
Binders (adhesives) Definitions:the substances that act as adhesives to bind powders together in the wet granulation process are known as binders.Moistening agents is a kind of liquid which is not adhesive,it can moisten and induce the adhesiveness of other drug powders. Binders can be added in two ways depending on the method of granulation solid binders As a powder in the formulation as in “slugging”or in dry granulation method. liquid binders As a solution to the mixed powder as in wet granulation. The binders can be sprayed,poured,or admixed into the powders to be agglomerated
Binders (adhesives) Definitions: the substances that act as adhesives to bind powders together in the wet granulation process are known as binders. Moistening agents is a kind of liquid which is not adhesive, it can moisten and induce the adhesiveness of other drug powders. Binders can be added in two ways depending on the method of granulation ✓solid binders : As a powder in the formulation as in “slugging” or in dry granulation method. ✓liquid binders :As a solution to the mixed powder as in wet granulation. The binders can be sprayed, poured, or admixed into the powders to be agglomerated

Commonly used binders >Distilled water:applied to easily hydratable materials. Moistening Ethanol:applied to easily hydratable agents materials.30-70% Binders classification >Natural polymers >Synthetic polymers Sugars
Commonly used binders ➢ Distilled water: applied to easily hydratable materials. ➢ Ethanol: applied to easily hydratable materials. 30-70% ➢ Binders classification ➢ Natural polymers ➢ Synthetic polymers ➢ Sugars Moistening agents
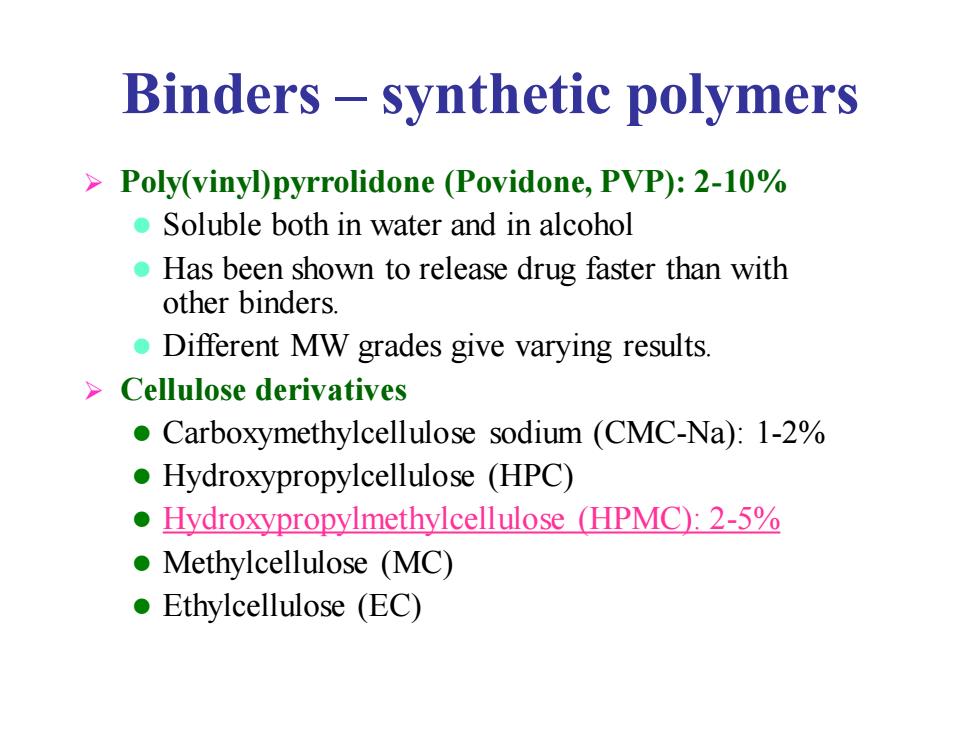
Binders-synthetic polymers Poly(vinyl)pyrrolidone (Povidone,PVP):2-10% Soluble both in water and in alcohol Has been shown to release drug faster than with other binders. Different MW grades give varying results. >Cellulose derivatives Carboxymethylcellulose sodium (CMC-Na):1-2% Hydroxypropylcellulose (HPC) Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC):2-5% Methylcellulose (MC) ●Ethylcellulose(EC)
Binders – synthetic polymers ➢ Poly(vinyl)pyrrolidone (Povidone, PVP): 2-10% ⚫ Soluble both in water and in alcohol ⚫ Has been shown to release drug faster than with other binders. ⚫ Different MW grades give varying results. ➢ Cellulose derivatives ⚫ Carboxymethylcellulose sodium (CMC-Na): 1-2% ⚫ Hydroxypropylcellulose (HPC) ⚫ Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC): 2-5% ⚫ Methylcellulose (MC) ⚫ Ethylcellulose (EC)

Disintegrants Disintegrants allow the tablet to break apart in the GI tract,usually in the stomach or small intestine,so that dissolution can occur,then the active component can be absorbed by the body. Essential for most tablets with exceptions in sustained/controlled release tablets, buccal/sublingual tablets
Disintegrants • Disintegrants allow the tablet to break apart in the GI tract, usually in the stomach or small intestine, so that dissolution can occur, then the active component can be absorbed by the body. • Essential for most tablets with exceptions in sustained/controlled release tablets, buccal/sublingual tablets

Diagrammatic representation of the disintegration and dissoluton steps prior to absorption from a tablet
Diagrammatic representation of the disintegration and dissoluton steps prior to absorption from a tablet