
新科学△△4
20

Chapter 2 Kinetics of Homogeneous Reaction Simple Reactor types Steady-state flow Batch Plug flow Mixed flow Uniform composition Fluid passes through the reactor Uniformly mixed,same everywhere in the reactor, with no mixing of earlier and later composition everywhere but of course the entering fluid,and with no overtaking. within the reactor and composition changes It is as if the fluid moved in single at the exit. with time. file through the reactor. Figure 2.1 Ideal reactor types. 21
21 Chapter 2 Kinetics of Homogeneous Reaction • Simple Reactor types

·The Rate Equation Suppose a single-phase reaction aA+bB→rR+SS The most useful measure of reaction rate for reactant A is then rate of disappearance of A 1 dNA(amount of A disappearing). mol A Vdt (volume)(time) m3.s note that this is an the minus sign intensive measure means disappearance 22
22 • The Rate Equation • Suppose a single-phase reaction • The most useful measure of reaction rate for reactant A is then aA+ bB →rR + sS

The rates of reaction of all materials are related by: -P=-rh==is a b S Experience shows that the rate of reaction is influenced by the composition and the energy of the material. Energy means temperature,light intensity, magnetic field intensity etc.Ordinarily we only need to consider the temperature. 23
23 • The rates of reaction of all materials are related by: • Experience shows that the rate of reaction is influenced by the composition and the energy of the material. • Energy means temperature, light intensity, magnetic field intensity etc. Ordinarily we only need to consider the temperature. s r r r b r a rA B R S = = − = −
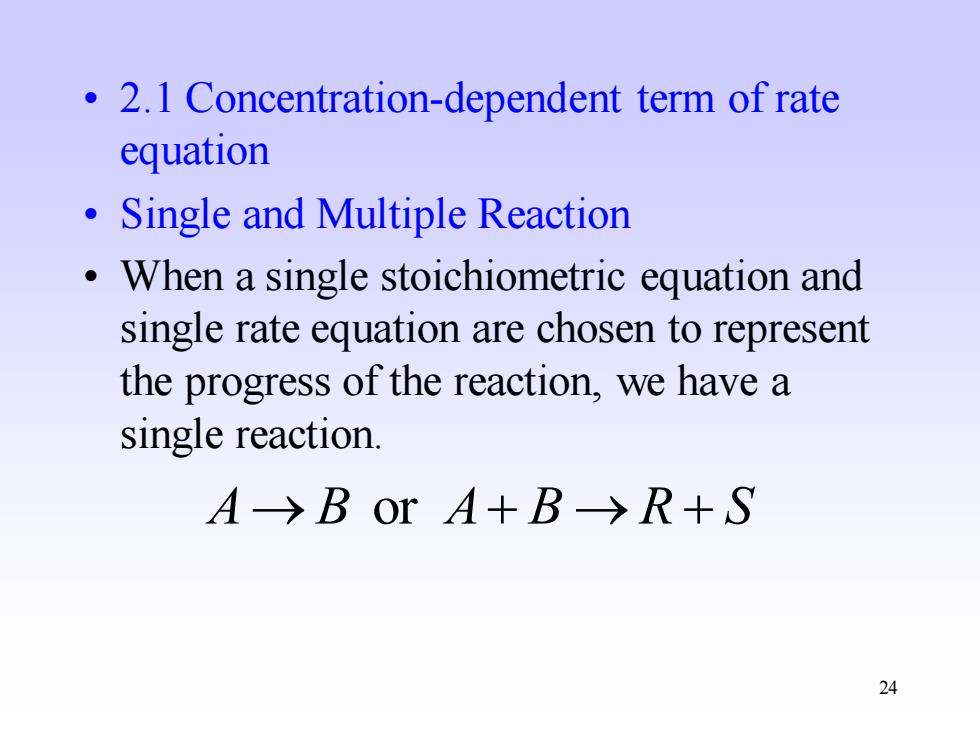
2.1 Concentration-dependent term of rate equation Single and Multiple Reaction When a single stoichiometric equation and single rate equation are chosen to represent the progress of the reaction,we have a single reaction. A→BOrA+B→R+S 24
24 • 2.1 Concentration-dependent term of rate equation • Single and Multiple Reaction • When a single stoichiometric equation and single rate equation are chosen to represent the progress of the reaction, we have a single reaction. A→ B or A+ B → R + S