
J={c(SO)}{c.(Ba2+)} =4.8×104×2.0×10-3 =9.6×10-7 K=1.1x100 J>Ke,Thus some of the BaSO will precipitate out of solution
7 9.6 10- = 4 3 4.8 1 0 2.0 1 0 - - = { (SO )}{ (Ba )} 2 o 2 o 4 - + J = c c 10 sp 1.1 10- K = precipitate out of solution. BaSO will 4 J > Ksp ,Thus some of the

BaSO(s)-Ba2(aq)+ SO(aq) Initial/(nol.L) 2.0×103 4.8×10-4 Aftermixing/(md.L) 2.0×10-3-4.8×10-4 0 Equlibrium/(molL)1.52x103+x X (1.52×103+x)x=1.1×1010 x is verysmall,,1.52x103+x≈1.52×103 x=7.3×108 c(S02)=7.3×10-8moL mBaS04)=(4.8×104-x)×50.0×233 ≈4.8×104×50.0×233=5.6g
3 2.0 10- 4 4.8 10- Initial/(mol L ) -1 3 10 (1.5 2 1 0 ) 1.1 1 0 - - + x x = 3 3 is very small 1.5 2 1 0 1.5 2 1 0 - - x , + x 3 4 2.0 1 0 4.8 1 0 - - After mixing/(mol L ) - 0 -1 + x -3 Equlibrium/(mol L ) 1.52 10 x -1 BaSO (s) Ba (aq) SO (aq) 2 4 2 4 + - + 4.8 1 0 5 0.0 233 5.6g 4 = - (BaSO ) (4.8 1 0 ) 5 0.0 233 4 4 = - - m x 2 8 1 (SO4 ) 7.3 1 0 mol L - - - c = 8 7.3 10- x =
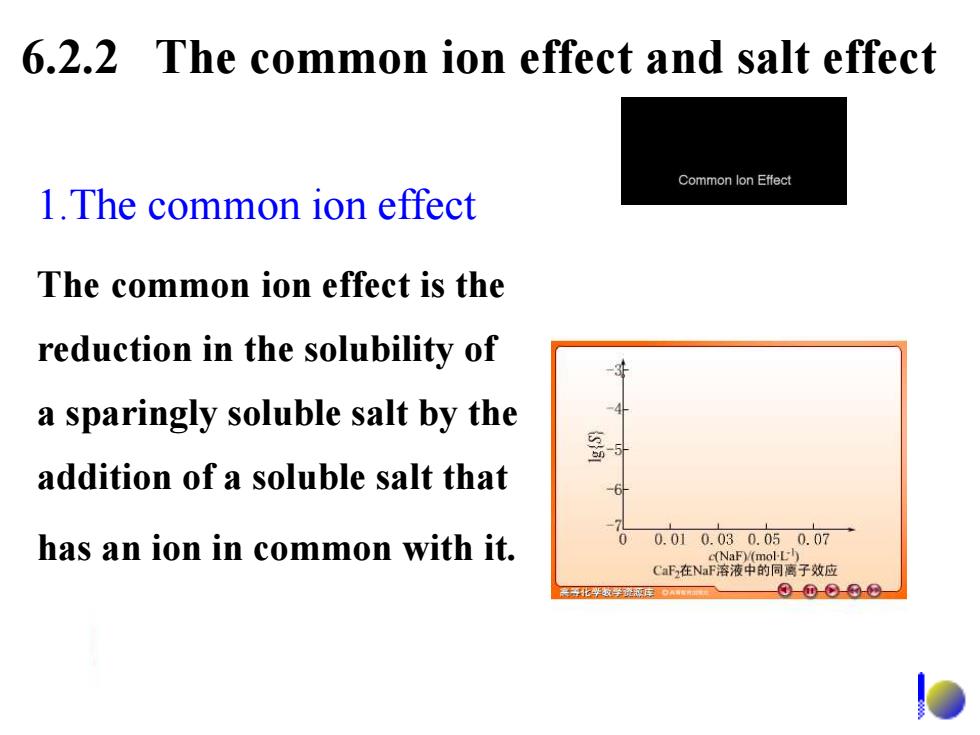
6.2.2 The common ion effect and salt effect Common lon Effect 1.The common ion effect The common ion effect is the reduction in the solubility of a sparingly soluble salt by the addition of a soluble salt that has an ion in common with it. 0 0.010.030.050.07 (NaF)(mol-L) CaF在NaF溶液中的同离子效应 ①①-⊙-⊙-⊙
6.2.2 The common ion effect and salt effect 1.The common ion effect The common ion effect is the reduction in the solubility of a sparingly soluble salt by the addition of a soluble salt that has an ion in common with it