
Chapter 4 Clusters and repeats 清苇大当
Chapter 4 Clusters and repeats

Gene clusters are formed by duplication and divergence Sequence divergence is the basis for the evolutionary clock Pseudogenes are dead ends of evolution Unequal crossing-over rearranges gene clusters Genes for rRNA form tandem repeats The repeated genes for rRNA maintain constant sequence) Crossover fixation could maintain identical repeats Satellite DNAs often lie in heterochromatin Arthropod satellites have very short identical repeats Mammalian satellites consist of hierarchical repeats Minisatellites are useful for genetic mapping 清苇大当
Gene clusters are formed by duplication and divergence Sequence divergence is the basis for the evolutionary clock Pseudogenes are dead ends of evolution Unequal crossing-over rearranges gene clusters Genes for rRNA form tandem repeats ( The repeated genes for rRNA maintain constant sequence) Crossover fixation could maintain identical repeats Satellite DNAs often lie in heterochromatin Arthropod satellites have very short identical repeats Mammalian satellites consist of hierarchical repeats Minisatellites are useful for genetic mapping

4.1 Introduction Gene cluster is a group of adjacent genes that are identical or related. Gene family consists of a set of genes whose exons are related;the members were derived by duplication and variation from some ancestral gene. Satellite DNA consists of many tandem repeats(identical or related) of a short basic repeating unit. Unequal crossing-over describes a recombination event in which the two recombining sites lie at nonidentical locations in the two parental DNA molecules. 情菜大当
Gene cluster is a group of adjacent genes that are identical or related. Gene family consists of a set of genes whose exons are related; the members were derived by duplication and variation from some ancestral gene. Satellite DNA consists of many tandem repeats (identical or related) of a short basic repeating unit. Unequal crossing-over describes a recombination event in which the two recombining sites lie at nonidentical locations in the two parental DNA molecules. 4.1 Introduction
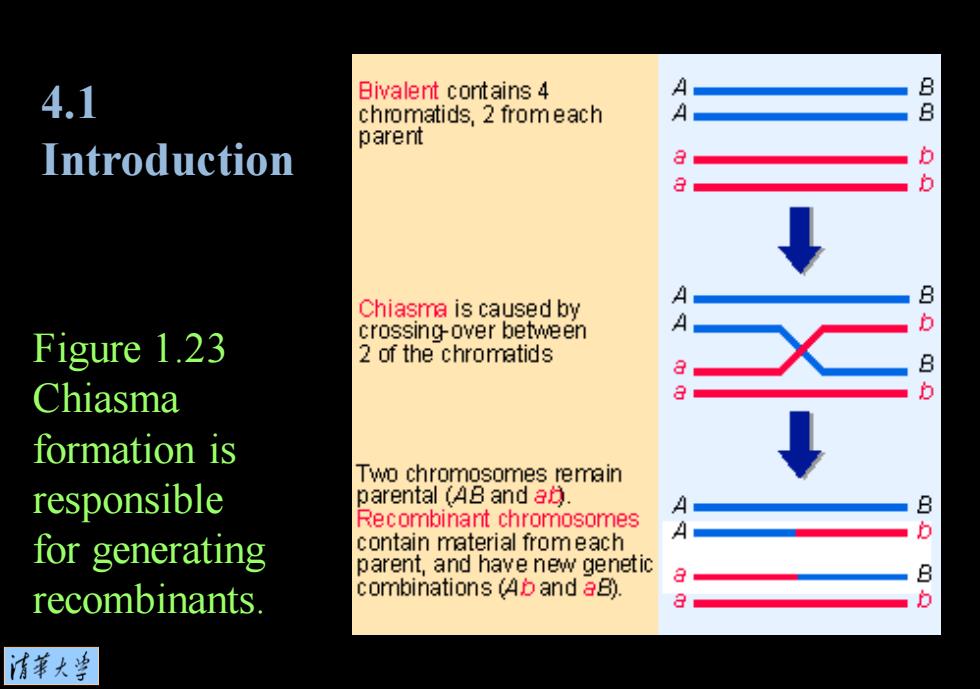
4.1 Bivalent contains 4 A chromatids,2 fromeach A parent Introduction aaQ b ↓ Chiasma is caused by A A aA Figure 1.23 crossing-over between 2 of the chromatids Chiasma formation is Two chromosomes remain responsible parental(48 and a月 A Recombinant chromosomes B A for generating contain material fromeach parent,and have new genetic recombinants. combinations (Ab and aB). a 清菜大当
Figure 1.23 Chiasma formation is responsible for generating recombinants. 4.1 Introduction
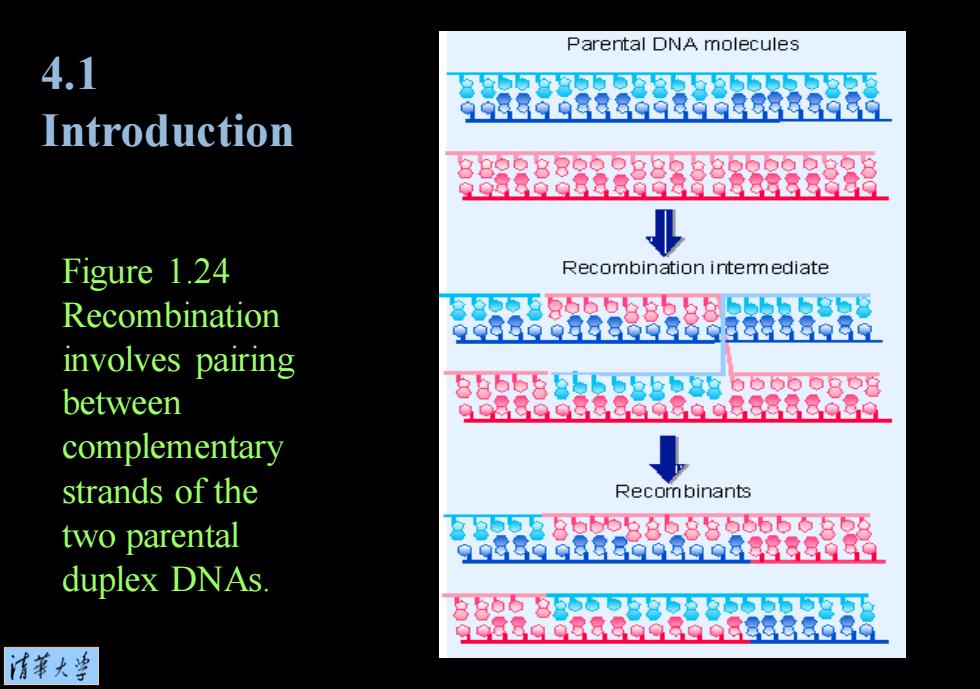
Parental DNA molecules 4.1 58533583553555555 99889白888698698B8898i Introduction Figure 1.24 Recombination intemmediate Recombination 38-555555558555555858 9988998863B898营88959 involves pairing 8355558555355885555o808 between 9G8889888a08a988888086 complementary strands of the Recombinants two parental 35558558588565688 88的9888G白8g988888的白 duplex DNAs. 88558358858855555 9G8Bg9B88G98位Q88意a3a 情華大兰
Figure 1.24 Recombination involves pairing between complementary strands of the two parental duplex DNAs. 4.1 Introduction