
Chapter 2 Fundamental Hydraulic Fluid Mechanics 2.2 Hydrostatics 2.2.1 Characteristics of Hydrostatics 2.2.2 The basic formula of hydrostatics 2.2.3 The principle of Pascal application 2.2.4 Effect of fluid pressure on curved surfaces 11 Homepage List Upwards Downwards Retun Exit
Chapter 2 Fundamental Hydraulic Fluid Mechanics 11 2.2.1 Characteristics of Hydrostatics 2.2.2 The basic formula of hydrostatics 2.2.3 The principle of Pascal application 2.2.4 Effect of fluid pressure on curved surfaces 2.2 Hydrostatics
Chapter 2 Fundamental Hydraulic Fluid Mechanics 2.2.1 Characteristics of Hydrostatics 1.The hydrostatics Static pressure:the action force in normal on a unit area.It is intituled pressure in physics and action force in engineering usually 2.The characteristics of hydrostatics (1)In any homogeneous fluid system at rest,the pressure increases with the depth of the fluid. (2)Pressure at any point in a homogeneous fluid system at rest acts perpendicularly to surfaces in contact with the fluid 12 Homepage List Upwards Downwards Retumn Exit
Chapter 2 Fundamental Hydraulic Fluid Mechanics 12 1. The hydrostatics Static pressure: the action force in normal on a unit area. It is intituled pressure in physics and action force in engineering usually. 2. The characteristics of hydrostatics (1) In any homogeneous fluid system at rest, the pressure increases with the depth of the fluid. (2) Pressure at any point in a homogeneous fluid system at rest acts perpendicularly to surfaces in contact with the fluid. 2.2.1 Characteristics of Hydrostatics
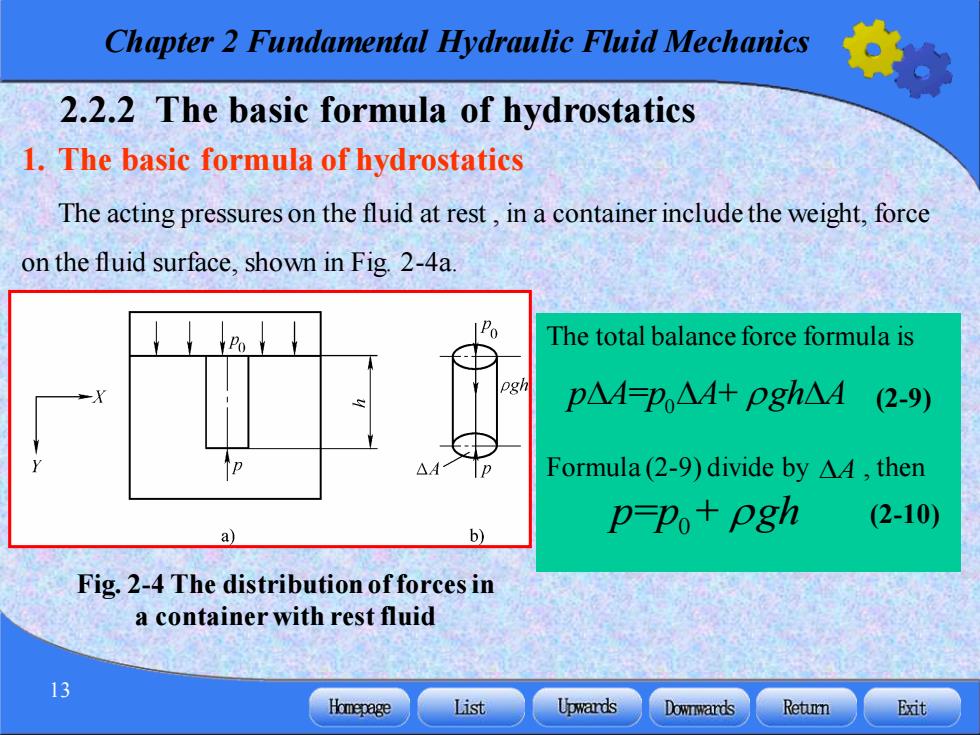
Chapter 2 Fundamental Hydraulic Fluid Mechanics 2.2.2 The basic formula of hydrostatics 1.The basic formula of hydrostatics The acting pressures on the fluid at rest,in a container include the weight,force on the fluid surface,shown in Fig.2-4a The total balance force formula is p△4=P△M+Pgh△M(2-9) Formula(2-9)divide by A4,then (2-10) a】 b) p-po+pgh Fig.2-4 The distribution of forces in a container with rest fluid 13 Homepage List Upwards Downwards Retumn Exit
Chapter 2 Fundamental Hydraulic Fluid Mechanics 13 2.2.2 The basic formula of hydrostatics 1. The basic formula of hydrostatics The acting pressures on the fluid at rest , in a container include the weight, force on the fluid surface, shown in Fig. 2-4a. Fig. 2-4 The distribution of forces in a container with rest fluid The total balance force formula is Formula (2-9) divide by , then = + 0 p A p A gh A (2-9) = + 0 p p gh (2-10) A
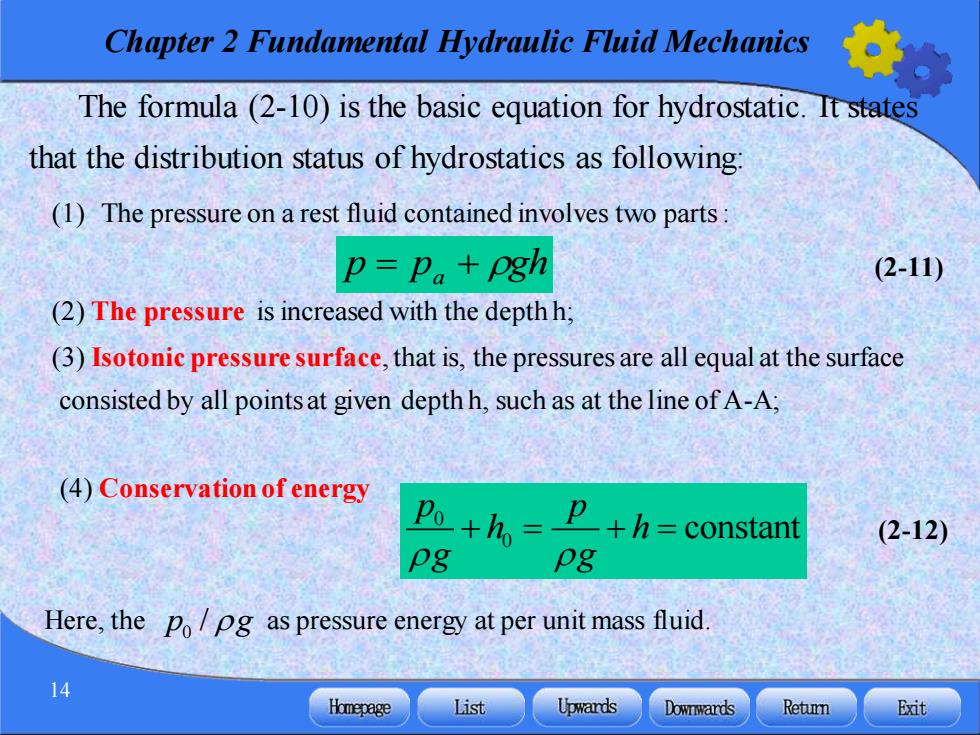
Chapter 2 Fundamental Hydraulic Fluid Mechanics The formula(2-10)is the basic equation for hydrostatic.It states that the distribution status of hydrostatics as following: (1)The pressure on a rest fluid contained involves two parts: p=p。+Pgh (2-11) (2)The pressure is increased with the depth h; (3)Isotonic pressure surface,that is,the pressures are all equal at the surface consisted by all points at given depth h,such as at the line of A-A; (4)Conservation of energy Po+ho +h=constant (2-12) pg pg Here,the po/pg as pressure energy at per unit mass fluid. 14 Homepage List Upwards Dowrwards Retumn Exit
Chapter 2 Fundamental Hydraulic Fluid Mechanics 14 (1) The pressure on a rest fluid contained involves two parts : The formula (2-10) is the basic equation for hydrostatic. It states that the distribution status of hydrostatics as following: (2) The pressure is increased with the depth h; (3) Isotonic pressure surface, that is, the pressures are all equal at the surface consisted by all points at given depth h, such as at the line of A-A; (4) Conservation of energy 0 0 constant p p h h g g + = + = (2-11) (2-12) p = pa + gh Here, the as pressure energy at per unit mass fluid. 0 p g /
Chapter 2 Fundamental Hydraulic Fluid Mechanics 2.The definition of pressure (1)Absolute pressure (2)Relative gauge pressure:The pressures measured by a pressure gauge are all relative pressure (3)Vacuum (negative pressure) The units of pressure and relations between different pressures 1Pa=1N/m2;1bar=1×105Pa=1×10sN/m2; 1at=1kgf/cm2=9.8×104N/m2;1mH20=9.8×103N/m2; 1mmHg=1.33×102N/m2. The relationship of three pressures is shown in Fig.2-5. 15 Homepage List Upwards Downwards Return Exit
Chapter 2 Fundamental Hydraulic Fluid Mechanics 15 2. The definition of pressure (1) Absolute pressure (2) Relative gauge pressure :The pressures measured by a pressure gauge are all relative pressure (3) Vacuum (negative pressure) 1Pa=1 N/m2;1bar=1×105 Pa=1×105 N/m2 ; 1at=1kgf/cm2=9.8×104 N/m2 ; 1mH2O=9.8×103 N/m2 ; 1mmHg =1.33×102 N/m2 . The relationship of three pressures is shown in Fig. 2-5. The units of pressure and relations between different pressures :