
11.2 Lytic development Infection is controlled by a Phage cascade DNA eveiopment ONA Syntnesis are made B酬cation Figure 11.3 Lytic development takes place by Late development producing phage genomes and protein particles that DNA packaged into heads; tails attached are assembled into progeny Lysis phages. erele asoken progery phages 情菜大当
Figure 11.3 Lytic development takes place by producing phage genomes and protein particles that are assembled into progeny phages. 11.2 Lytic development is controlled by a cascade
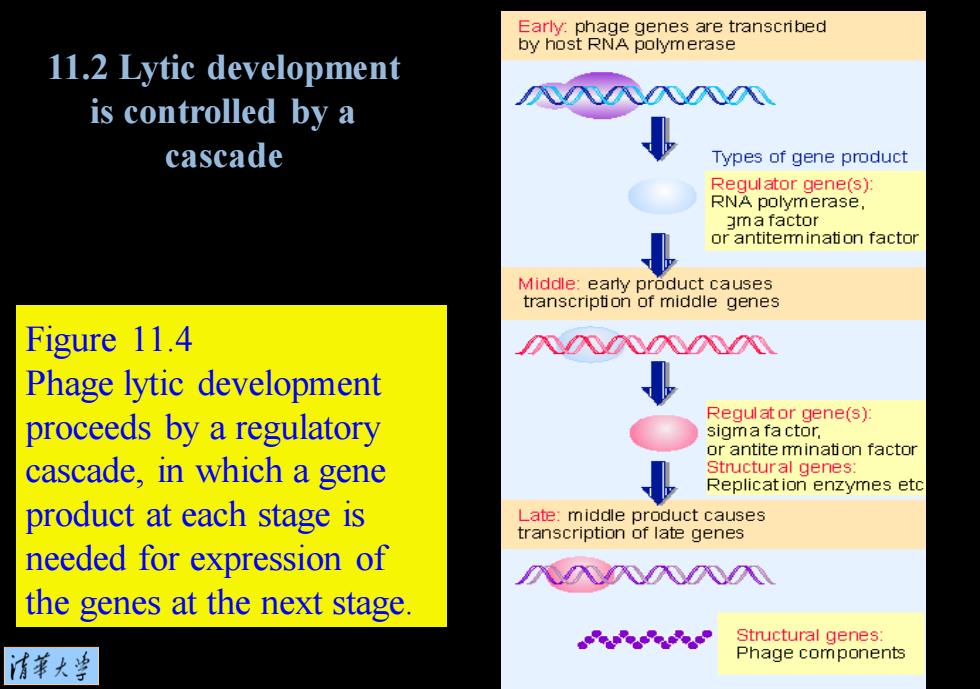
Early:phage genes are transcribed by host RNA polymerase 11.2 Lytic development is controlled by a cascade Types of gene product Requlator gene(s): RNA polymerase, gma factor or antitemmination factor Middle:early product causes transcription of middle genes Figure 11.4 入入入N Phage lytic development Regul at or gene(s): proceeds by a regulatory sigm a fa ctor, or antite mination factor cascade,in which a gene Structural genes Replication enzymes etc product at each stage is Late:middle product causes transcription of late genes needed for expression of 八风入八八 the genes at the next stage. Structural genes: 清第大当 Phage components
Figure 11.4 Phage lytic development proceeds by a regulatory cascade, in which a gene product at each stage is needed for expression of the genes at the next stage. 11.2 Lytic development is controlled by a cascade
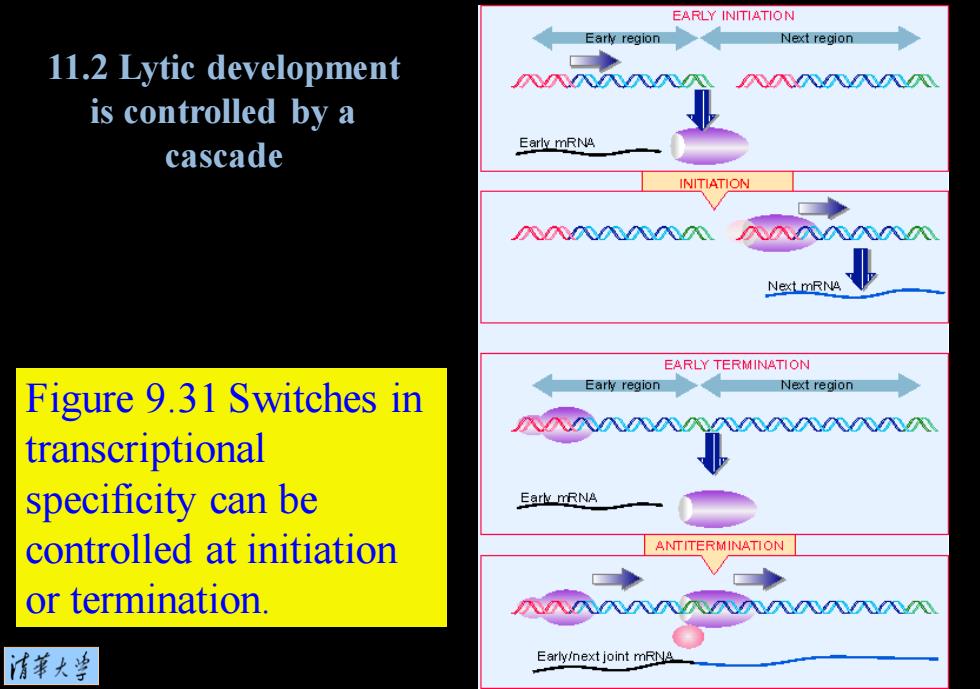
EARLY INITIATION Early region Next region 11.2 Lytic development 入入NNNN is controlled by a Early mRNA cascade INITIATION 八八八0Z02020 八入入入八NN Next mRNA EARLY TERMINATION Figure 9.31 Switches in Early region Next region transcriptional specificity can be Eark mRNA controlled at initiation ANTITERMINATION or termination. 入八NN入八八八入八N 情華大当 Early/next joint mRNA
Figure 9.31 Switches in transcriptional specificity can be controlled at initiation or termination. 11.2 Lytic development is controlled by a cascade

11.3 Functional Class I Class lI Class Ill clustering in phages T7 and T4 5 genes 7 genes 13 genes RNA polymerase ■■■■■■ Host interference Figure 11.5 Phage T7 contains three classes DNA synthesis of genes that are Lysozyme expressed sequentially.The Heads tails genome is ~38 kb DNA maturatior 清第大当
Figure 11.5 Phage T7 contains three classes of genes that are expressed sequentially. The genome is ~38 kb. 11.3 Functional clustering in phages T7 and T4

11.3 Functional clustering in phages T7 and T4 Figure 11.6 late RNA 55 The map ofT4 late RNA 45 tthymidine kinase is circular. de7V endonuclease V 42,43.62,44 io//,ip internal proteins There is DNA polymerase ete. 40 lys ozyme 57 tail fiber extensive head 40 dNMP kinase clustering of 3 sheath terminato 2 head completion genes coding 朗se 50 head completion for 65 head completion 80 5 baseplate plug components of topoisomerase the phage and Okb 6.7.89.10.12 A.日 processes such 160 b aseplate wvedge topoisomerase as DNA ac.13.19.1伦.7 replication,but 3837,363534 head there is also tail fibers 120 dispersion of late RNA 33 格sheath.19tal dTMP synthetase 2 genes coding for a variety of DNA ligase 30 baseplate 54.48 裂0mm0好2斗 enzymatic and 27.51.2626 baseplate plug other functions Essential genes are indicated by numbers.Nonessential genes are identified by letters.Only some representative T4 genes are shown on the map
Essential genes are indicated by numbers. Nonessential genes are identified by letters. Only some representative T4 genes are shown on the map. 11.3 Functional clustering in phages T7 and T4 Figure 11.6 The map of T4 is circular. There is extensive clustering of genes coding for components of the phage and processes such as DNA replication, but there is also dispersion of genes coding for a variety of enzymatic and other functions