
A chemical equilibrium: A reversible chemical reaction can be at equilibrium under certain conditions: D正=D道≠0 The basic features of chemical equilibrium: (1)the composition of an equilibrium mixture undergoes no further change with time. (2)chemical equilibria are dynamic. (3)the equilibrium composition is independent of the path of approach

4.1.2 The standard equilibrium constant expression *Equilibria involving gases H2(g)+I2(g)=2HI(g) [p(HI)/p2 K= pe=100kpa [p(H2)/pe]p(I,)/pe] *Equilibria in aqueous solution: Sn2(aq)+2Fe3+(aq)-Sn4+(aq)+2Fe2+(aq) ke_Lc(Sn "c)lle(Fc2)2 [c(Sn 2/ce )l[c(Fe 3*/c)] ce=1 mol.H1
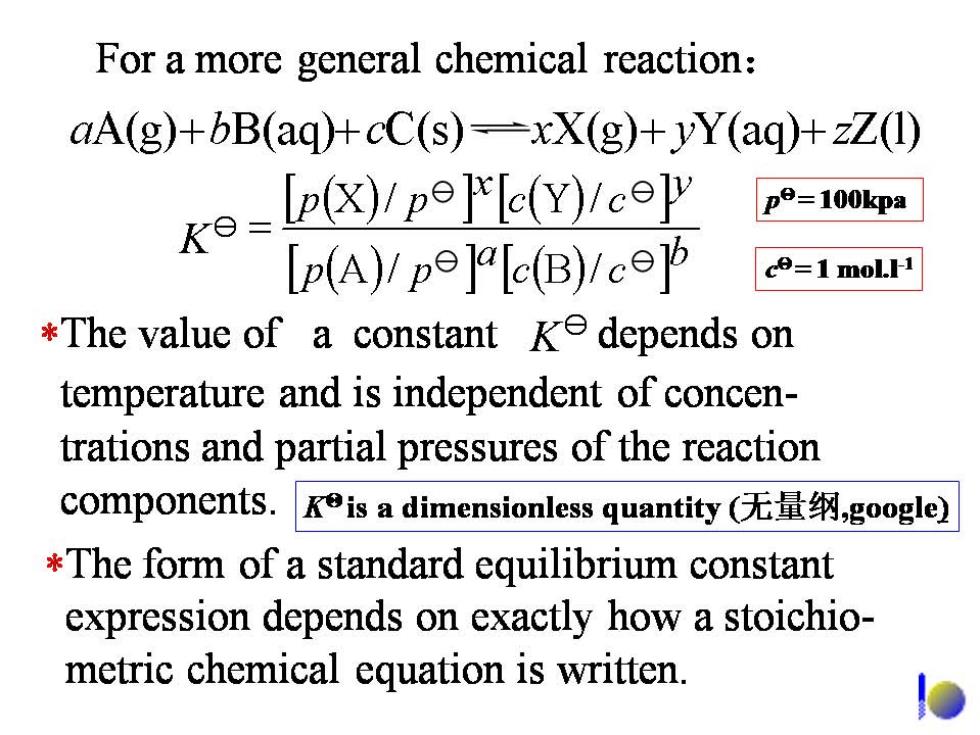
For a more general chemical reaction: aA(g)+bB(aq)+cC(s)=xX(g)+yY(aq)+zZ(1) Ke=pyp9]'eY/ceΨ pe=100kpa [p(A)/pe]r[c(B)1co的 co=1 molH *The value of a constant ke depends on temperature and is independent of concen- trations and partial pressures of the reaction components.Kis a dimensionless quantity(无量纲,google) *The form of a standard equilibrium constant expression depends on exactly how a stoichio- metric chemical equation is written
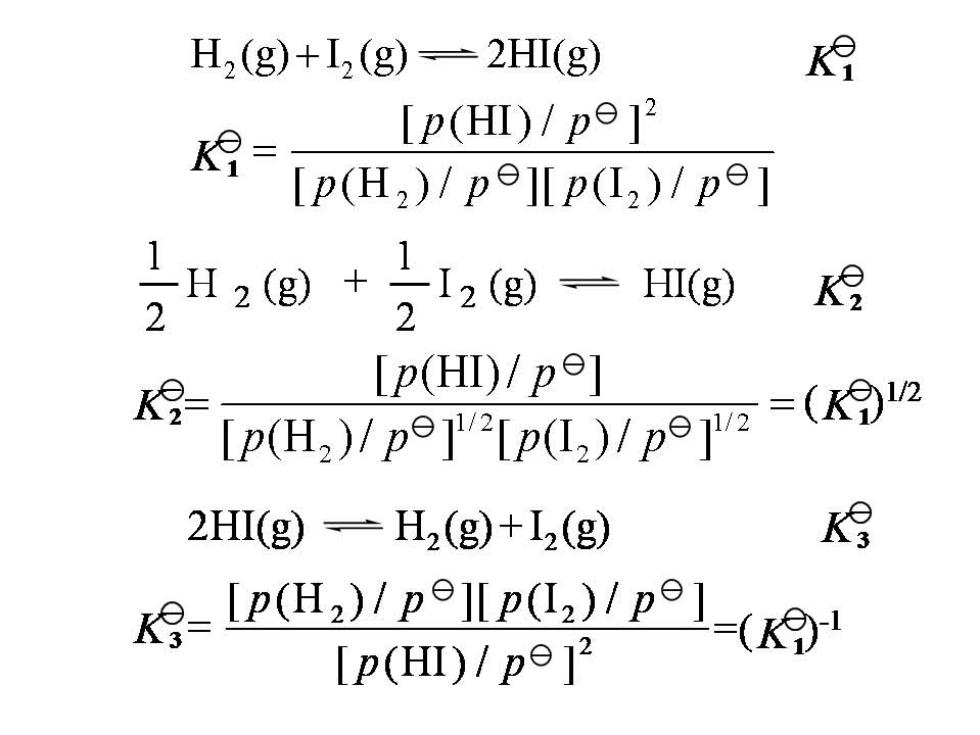
H2(g)+I(g)=2HΠ(g) [p(HⅢ)/po12 [p(H,)/pelp(I2)/pe] H2g)+号12g一Hg) 月 2 2 [p(HI)/p] Ip(H)p( 2HI(g)=H2(g)+L2(g) 月 -PCH)/P1-( [P(HI)/p]
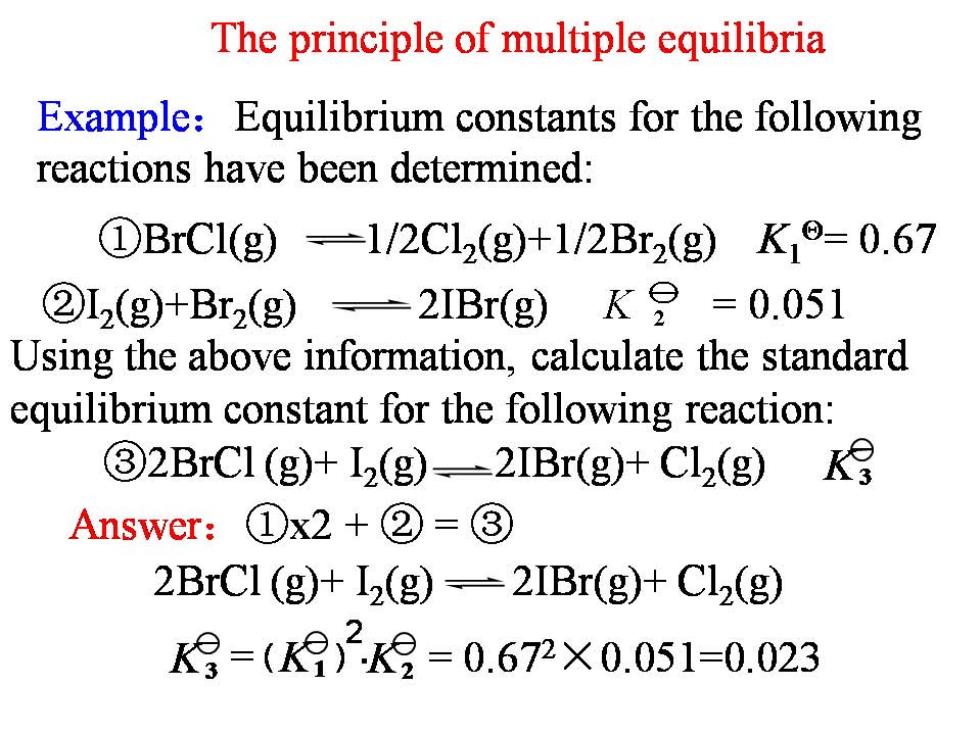
The principle of multiple equilibria Example:Equilibrium constants for the following reactions have been determined: ①BrC1(g)=1/2Cl2(g+1/2Br2(gK19=0.67 ②L2(g)+Br2(g)=2IBr(g)K9=0.051 Using the above information,calculate the standard equilibrium constant for the following reaction: 32BrCl (g)+I2(g)-2IBr(g)+Cl2(g) Answer:①x2+②=③ 2BrCl(g)+I2(g)=2IBr(g)+Cl2(g) K9=()2=0.672×0.051=0.023