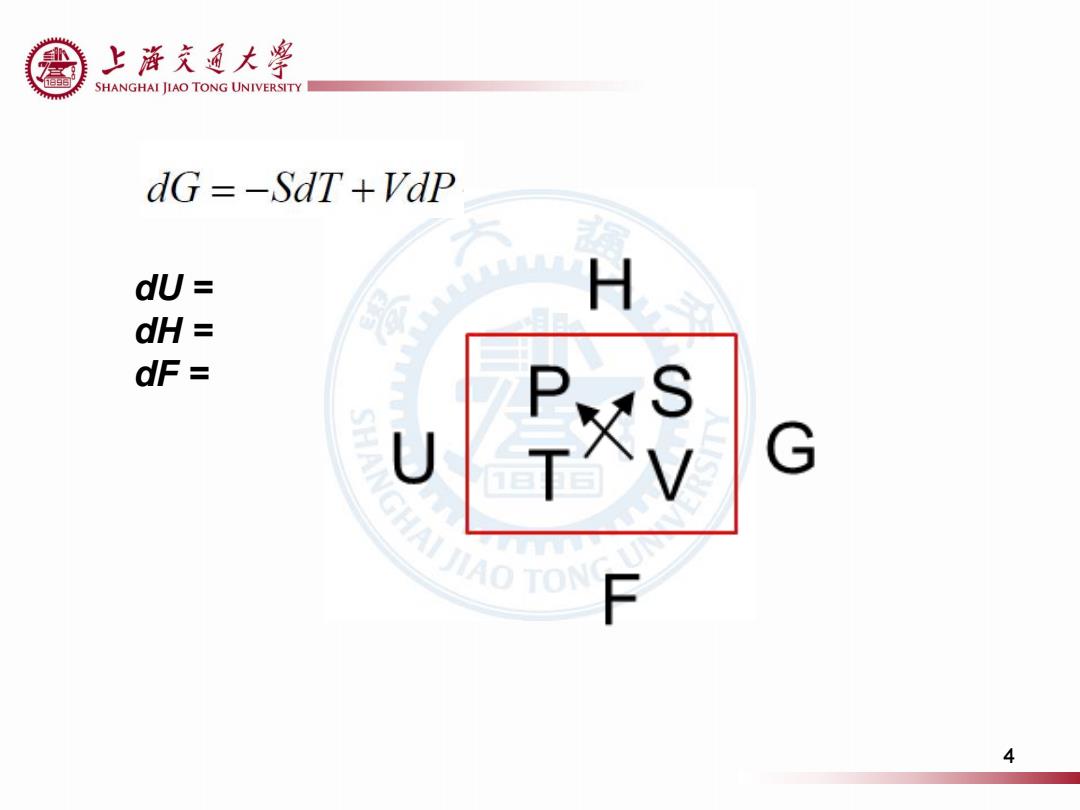
上浒充通大粤 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY dG =-SdT +VdP dU H dH 是 dF= P SHANGHAIAO TON U G F 4
4 dU = dH = dF =

上游充通大粤 SHANGHALILAO TONG UNIVERSITY Bareret Media
5