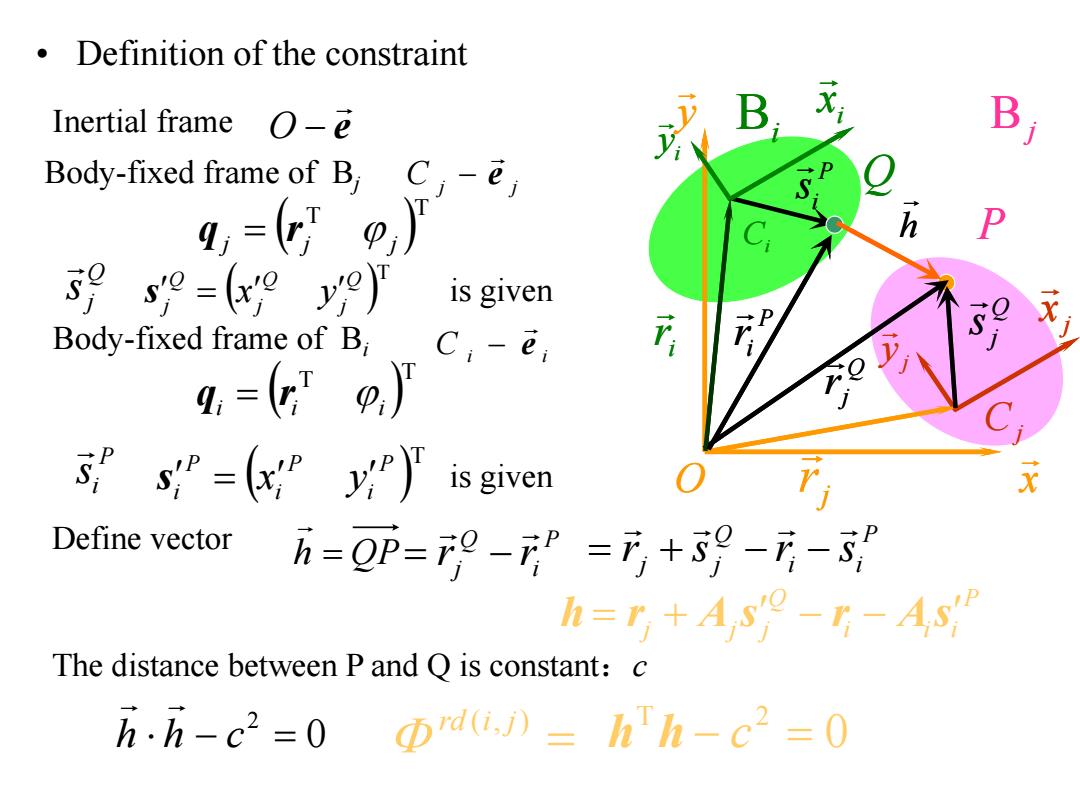
Definition of the constraint Inertial frame O-e B Body-fixed frame of B C, 9,=,) P 9s=(9 is given Body-fixed frame of B, C,-e; 4=9,)厂 5=y)is given Define vector h=0p=9-=时+9--s” h=r+As-r-As The distance between P and Q is constant:c h.h-c2=0 rd(i.i)=hh-c2=0
• Definition of the constraint Bj y x O j x j y Cj j r P Q j r Q j s e Inertial frame O C j j e Body-fixed frame of Bj T T j j j q r Q j s Q T j Q j Q j s x y is given P i s T T i i i q r P i s T P i P i P i s x y is given C i i e Body-fixed frame of Bi i x i y Ci Bi ir Q h P ir Define vector h QP P i Q j r r P i i Q j j r s r s P i i i Q j j j h r A s r As 0 2 h h c The distance between P and Q is constant:c 0 T 2 h h c rd (i, j) Bj y x O j x j y Cj j r P Q j r Q j s P i s i x i y Ci Bi ir Q h P ir

Φai,)=hTh-c2=0 B h=r+A s'o-r-As P Number of constraint equation:s- 4,=9,4,=p, P q=g)=tg9,rp,) O x Degrees of freedom:=5 Parameters of the constraint i,j,s=(,s9=(°y9,c
0 P i i i Q j j j h r A s r As ( , ) T 2 c rd i j Φ h h s 1 Degrees of freedom: 5 Number of constraint equation: T T i i i q r Parameters of the constraint T T j j j q r T T T T T T i j i i j j q q q r r i j x y x y c Q j Q j Q j P i P i P i , , , , T T s s Bj y x O j x j y Cj j r P Q j r Q j s P i s i x i y Ci Bi ir Q h P ir
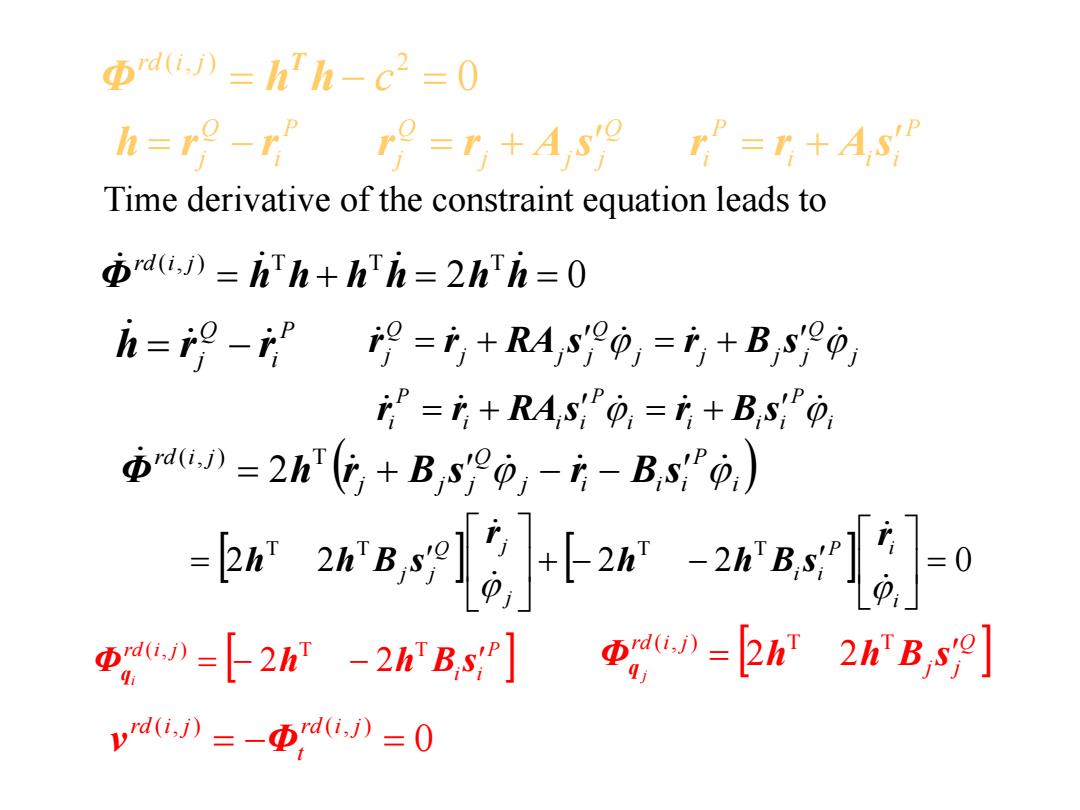
Φdi)=hTh-c2=0 h=ro-r ro=r+A s'o r=r+As. Time derivative of the constraint equation leads to Φai,)=hTh+hh=2hTi=0 h=2-”9=i+RA,0,=月+B,yp, =+RA,s0,=+B,s0 本u》=2h(G+Bsp,--B,s0,) -bha6l-26]-0 D=【2h-2hBsr本,D=2n2hBs9] vd》=-Dyd》=0
Time derivative of the constraint equation leads to • 速度约束方程 P i Q j h r r 0 ( , ) 2 c rd i j Φ h h T 2 0 ( , ) T T T Φ h h h h h h rd i j P i Q j h r r Q j j j Q j r r A s P i i i P ir r A s j Q j j j j Q j j j Q r j r RA s r B s i P i i i i P i i i P r i r RA s r B s i P j i i i Q j j j rd i j Φ h r B s r B s ( , ) T 2 2 2 2 2 0 T T T T i P i i i j Q j j j r h h B s r h h B s P i i rd i j i Φ h h B s q ( , ) T T 2 2 Q j j rd i j j Φ h h B s q ( , ) T T 2 2 0 ( , ) ( , ) rd i j t rd i j v Φ

prd(i))=hTh+hTh=2hh=0 h=ro-r ro=r+A so r=r+As i=9-9=i+RA,0,=+B,s0 =+RAs0,=产+B,s0, Time derivative of the velocity constraint equation leads to rd(i.))=2hTh+2hh h=9-”9=书+R4,s0,+RA,s90=-A,9+Bs9, =i+RAs+RAs =-As+Bs 6n-w2al质}r-28看 +2hih-2hTA,syp+2h'As2=Φ,awi-yaD=0 y=-2hh+2h(As-As2)
P i Q j h r r 2 0 ( , ) T T T Φ h h h h h h rd i j Φ h h h h T T ( , ) 2 2 rd i j P i Q j h r r Q j j j Q j r r A s P i i i P ir r A s j Q j j j j Q j j j Q r j r RA s r B s i P i i i i P i i i P r i r RA s r B s Time derivative of the velocity constraint equation leads to P i Q j h r r j Q j j j Q j j j j Q j j j Q j j j Q j r r RA s RA s r A s B s 2 i P i i i P i i i i P i i i P i i i P i r r RA s RA s r A s B s 2 T T 2 T 2 ( , ) T T T T 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 i P j i i Q j j i P i i i j Q j j j rd i j h h h A s h A s r h h B s r Φ h h B s 0 ( , ) ( , ) rd i j rd i j Φ q q ( , ) T T 2 2 2 2 i P j i i Q j j rd i j h h h A s A s
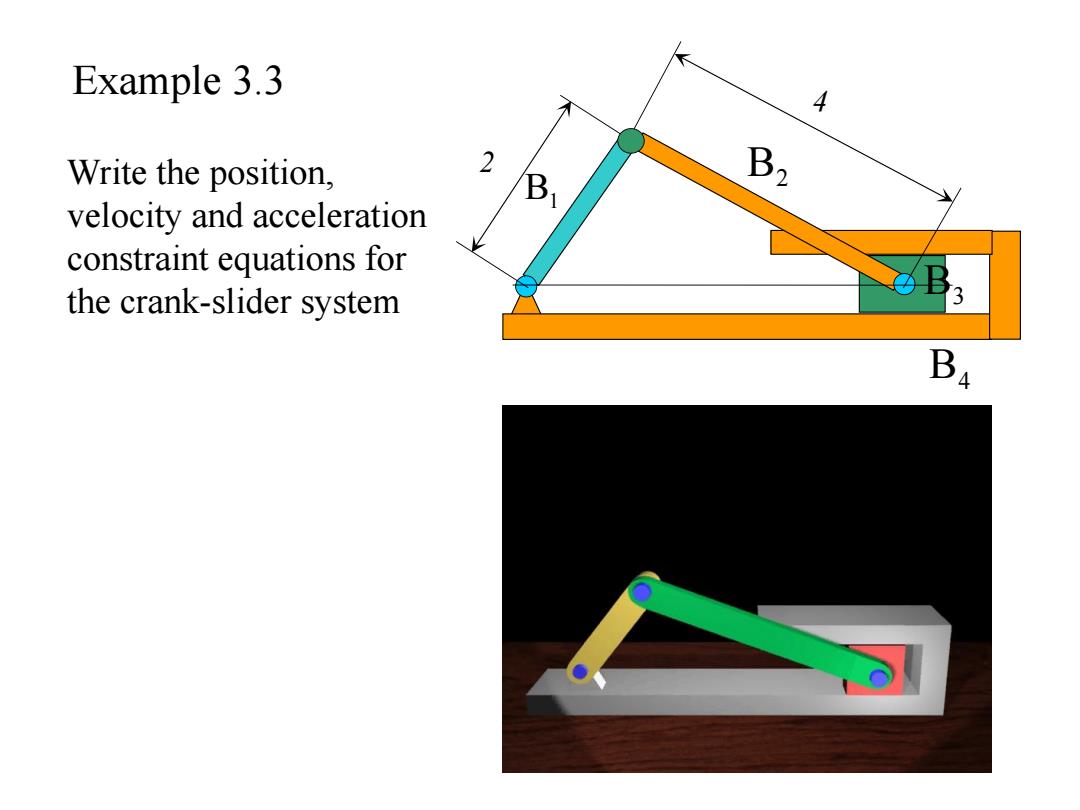
Example 3.3 4 Write the position, 2 B2 velocity and acceleration constraint equations for the crank-slider system 3 Ba
W 2 rite the position, velocity and acceleration constraint equations for the crank-slider system 4 B1 B2 B3 B4 Example 3.3