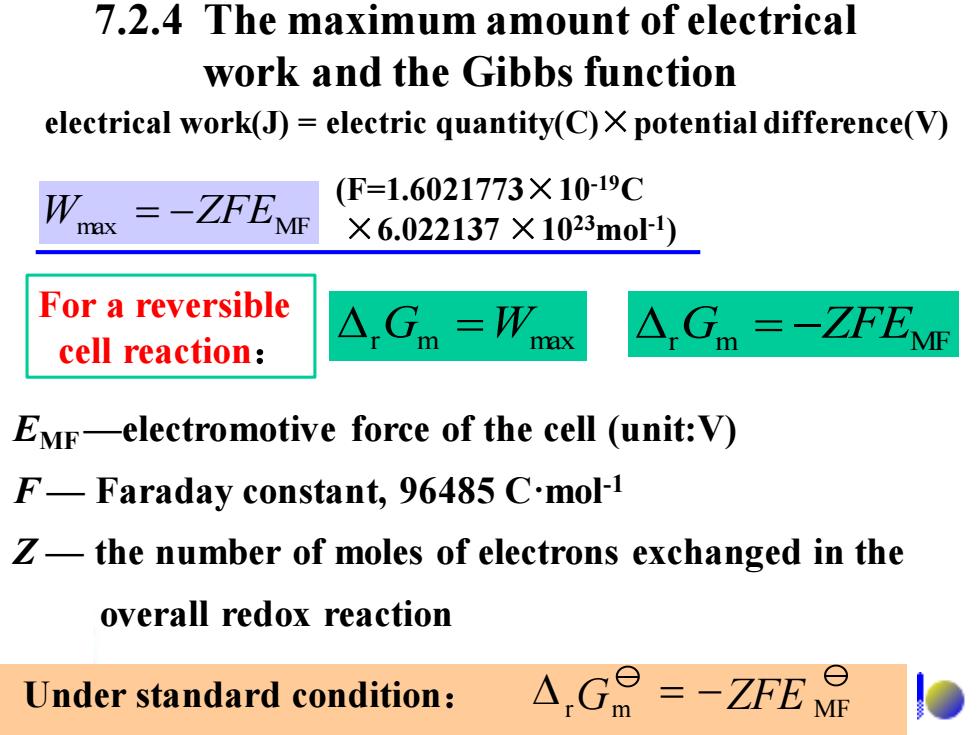
7.2.4 The maximum amount of electrical work and the Gibbs function electrical work(J)=electric quantity(C)X potential difference(V) W (F=1.6021773×10-19C ax =-ZFEMF ×6.022137×1023mo1) For a reversible 、=W cell reaction: m ax △Gm=-ZfEM EMF-electromotive force of the cell (unit:V) F-Faraday constant,96485 C.mol-1 Z-the number of moles of electrons exchanged in the overall redox reaction Under standard condition: A,G=-ZfE品
7.2.4 The maximum amount of electrical work and the Gibbs function EMF —electromotive force of the cell (unit:V) F — Faraday constant, 96485 C·mol-1 Z — the number of moles of electrons exchanged in the overall redox reaction r Gm =Wmax Wmax = −ZFEMF electrical work(J) = electric quantity(C)×potential difference(V) For a reversible cell reaction: Under standard condition: rGm ZFE MF = − (F=1.6021773×10-19C ×6.022137 ×1023mol-1 ) r Gm = −ZFEMF

7.3 Electrode potentials -7.3.1 The standard hydrogen electrode(SHE)and calomel electrode 7.3.2 Standard electrode potentials 7.3.3 The Nernst equation -*7.3.4 E-pH diagram
§7.3 Electrode potentials 7.3.1 The standard hydrogen electrode(SHE) and calomel electrode 7.3.2 Standard electrode potentials 7.3.3 The Nernst equation *7.3.4 E-pH diagram
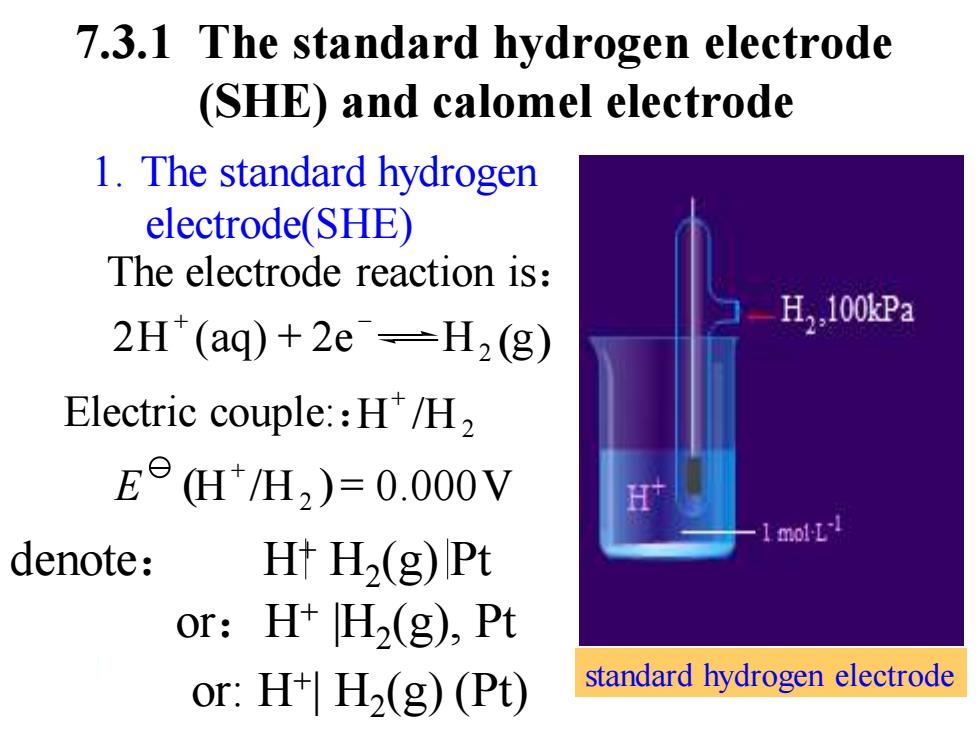
7.3.1 The standard hydrogen electrode (SHE)and calomel electrode 1.The standard hydrogen electrode(SHE) The electrode reaction is: H,,100kPa 2H(aq)+2e=H2(g) Electric couple:H/H, EeH/H2)=0.000V 1 mol-L-1 denote: H+H2(g)Pt or: H+H2(g),Pt or:H+H2(g)(Pt) standard hydrogen electrode
7.3.1 The standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) and calomel electrode Electric couple::H /H2 + The electrode reaction is: denote: H+ H2 (g) Pt 1. The standard hydrogen electrode(SHE) (H /H2 )= 0.000V + E 2H (aq) + 2e H2 (g) + − standard hydrogen electrode or:H+ |H2 (g), Pt or: H+ | H2 (g) (Pt)
2.Calomel electrode a reference electrode; the reaction between elemental mercury Hg and mercury(D)chloride Hg2Cl2 “calomel'") Electrode notation: Pt,Hg(1)Hg2Cl(s)CI(2.8mol-L) or:Pt Hg(1)Hg2Cl2(s)CI(2.8mol-L) Electrode reaction:Hg2Cl2(s)+2e--2Hg(1)+2 Cl (aq
2. Calomel electrode a reference electrode; the reaction between elemental mercury Hg and mercury(I) chloride Hg2Cl2 “calomel") Pt, Hg(l) Hg Cl (s) Cl (2.8mol L ) 1 2 2 Electrode notation: − − Electrode reaction: − Hg Cl (s)+2e− 2Hg(l)+2Cl (aq) 2 2 Pt |Hg(l) Hg Cl (s) Cl (2.8mol L ) 1 2 2 − − or: