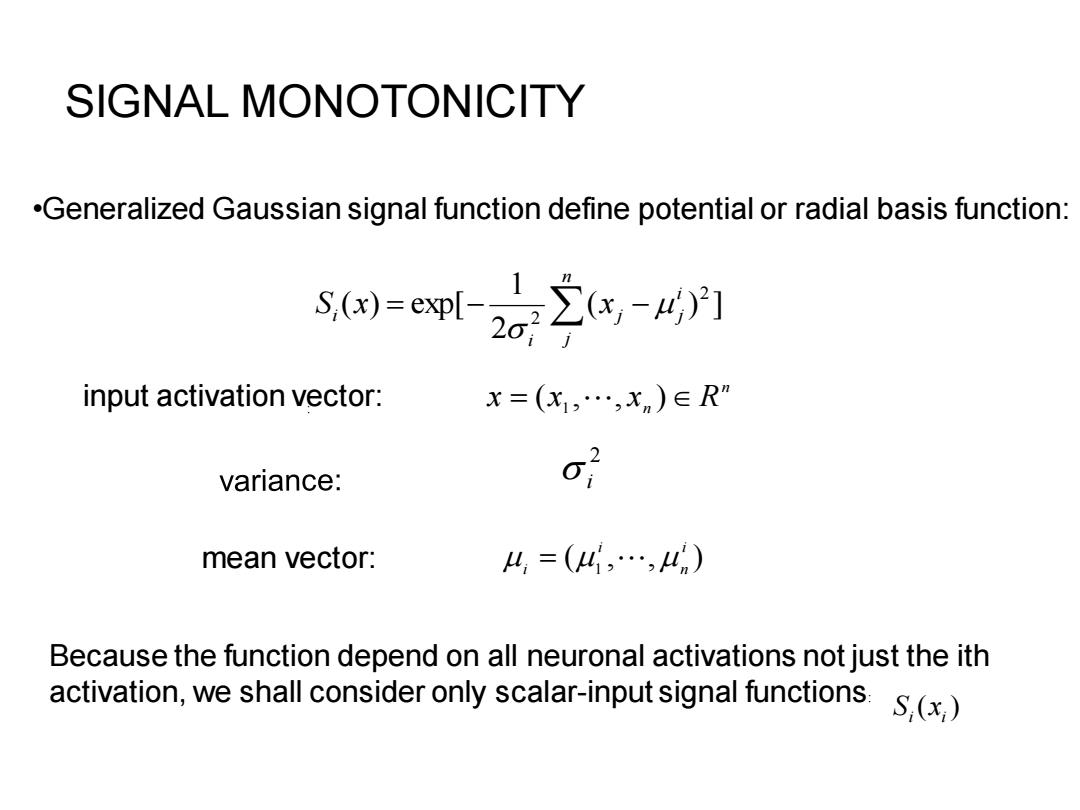
SIGNAL MONOTONICITY .Generalized Gaussian signal function define potential or radial basis function: x)x-] input activation vector: x=(X1,…,xn)∈R variance: o mean vector: 4,=(4,…,4) Because the function depend on all neuronal activations not just the ith activation,we shall consider only scalar-input signal functions.S(x
SIGNAL MONOTONICITY ( ) ] 2 1 ( ) exp[ 2 = − 2 − n j i j j i i S x x 2 i : •Generalized Gaussian signal function define potential or radial basis function: n input activation vector: x = (x1 , , x n ) R mean vector: ( , , ) 1 i n i i = ( ) i i S x Because the function depend on all neuronal activations not just the ith activation, we shall consider only scalar-input signal functions:

SIGNAL MONOTONICITY A property of signal monotonicity:semi-linearity 、Comparation: a.Linear signal functions: computation and analysis is comparatively easy;do not suppress noise. b.Nonlinear signal functions: Increases a network's computational richness and facilitates noise suppression;risks computational and analytical intractability;
SIGNAL MONOTONICITY • A property of signal monotonicity: semi-linearity • Comparation: a. Linear signal functions: computation and analysis is comparatively easy; do not suppress noise. b. Nonlinear signal functions: Increases a network’s computational richness and facilitates noise suppression; risks computational and analytical intractability;
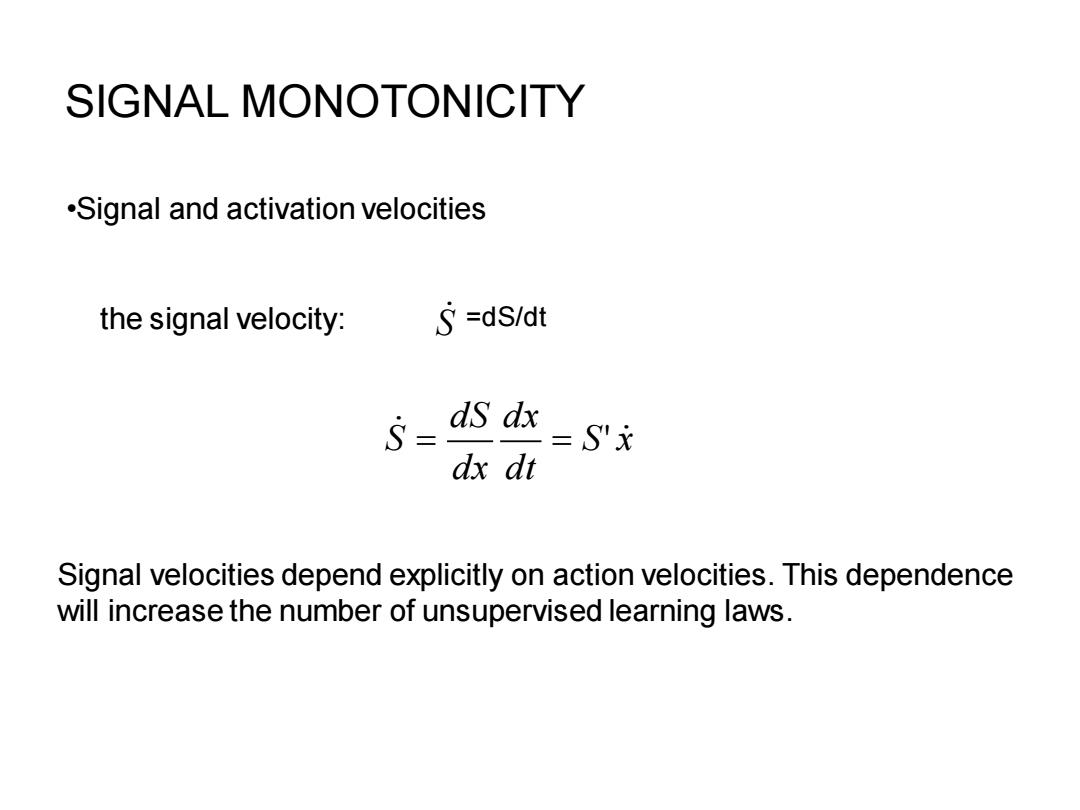
SIGNAL MONOTONICITY .Signal and activation velocities the signal velocity: S=dS/dt S= dS dx dx dt -Sx Signal velocities depend explicitly on action velocities.This dependence will increase the number of unsupervised learning laws
SIGNAL MONOTONICITY S x dt dx dx dS S = = ' •Signal and activation velocities the signal velocity: =dS/dt S Signal velocities depend explicitly on action velocities. This dependence will increase the number of unsupervised learning laws

BIOLOGICAL ACTIVATIONS AND SIGNALS .Introduction to units 细胞体(soma) Dendrite:input 树突(dendrites) Axon:output Synapse:transduce signal 轴突(aRon) 突触(synapse Membrane:potential difference between inside and outside of neuron Fig3.Key functional units of a biological neuron
BIOLOGICAL ACTIVATIONS AND SIGNALS Fig3. Key functional units of a biological neuron •Introduction to units : Dendrite: input Axon: output Synapse: transduce signal Membrane: potential difference between inside and outside of neuron