
Chapter 7 Using the genetic code 清革大当
Chapter 7 Using the genetic code

7.1 Introduction 7.2 Codon-anticodon recognition involves wobbling 7.3 tRNA contains modified bases that influence its pairing properties 7.4 (There are sporadic alterations of the universal code) 7.5 tRNAs are charged with amino acids by synthetases 7.6 Accuracy depends on proofreading 7.7 Suppressor tRNAs have mutated anticodons that read new codons 7.8 The accuracy of translation 7.9 tRNA may influence the reading frame 情莘大当
7.1 Introduction 7.2 Codon-anticodon recognition involves wobbling 7.3 tRNA contains modified bases that influence its pairing properties 7.4 (There are sporadic alterations of the universal code) 7.5 tRNAs are charged with amino acids by synthetases 7.6 Accuracy depends on proofreading 7.7 Suppressor tRNAs have mutated anticodons that read new codons 7.8 The accuracy of translation 7.9 tRNA may influence the reading frame

7.1 Introduction Stop codons are the three triplets (UAA,UAG. UGA)which terminate protein synthesis. 清苇大当
Stop codons are the three triplets (UAA, UAG, UGA) which terminate protein synthesis. 7.1 Introduction

900h啊 7.1 Introduction U 0 UUU Phe UCU UAU UUC UAC Tyr UGU UGC Cys UUA Ser UAA UUG Leu UAG STOPUGA STOP UGG Trp Figure 7.1 All the CUU triplet codons have cuc Leu CAU CAC His CGU cGc CUA CCA CAA CGA Arg CUG cce GIn meaning:61 CAG cGG represent amino Asn AGU AGCI Ser acids,and 3 cause AA Met Lys AGA AGG Arg termination (STOP) 勇 GAU GGU Val Ala GAC GGc GUG Glu GGA Gly CGG 情華大当
Figure 7.1 All the triplet codons have meaning: 61 represent amino acids, and 3 cause termination (STOP). 7.1 Introduction
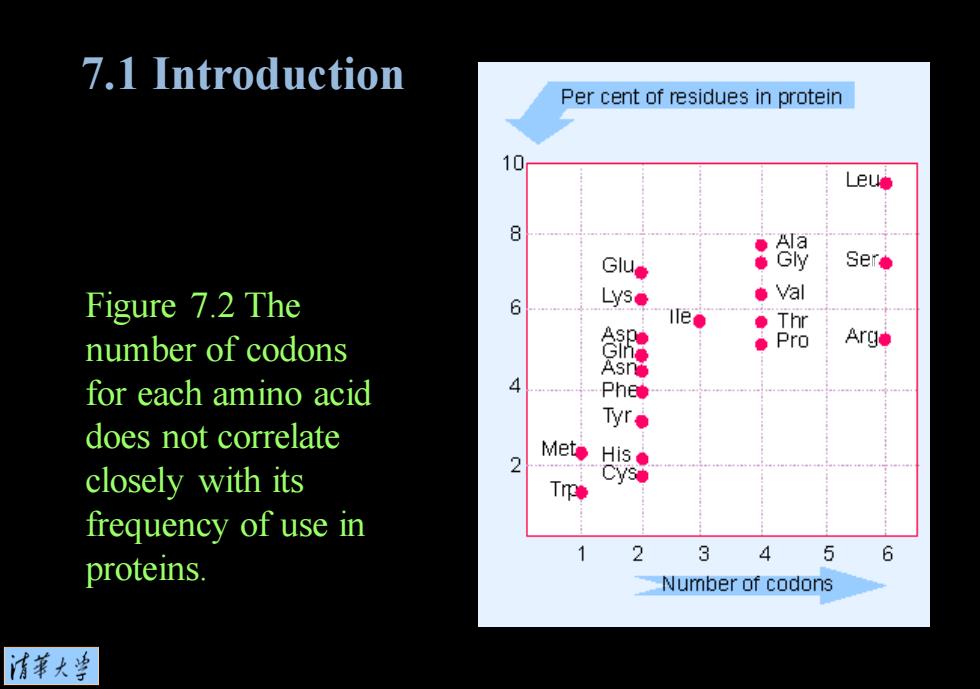
7.1 Introduction Per cent of residues in protein 10 Le墙 8 Ala Gu● Gly Ser◆ Figure 7.2 The ●Val 6 ●Thr number of codons Pro Arge for each amino acid 4 does not correlate Mete closely with its T frequency of use in 2 3 4 5 6 proteins. Number of codons 清苇大当
Figure 7.2 The number of codons for each amino acid does not correlate closely with its frequency of use in proteins. 7.1 Introduction