
Chapter 5 Messenger RNA 清苇大当
Chapter 5 Messenger RNA
5.1 Introduction 5.2 Transfer RNA is the adapter 5.3 Messenger RNA is translated by ribosomes 5.4 The life cycle of bacterial messenger RNA 5.5 Translation of eukaryotic mRNA 5.6 The 5'end of eukaryotic mRNA is capped 5.7 The 3'terminus is polyadenylated 5.8 Bacterial mRNA degradation involves multiple enzymes 5.9 mRNA degradation involves multiple activities 5.10 Sequence elements may destabilize mRNA 5.11 Nonsense mutations trigger a surveillance system 清苇大当
5.1 Introduction 5.2 Transfer RNA is the adapter 5.3 Messenger RNA is translated by ribosomes 5.4 The life cycle of bacterial messenger RNA 5.5 Translation of eukaryotic mRNA 5.6 The 5 end of eukaryotic mRNA is capped 5.7 The 3 terminus is polyadenylated 5.8 Bacterial mRNA degradation involves multiple enzymes 5.9 mRNA degradation involves multiple activities 5.10 Sequence elements may destabilize mRNA 5.11 Nonsense mutations trigger a surveillance system

5.1 Introduction Coding region is a part of the gene that represents a protein sequence Coding strand of DNA has the same sequence as mRNA. template strand of double-stranded DNA is the one that is used to specify the sequence of a complementary single strand of RNA.(The non-template strand is identical in sequence to the RNA product. Transcription is synthesis of RNA on a DNA template. Translation is synthesis of protein on the mRNA template. 情華大当
Coding region is a part of the gene that represents a protein sequence. Coding strand of DNA has the same sequence as mRNA. template strand of double-stranded DNA is the one that is used to specify the sequence of a complementary single strand of RNA. (The non-template strand is identical in sequence to the RNA product.) Transcription is synthesis of RNA on a DNA template. Translation is synthesis of protein on the mRNA template. 5.1 Introduction
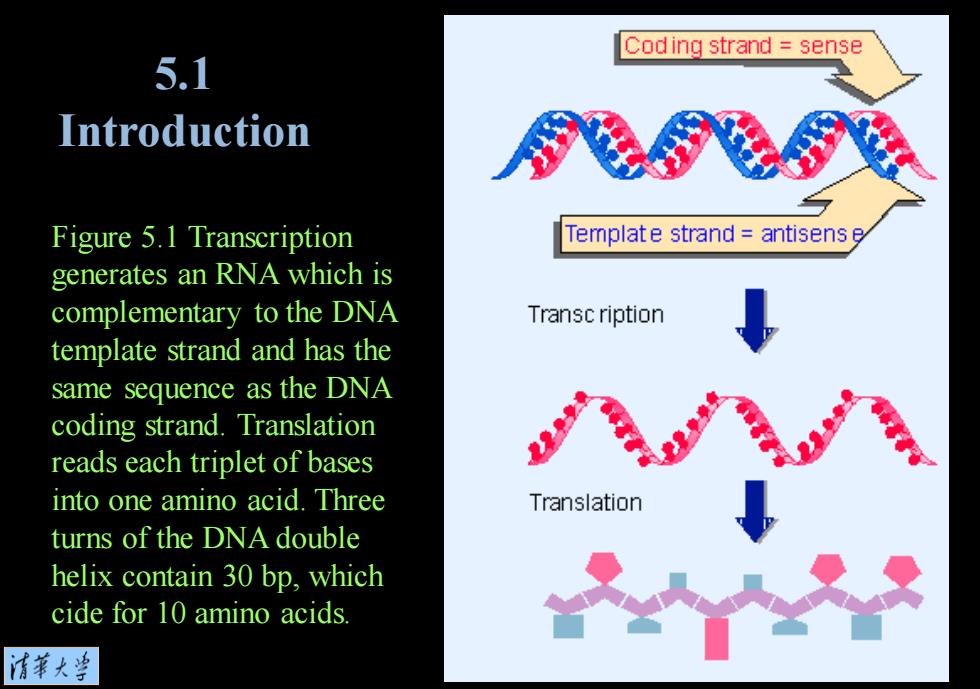
Coding strand sense 5.1 Introduction Figure 5.1 Transcription Template strand antisens e generates an RNA which is complementary to the DNA Transc ription template strand and has the same sequence as the DNA coding strand.Translation reads each triplet of bases into one amino acid.Three Translation turns of the DNA double helix contain 30 bp,which cide for 10 amino acids 清菜大当
Figure 5.1 Transcription generates an RNA which is complementary to the DNA template strand and has the same sequence as the DNA coding strand. Translation reads each triplet of bases into one amino acid. Three turns of the DNA double helix contain 30 bp, which cide for 10 amino acids. 5.1 Introduction

5.2 Transfer RNA is the adapter Aminoacyl-tRNA is transfer RNA carrying an amino acid;the covalent linkage is between the NH2 group of the amino acid and either the 3'- or 2'-OH group of the terminal base of the tRNA. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are enzymes responsible for covalently linking amino acids to the 2'-or 3'-OH position of tRNA. Anticodon is a trinucleotide sequence in tRNA which is complementary to the codon in mRNA and enables the tRNA to place the appropriate amino acid in response to the codon. Loop is a single-stranded region at the end of a hairpin in RNA (or single-stranded DNA);corresponds to the sequence between inverted repeats in duplex DNA. Stem is the base-paired segment of a hairpin 情苇大兰
Aminoacyl-tRNA is transfer RNA carrying an amino acid; the covalent linkage is between the NH2 group of the amino acid and either the 3′- or 2′-OH group of the terminal base of the tRNA. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are enzymes responsible for covalently linking amino acids to the 2′- or 3′-OH position of tRNA. Anticodon is a trinucleotide sequence in tRNA which is complementary to the codon in mRNA and enables the tRNA to place the appropriate amino acid in response to the codon. Loop is a single-stranded region at the end of a hairpin in RNA (or single-stranded DNA); corresponds to the sequence between inverted repeats in duplex DNA. Stem is the base-paired segment of a hairpin. 5.2 Transfer RNA is the adapter