
Chapter 6 Precipitation-Solubility Equilibria X 6.1 Solubility and solubility product x 6.2 Forming and dissolving of precipitates x 6.3 Equilibrium between two precipitates
Chapter 6 Precipitation-Solubility Equilibria § 6.3 Equilibrium between two precipitates § 6.2 Forming and dissolving of precipitates § 6.1 Solubility and solubility product

6.1 Solubility and solubility product 6.1.1 Solubility 3一 6.1.2 Solubility product 6.1.3 Relationship between solubility and solubility product
§6.1 Solubility and solubility product 6.1.3 Relationship between solubility and solubility product 6.1.2 Solubility product 6.1.1 Solubility

6.1.1 Solubility Solubility is the maximum amount of solute that will dissolve in a given quantity of solvent when dynamic equilibrium is established between undissolved solute and the solution at a specific temperature.We usually use the symbol "S"to express it. Solubility usually is expressed in grams of solute per 100g of water(g/100g)for aqueous solution
Solubility is the maximum amount of solute that will dissolve in a given quantity of solvent when dynamic equilibrium is established between undissolved solute and the solution at a specific temperature. We usually use the symbol ―S‖ to express it. Solubility usually is expressed in grams of solute per 100g of water (g /100g) for aqueous solution. 6.1.1 Solubility

6.1.2 Solubility product The process which involves the dissolution and precipitation of an insoluble electrolyte occurs when it is added to a solvent like water at a certain temperature. NaCl Dissolution of NaCl in Water
The process which involves the dissolution and precipitation of an insoluble electrolyte occurs when it is added to a solvent like water at a certain temperature. 6.1.2 Solubility product NaCl
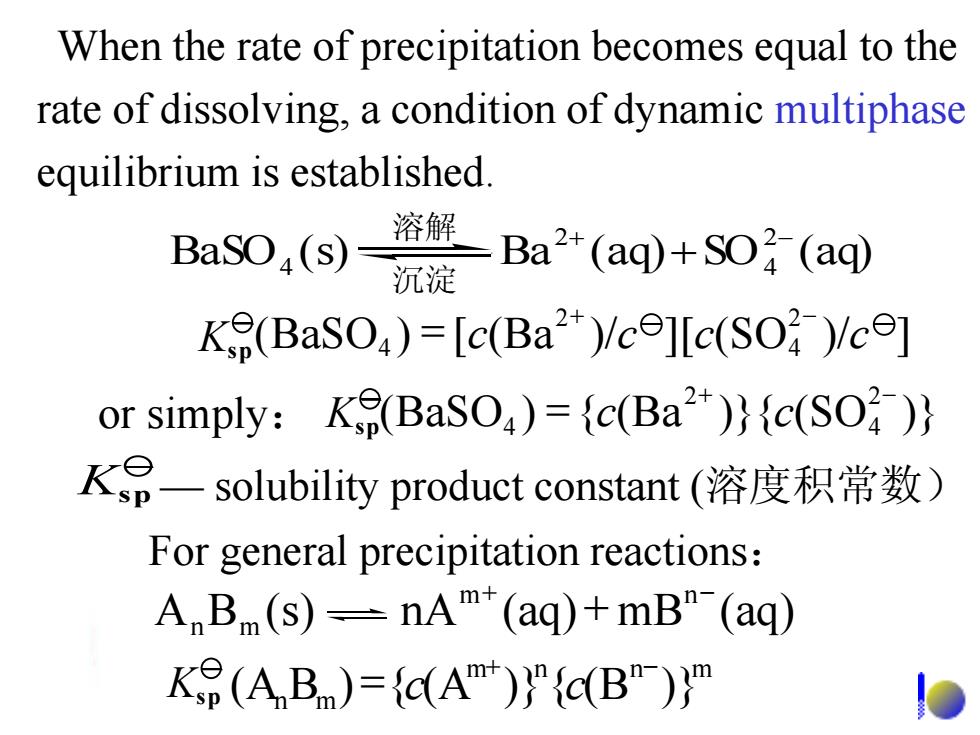
When the rate of precipitation becomes equal to the rate of dissolving,a condition of dynamic multiphase equilibrium is established. BaSO(s) 溶 沉 -Ba2(aq)+O (aq K(BaSO)=[c(Ba)/cellc(SO )/c] or simply:Ke(BaSO)={c(Ba))(c(SO ) KP一solubility product constant(溶度积常数) For general precipitation reactions: A,B(s)=nAT(aq)+mB"-(ag) Ke(A B)=(A)"(B"))
When the rate of precipitation becomes equal to the rate of dissolving, a condition of dynamic multiphase equilibrium is established. For general precipitation reactions: Ksp — solubility product constant (溶度积常数) A B (s) nA (aq) mB (aq) m n n m + - + m n n m (AnBm) { (A )} { (B )} + - Ksp = c c (BaSO ) { (Ba )}{ (SO )} 2 4 2 4 + - or simply: Ksp = c c (BaSO ) [ (Ba )/ ][ (SO )/ ] 2 4 2 4 + - K = c c c c sp 溶解 BaSO (s) Ba (aq) SO (aq) 2 4 2 4 + - + 沉淀