
Chapter 9 Transcription 清革大当
Chapter 9 Transcription

9.1 Introduction 9.2 Transcription is catalyzed by RNA polymerase 9.3 The transcription reaction has three stages 9.4 A stalled RNA polymerase can restart 9.5 RNA polymerase consists of multiple subunits 9.6 RNA Polymerase consists of the core enzyme and sigma factor 9.7 Sigma factor is released at initiation 9.8 Sigma factor controls binding to DNA 9.9 Promoter recognition depends on consensus sequences 9.10 Promoter efficiencies can be increased or decreased by mutation 9.11 RNA polymerase binds to one face of DNA 9.12 Supercoiling is an important feature of transcription 9.13 Substitution of sigma factors may control initiation 9.14 Sigma factors directly contact DNA 9.15 Sigma factors may be organized into cascades 9.16 Sporulation is controlled by sigma factors 9.17 Bacterial RNA polymerase has two modes of termination 9.18 There are two types of terminator in E.coli 9.19 How does rho factor work? 9.20 Antitermination is a regulatory event 9.21 Antitermination requires sites that are independent of the terminators 9.22 More subunits for RNA polymerase 情菜大当
9.1 Introduction 9.2 Transcription is catalyzed by RNA polymerase 9.3 The transcription reaction has three stages 9.4 A stalled RNA polymerase can restart 9.5 RNA polymerase consists of multiple subunits 9.6 RNA Polymerase consists of the core enzyme and sigma factor 9.7 Sigma factor is released at initiation 9.8 Sigma factor controls binding to DNA 9.9 Promoter recognition depends on consensus sequences 9.10 Promoter efficiencies can be increased or decreased by mutation 9.11 RNA polymerase binds to one face of DNA 9.12 Supercoiling is an important feature of transcription 9.13 Substitution of sigma factors may control initiation 9.14 Sigma factors directly contact DNA 9.15 Sigma factors may be organized into cascades 9.16 Sporulation is controlled by sigma factors 9.17 Bacterial RNA polymerase has two modes of termination 9.18 There are two types of terminator in E. coli. 9.19 How does rho factor work? 9.20 Antitermination is a regulatory event 9.21 Antitermination requires sites that are independent of the terminators 9.22 More subunits for RNA polymerase
9.1 Introduction Coding strand of DNA has the same sequence as mRNA. Downstream identifies sequences proceeding farther in the direction of expression;for example,the coding region is downstream of the initiation codon. Primary transcript is the original unmodified RNA product corresponding to a transcription unit. Promoter is a region of DNA involved in binding of RNA polymerase to initiate transcription. RNA polymerases are enzymes that synthesize RNA using a DNA template (formally described as DNA-dependent RNA polymerases). Terminator is a sequence of DNA,represented at the end of the transcript,that causes RNA polymerase to terminate transcription. Transeription unit is the distance between sites of initiation and termination by RNA polymerase;may include more than one gene. Upstream identifies sequences proceeding in the opposite direction from expression;for example,the bacterial promoter is upstream from the transcription unit,the initiation codon is upstream of the coding region. 清菜大兰
Coding strand of DNA has the same sequence as mRNA. Downstream identifies sequences proceeding farther in the direction of expression; for example, the coding region is downstream of the initiation codon. Primary transcript is the original unmodified RNA product corresponding to a transcription unit. Promoter is a region of DNA involved in binding of RNA polymerase to initiate transcription. RNA polymerases are enzymes that synthesize RNA using a DNA template (formally described as DNA-dependent RNA polymerases). Terminator is a sequence of DNA, represented at the end of the transcript, that causes RNA polymerase to terminate transcription. Transcription unit is the distance between sites of initiation and termination by RNA polymerase; may include more than one gene. Upstream identifies sequences proceeding in the opposite direction from expression; for example, the bacterial promoter is upstream from the transcription unit, the initiation codon is upstream of the coding region. 9.1 Introduction
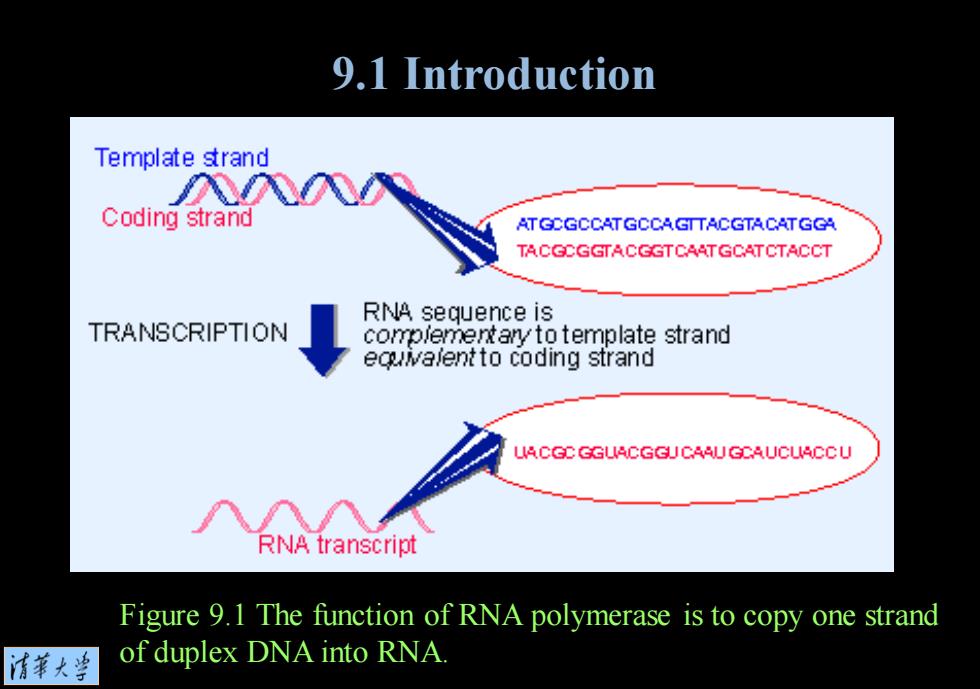
9.1 Introduction Template strand 入入0 Coding strand ATGCGCCATGCCAGTTACGTACATGGA TACGCGGTACGGTCAATGCATCTACCT RNA sequence is TRANSCRIPTION comp/emertary to template strand equva/entto coding strand LACGC GGUACGGUCAAUGCAUCUACCU RNA transcript Figure 9.1 The function of RNA polymerase is to copy one strand 情莱大当 of duplex DNA into RNA
Figure 9.1 The function of RNA polymerase is to copy one strand of duplex DNA into RNA. 9.1 Introduction
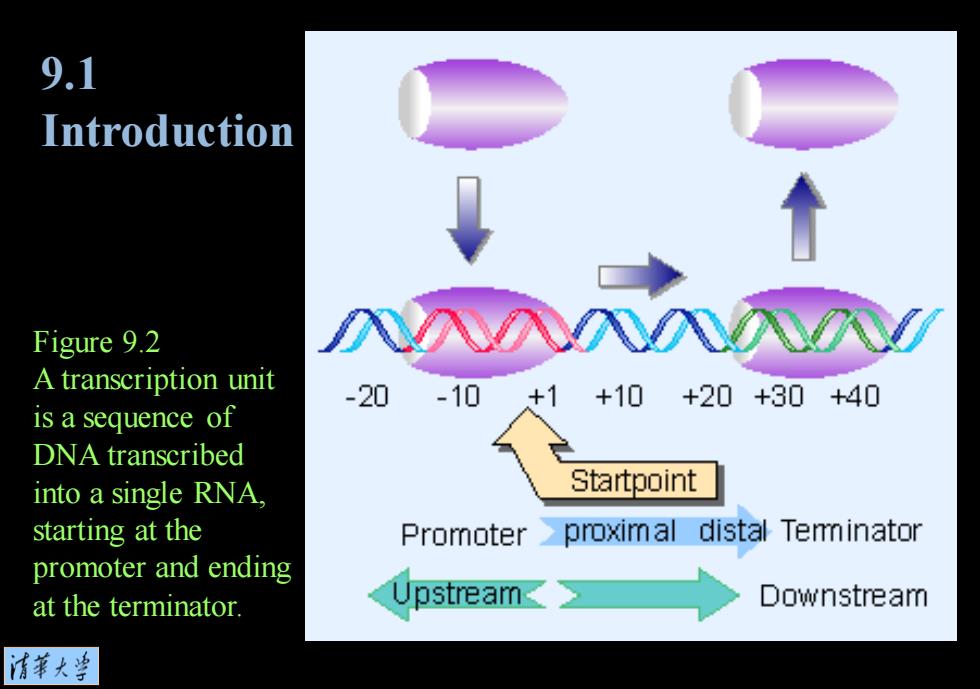
9.1 Introduction Figure 9.2 A transcription unit -20 -10 +1 +10+20+30+40 is a sequence of DNA transcribed into a single RNA, Startpoint starting at the Promoter proximal distal Teminator promoter and ending at the terminator. Downstream 清第大当
Figure 9.2 A transcription unit is a sequence of DNA transcribed into a single RNA, starting at the promoter and ending at the terminator. 9.1 Introduction