
电子转发女学光电科学与工程学院 SCHOOL OF OPTOELECTRONIC SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING OF UESTC Outline A Model of the Image Degradation/Restoration Process Noise Models Restoration in the Presence of Noise Only-Spatial Filtering Periodic Noise Reduction by Frequency Domain Filtering Linear,Position-Invariant Degradations ◆ Estimating the Degradation Function Inverse Filtering Minimum Mean Square Error (Wiener)Filtering Constrained Least Squares Filtering Geometric Mean Filter Image Reconstruction from Projections*
Outline ◆ A Model of the Image Degradation/Restoration Process ◆ Noise Models ◆ Restoration in the Presence of Noise Only-Spatial Filtering ◆ Periodic Noise Reduction by Frequency Domain Filtering ◆ Linear, Position-Invariant Degradations ◆ Estimating the Degradation Function ◆ Inverse Filtering ◆ Minimum Mean Square Error (Wiener) Filtering ◆ Constrained Least Squares Filtering ◆ Geometric Mean Filter ◆ Image Reconstruction from Projections*

电子转发女学光电科学与工程学院 SCHOOL OF OPTOELECTRONIC SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING OF UESTC 5,2 Noise Models Agenda Noise Probability Density Functions g Periodic Noise Estimation of Noise Parameters Agenda
Noise Probability Density Functions Periodic Noise Estimation of Noise Parameters 5.2 Noise Models Agenda

电子科线女学光电科学与工程学院 SCHOOL OF OPTOELECTRONIC SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING OF UESTC 1.Noise Probability Density Functions Gaussian noise Rayleigh noise Erlang (Gamma)noise Exponential noise Uniform noise Impulse(Salt Pepper)noise
Gaussian noise Rayleigh noise Erlang (Gamma) noise Exponential noise Uniform noise Impulse (Salt & Pepper) noise 1. Noise Probability Density Functions
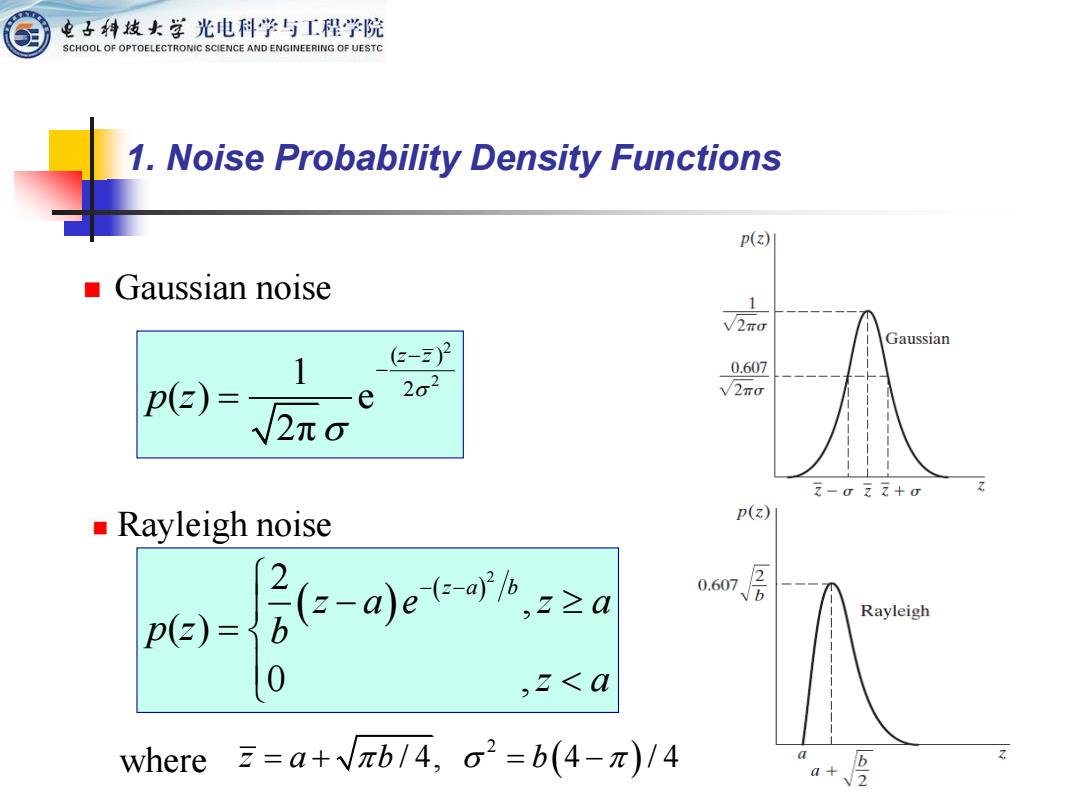
电子转发女学光电科学与工程学院 SCHOOL OF OPTOELECTRONIC SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING OF UESTC 1.Noise Probability Density Functions p(z) ■Gaussian noise 1 V2To Gaussian 1 e-2)2 0.607 p2)=1 29 2o2 V2mG i-o ii+o 1 Rayleigh noise p(z) pe=2e-ae:≥a 0.607 Rayleigh ,2<a where 三=a+Vπb/4,o2=b(4-π)/4 a+ √2
2 2 ( ) 2 1 ( ) e 2π z z p z − − = ◼ Gaussian noise 1. Noise Probability Density Functions ( ) ( ) 2 2 , ( ) 0 , z a b z a e z a p z b z a − − − = ◼ Rayleigh noise where ( ) 2 z a b b = + = − / 4, 4 / 4
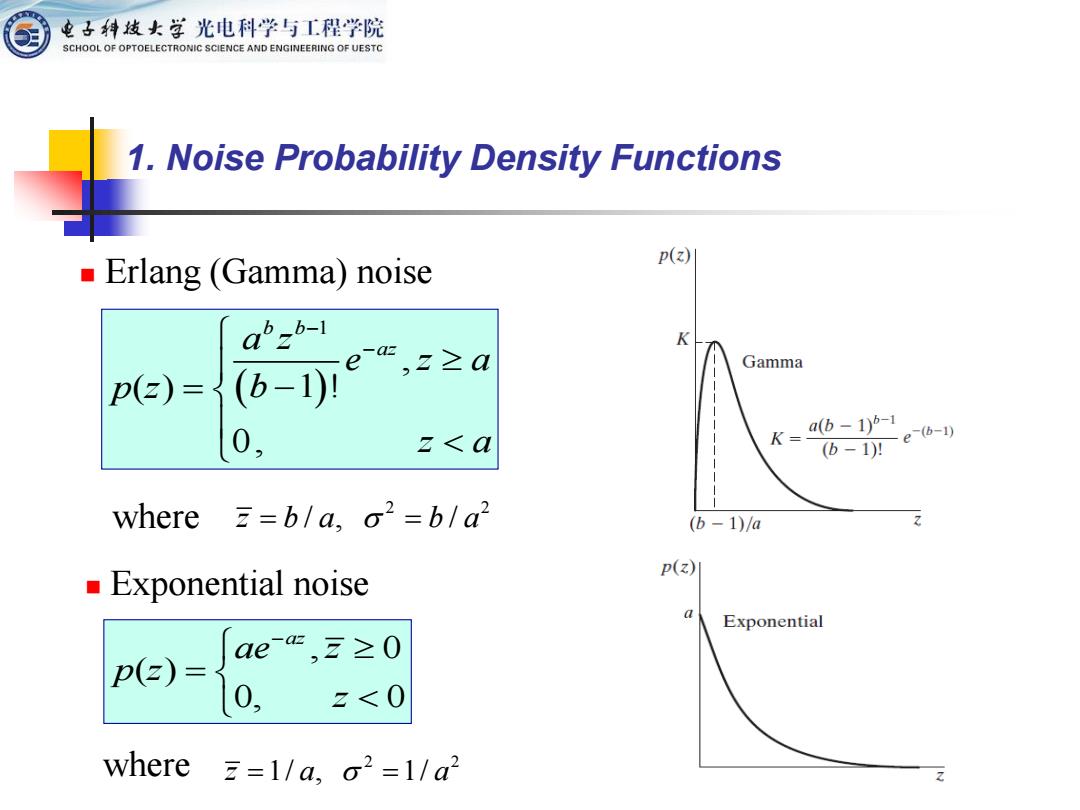
电子转发女学光电科学与工程学院 SCHOOL OF OPTOELECTRONIC SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING OF UESTC 1.Noise Probability Density Functions p(z)1 Erlang (Gamma)noise abzb-1 K p(z)={(b-1)川 ,2≥a e Gamma 0, a(b-1)b-1 z<a (6-1)!e-(6-1) where z=bla,o2=bla2 (b-1)/a p(z) Exponential noise a Exponential ae,z≥0 p(z)= 0, z<0 where z=1/a,o2=1/a2
, 0 ( ) 0, 0 az ae z p z z − = ◼ Erlang (Gamma) noise 1. Noise Probability Density Functions ( ) 1 , ( ) 1 ! 0 , b b a z az e z a p z b z a − − = − ◼ Exponential noise 2 2 where z b a b a = = / , / 2 2 where z a a = = 1/ , 1/