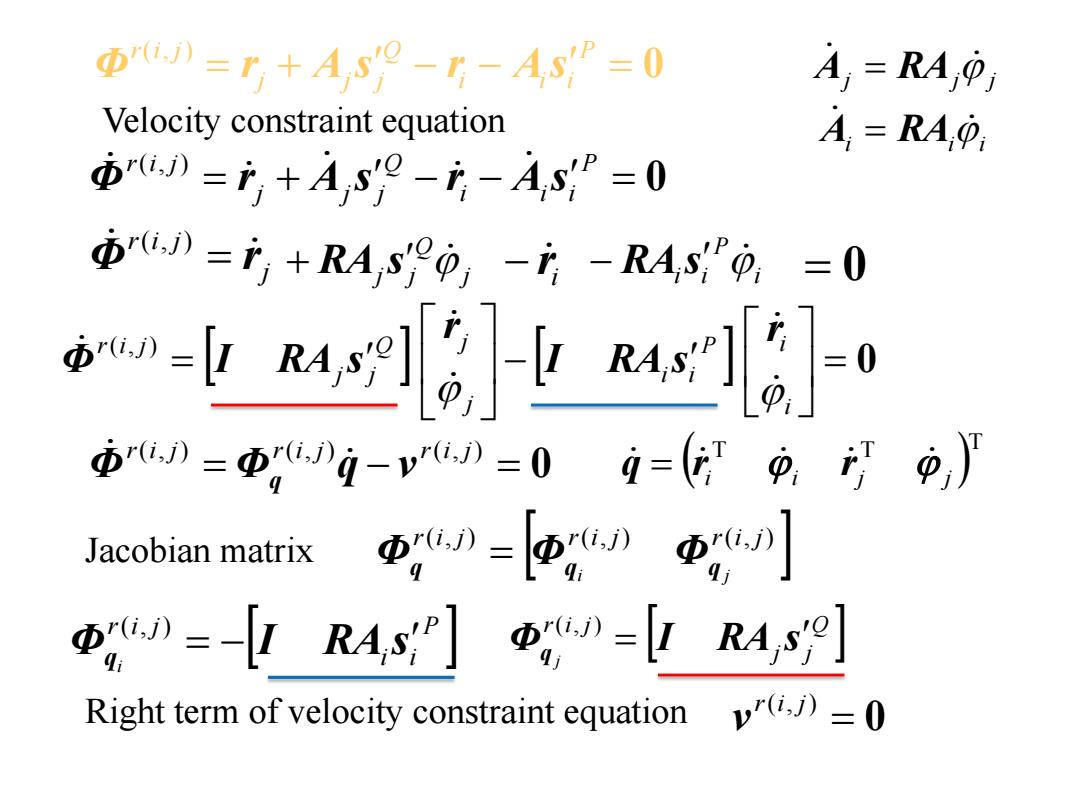
Φw)=T+A,s-片-A5y=0 A =RA Velocity constraint equation A=RAO 》=f+Asye--As”=0 重》=产+R4,s0-店-RAs,0, =0 -646业46-。 w=电,i-v》=09=(9p,) Jacobian matrix 更》=西》中列 ,》=-[R4s]Φ,D=R4s9] Right term of velocity constraint equation y"(ij)=0
j j j A RA j r i j Φ r ( , ) 0 P i i i Q j j j r i j Φ r A s r As ( , ) 0 P i i i Q j j j r i j Φ r A s r A s ( , ) 0 • Velocity constraint equation • Jacobian matrix 0 r(i, j) r(i, j) r(i, j) Φ Φ q v q i ii A RA j Q RAjs j i r i P RAisi T T T i i j j q r r r(i, j) r(i, j) r(i, j) q qi q j Φ Φ Φ 0 i P i i i j Q j j j r i j r I RA s r Φ I RA s ( , ) Q j j r i j j Φ I RA s q ( , ) P i i r i j i Φ I RA s q ( , ) • Right term of velocity constraint equation 0 r(i, j) v
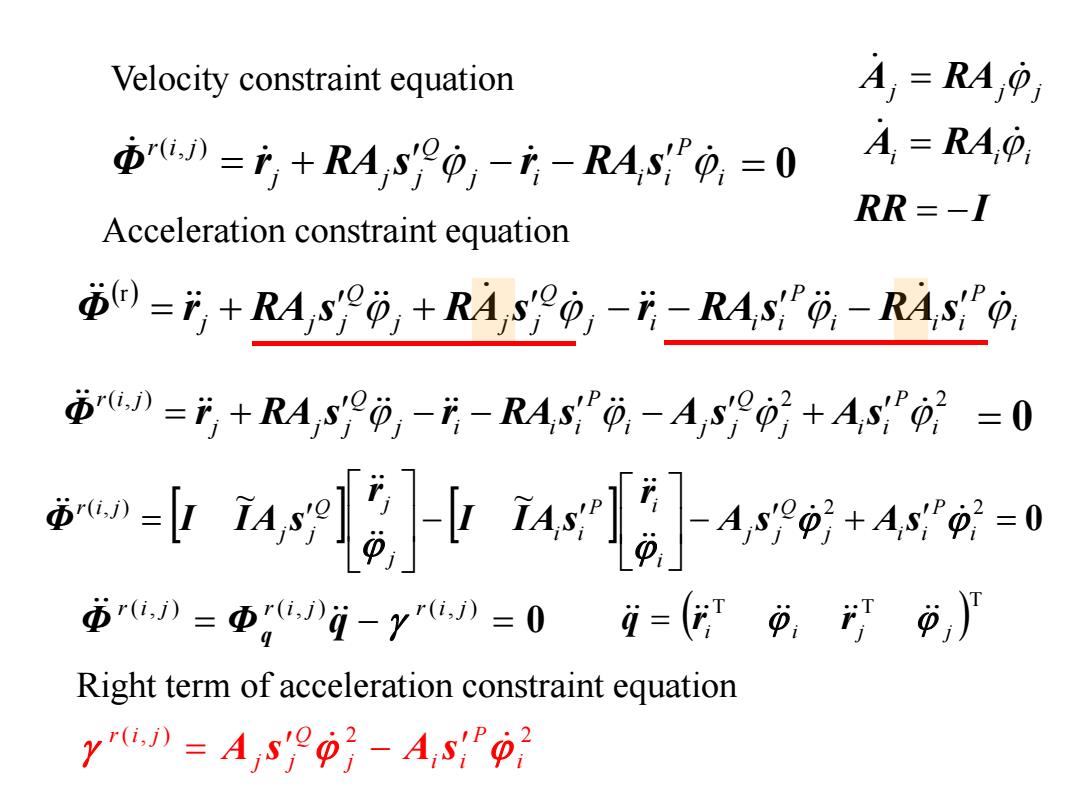
Velocity constraint equation A,=RA 市W=产+RA,S0,-i-RAs9,=0 A=RA RR=-1 Acceleration constraint equation 0=月+RA,s6+RA,0-月-R4,s"9,-R4s0 市》=月+RA,90-月-RAs西-Asy0}+As02=0 o-业a日i4e+4食-0 r》=g》日-y》=0i=(,p,) Right term of acceleration constraint equation yu.》=A,sy9p}-A,sp
j j j A RA i P j i i i Q j j j r i j Φ r RA s r RA s ( , ) 0 • Acceleration constraint equation 0 i P i i i P j i i i Q j j j Q j j j Φ r RA s RA s r RA s RA s r RR I ( , ) 2 2 i P j i i Q i j j P j i i i Q j j j r i j Φ r RA s r RA s A s A s • Velocity constraint equation i ii A RA 0 r(i, j) r(i, j) r(i, j) Φ Φ q q T T T i i j j q r r • Right term of acceleration constraint equation ( , ) 2 2 i P j i i Q j j r i j A s A s 0 ( , ) ~ ~ 2 2 i P j i i Q j j i P i i i j Q j j j r i j A s A s r I IA s r Φ I IA s

Translational joint Definition: B,is constrained to undergo translational motion without rotation relative to Bi The translational motion is along a specified axis Translational constraint
2022年3月11日 理论力学CAI 运动学计算机辅助分 析 8 Translational joint Definition: – Bi is constrained to undergo translational motion without rotation relative to Bj – The translational motion is along a specified axis Translational constraint
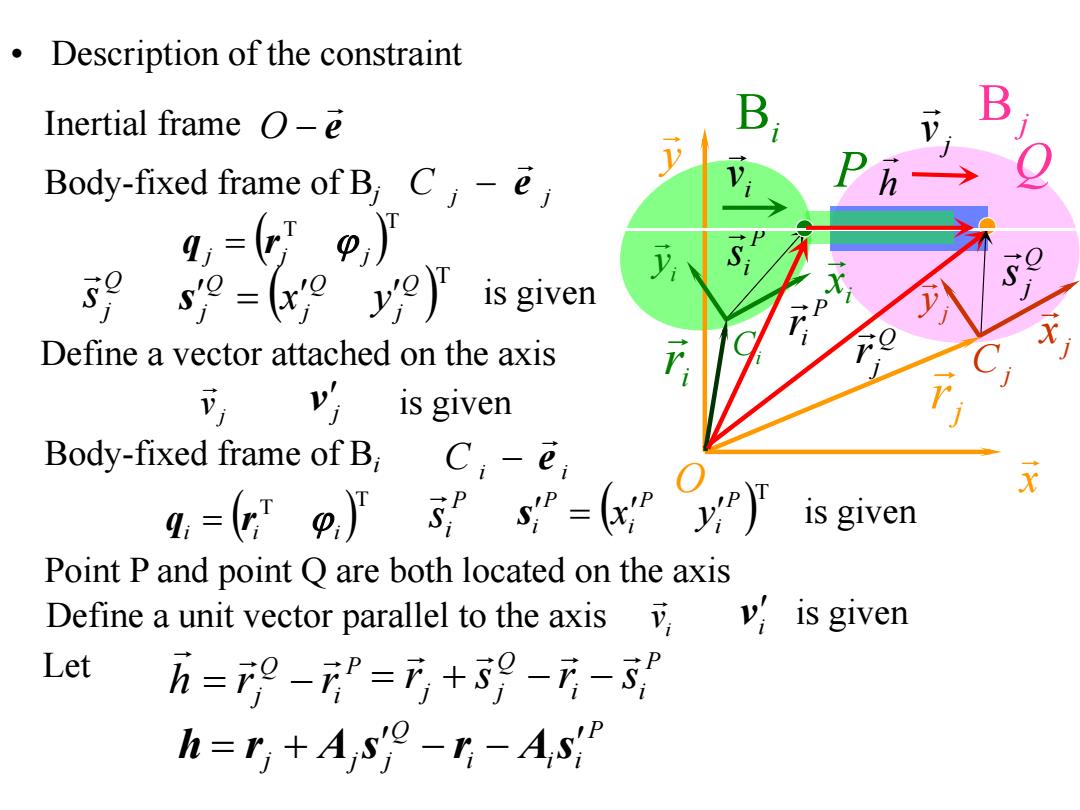
Description of the constraint Inertial frame o-e Body-fixed frame of B,C y Define a vector attached on the axis is given Body-fixed frame of B; C,-e, a.)is given Point P and point Q are both located on the axis Define a unit vector parallel to the axis可, v is given Let h=2-”=可+9-月-,” h=r+A se-r-As
• Description of the constraint Bj y x O j x y j Cj j r Q Q j r Q j s e Inertial frame O C j j e Body-fixed frame of Bj T T j j j q r Q j s Q T j Q j Q j s x y Point P and point Q are both located on the axis P i s Let T T i i i q r P i s T P i P i P i s x y is given C i i e Body-fixed frame of Bi i x i y Ci Bi ir P P ir h Define a vector attached on the axis j v j v is given Define a unit vector parallel to the axis i v i v is given i v j v P i Q j h r r P i i Q j j r s r s P i i i Q j j j h r A s r A s is given
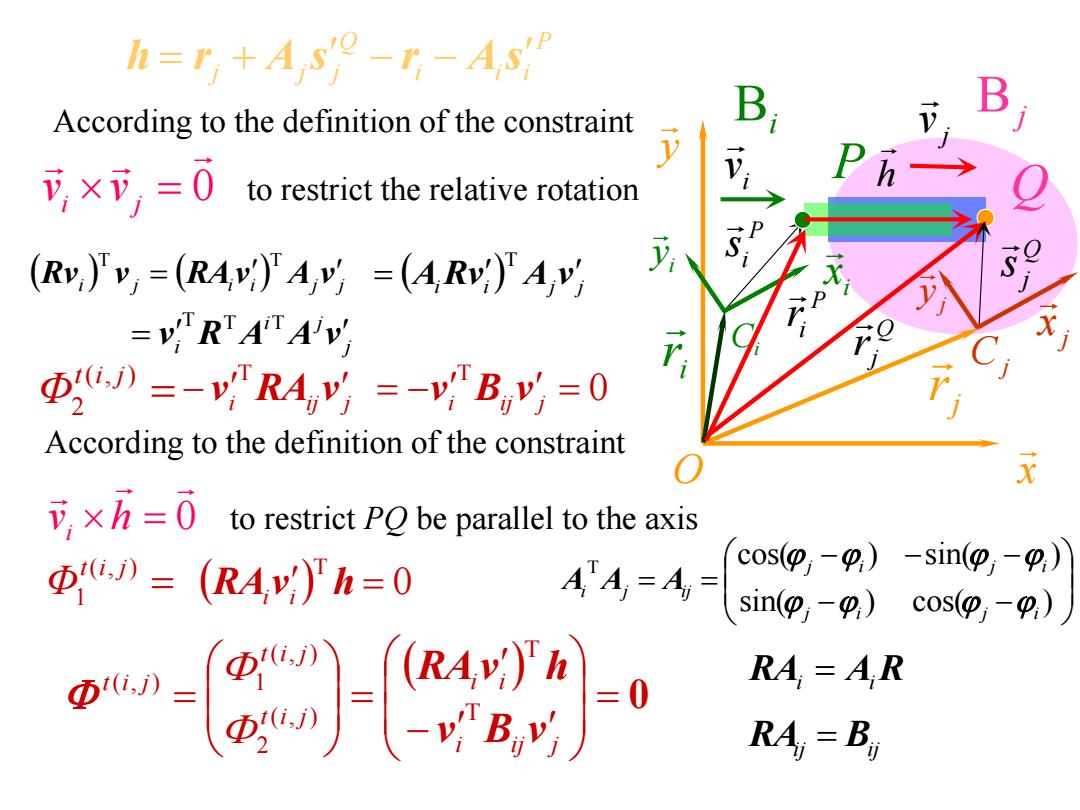
h=r+A s -r-As According to the definition of the constraint B ,×可,=0 toeitheativeoation (Rv)v,=(RAv:)A=(A Rv:)Av =VRTATAV F D》=-yRAy=-vB,y=0 According to the definition of the constraint 0to restrict P be parallel to the axis D》=(RA,)'h=0 AA=A= cos(p,-9,)-sin(p,-9,) sin(,-)cos(o;-) 。--a =0 RA=AR RA=B
According to the definition of the constraint 0 vi v j 0 vi h i j i i j j Rv v RAv A v T T 0 T RAivi h i ij j v RA v T i i j j A Rv A v T sin( ) cos( ) cos( ) sin( ) T j i j i j i j i i j ij A A A 0 i ij j i i t i j t i j t i j v B v RAv h T T ( , ) 2 ( , ) ( , ) 1 to restrict the relative rotation P i i i Q j j j h r A s r A s ( , ) 2 t i j Φ ( , ) 1 t i j Φ Bj y x O j x y j Cj j r Q Q j r Q j s P i s i x i y Ci Bi ir P P ir h i v j v 0 T vi Bijv j RAi AiR j i j i v R A A v T T T RAij Bij According to the definition of the constraint to restrict PQ be parallel to the axis