
Chapter 2 From Genes to Genomes 清革大当
Chapter 2 From Genes to Genomes

2.1 Introduction We can think about mapping genes and genomes at several levels of resolution: A genetic (or linkage)map identifies the distance between mutations in terms of recombination frequencies A linkage map can also be constructed by measuring recombination between sites in genomic DNA A restriction map is constructed by cleaving DNA into fragments with restriction enzymes and measuring the distances between the sites of cleavage. The ultimate map is to determine the sequence of the DNA From the sequence.we can identify genes and the distances between them 清菜大当
2.1 Introduction We can think about mapping genes and genomes at several levels of resolution: A genetic (or linkage) map identifies the distance between mutations in terms of recombination frequencies. A linkage map can also be constructed by measuring recombination between sites in genomic DNA. A restriction map is constructed by cleaving DNA into fragments with restriction enzymes and measuring the distances between the sites of cleavage. The ultimate map is to determine the sequence of the DNA. From the sequence, we can identify genes and the distances between them

2.1 Introduction 2.2 The nature of interrupted genes 2.3 Organization of interrupted genes may be conserved 2.4 Exon sequences are conserved but introns vary 2.5 Genes can be isolated by the conservation of exons 2.6 Genes show a wide distribution of sizes 2.7 Some DNA sequences code for more than one protein 2.8 How did interrupted genes evolve? 2.9 The scope of the paradigm 清苇大当
2.1 Introduction 2.2 The nature of interrupted genes 2.3 Organization of interrupted genes may be conserved 2.4 Exon sequences are conserved but introns vary 2.5 Genes can be isolated by the conservation of exons 2.6 Genes show a wide distribution of sizes 2.7 Some DNA sequences code for more than one protein 2.8 How did interrupted genes evolve? 2.9 The scope of the paradigm

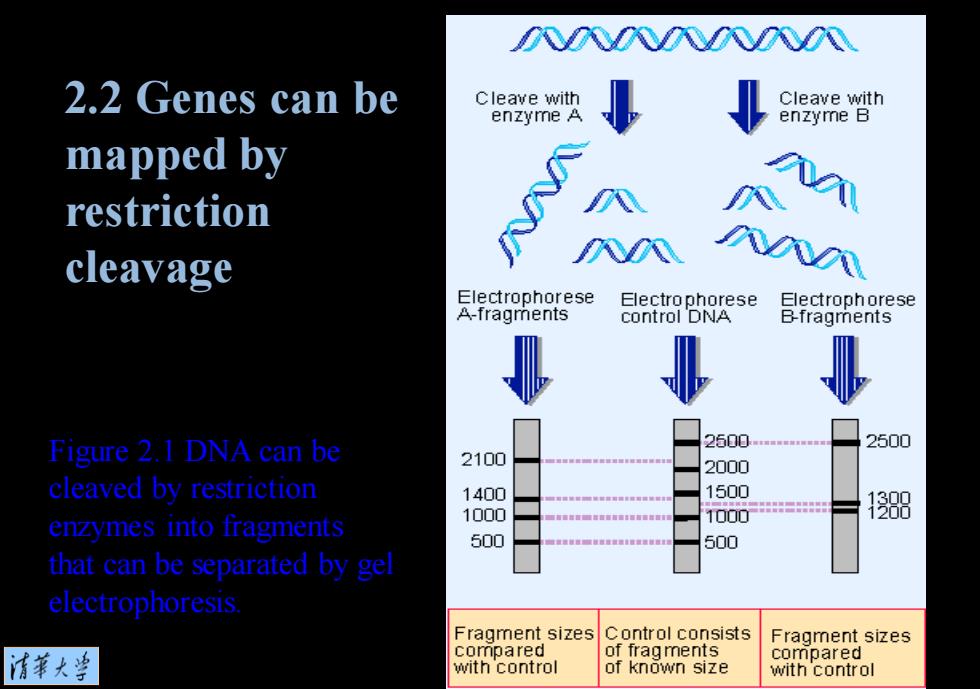
2.2 Genes can be mapped by restriction cleavage bp is an abbreviation for base pairs; distance along DNA is measured in bp Restriction enzymes recognize specific short sequences of DNA and cleave the duplex (sometimes at target site,sometimes elsewhere. depending on type) Restriction map is a inear array of sites c DNA cleaved 情菜大当
bp is an abbreviation for base pairs; distance along DNA is measured in bp. Restriction enzymes recognize specific short sequences of DNA and cleave the duplex (sometimes at target site, sometimes elsewhere, depending on type). Restriction map is a linear array of sites on DNA cleaved by various restriction enzymes. 2.2 Genes can be mapped by restriction cleavage
NA八入NN 2.2 Genes can be Cleave with Cleave with enzyme A enzyme B mapped by restriction cleavage Electrophorese Electrophorese Electrophorese A-fragments control DNA B-fragments ↓ Figure 2.1 DNA can be 2600.mm 2500 2100 2000 cleaved by restriction 1400 1500 1000 1000 18 enzymes into fragments 500 500 that can be separated by ge electrophoresis. Fragment sizes Control consists Fragment sizes compared 清菜大当 of fragments compared with control of known size with control
Figure 2.1 DNA can be cleaved by restriction enzymes into fragments that can be separated by gel electrophoresis. 2.2 Genes can be mapped by restriction cleavage