3.7 Singular configuration Definition Singular configuration The configuration of a mechanism,beyond which the motion can not continue or more than one possible motion can occur (1)Bifurcation-A branching of motion to two possible paths (2)Lock-up-in this configuration,the mechanism can not be driven in certain direction
Definition 3.7 Singular configuration Singular configuration The configuration of a mechanism, beyond which the motion can not continue or more than one possible motion can occur (1) Bifurcation — A branching of motion to two possible paths (2) Lock-up — in this configuration, the mechanism can not be driven in certain direction

Example 3.7.1 Slider-crank lock up bifurcation
Example 3.7.1 Slider-crank lock up bifurcation
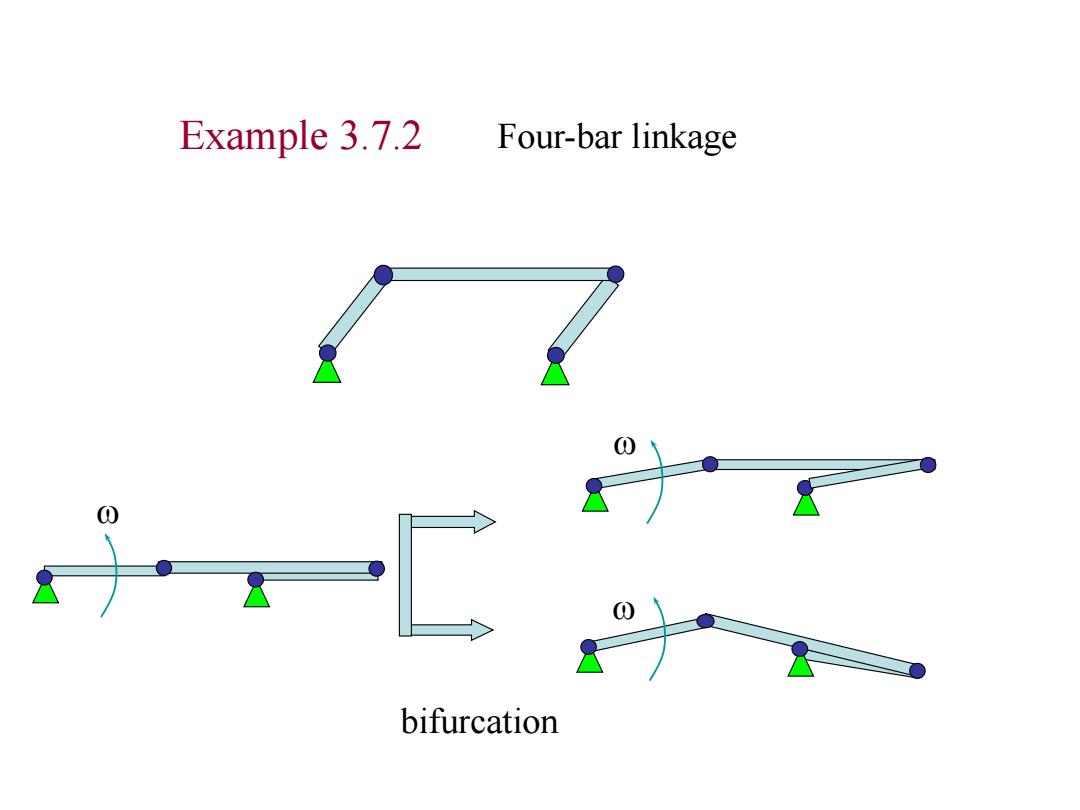
Example 3.7.2 Four-bar linkage bifurcation
Example 3.7.2 Four-bar linkage bifurcation w w w
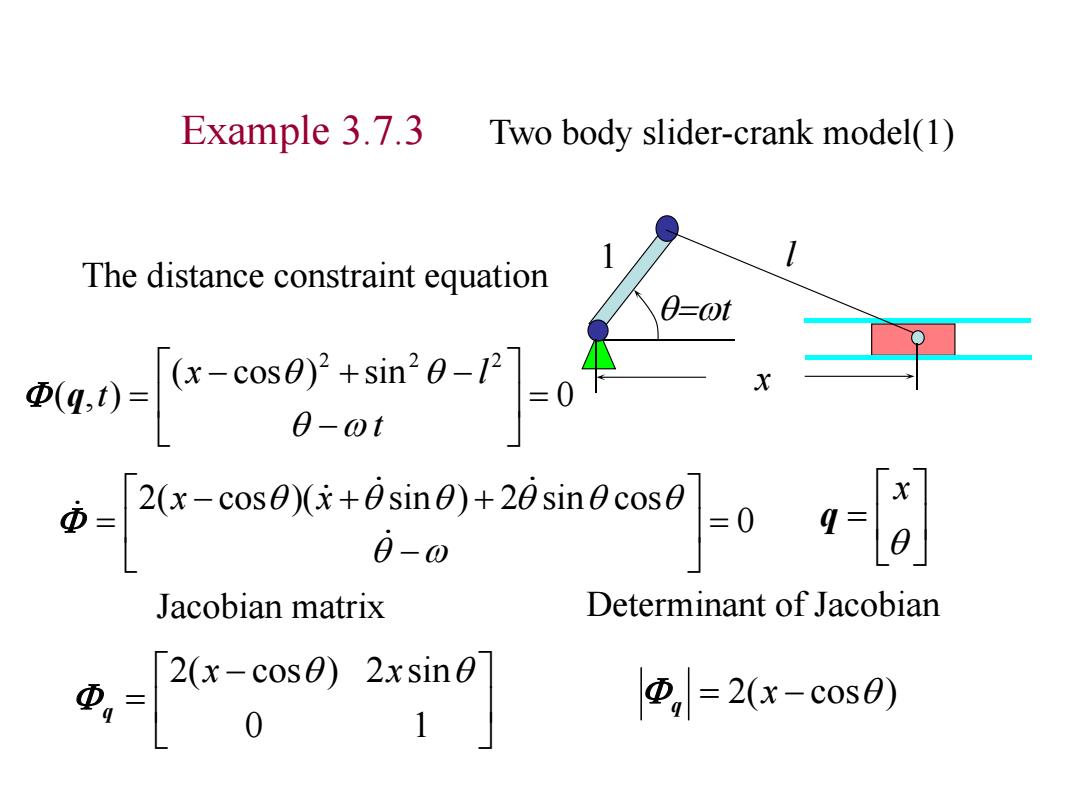
Example 3.7.3 Two body slider-crank model(1) The distance constraint equation 0-ot 0-0 Jacobian matrix Determinant of Jacobian D,=2(x-c0s0)
Example 3.7.3 Two body slider-crank model(1) 0 ( cos ) sin ( , ) 2 2 2 t x l t w q The distance constraint equation 1 l wt x 0 1 2(x cos ) 2x sin q x 0 q 2( cos )( sin ) 2 sin cos w x x 2(x cos ) q Jacobian matrix Determinant of Jacobian
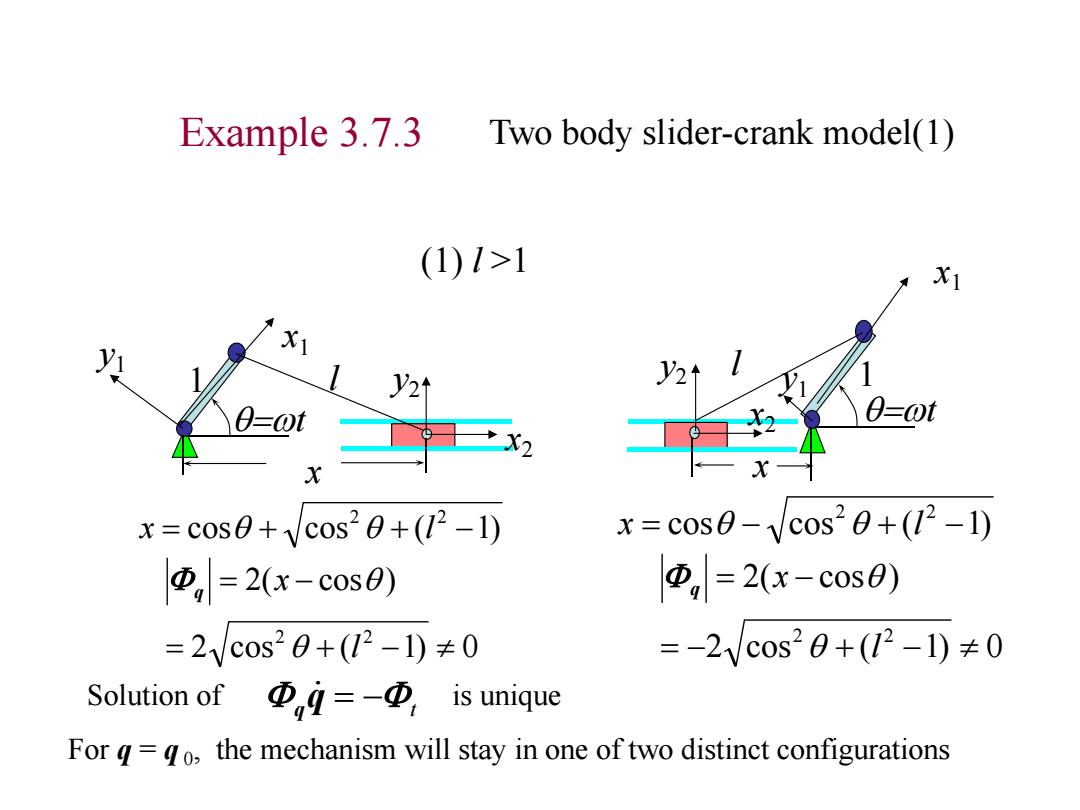
Example 3.7.3 Two body slider-crank model(1) (1)1>1 1 y2↑ 2 0-0t =t X2 X x=cos0+cos20+(12-1) x cos0-/cos20+(12-1) D,=2(x-c0s8) =2(x-cos0) =2Vcos20+(12-1)≠0 =-2Vc0s20+(12-1)≠0 Solution ofΦ,A=-Φ,is unique For g=go,the mechanism will stay in one of two distinct configurations
Example 3.7.3 Two body slider-crank model(1) cos cos ( 1) 2 2 x l (1) l >1 cos cos ( 1) 2 2 x l x1 1 l wt x x1 y1 x2 y2 l 1 x y1 x2 y2 wt 2 cos ( 1) 0 2( cos ) 2 2 l x q 2 cos ( 1) 0 2( cos ) 2 2 l x q For q = q 0 , the mechanism will stay in one of two distinct configurations qq t Solution of is unique