
Chemical Reaction Engineering Teacher:Dr.&Prof.Kai Guo Beijing University of Chemical Technology
1 Chemical Reaction Engineering Teacher: Dr.&Prof. Kai Guo Beijing University of Chemical Technology
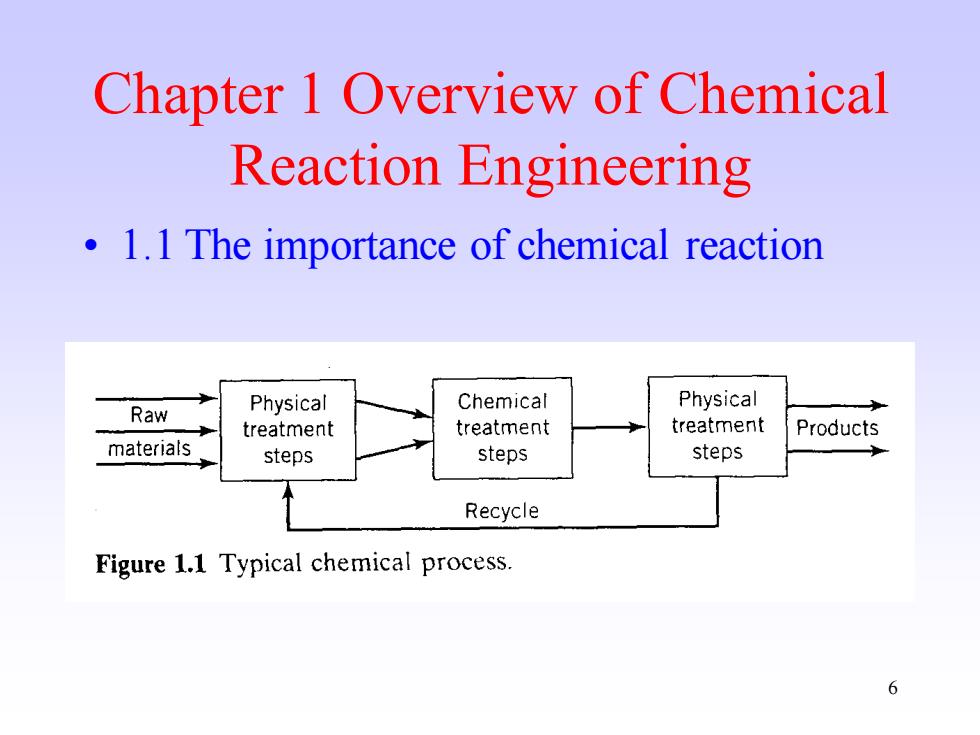
Chapter 1 Overview of Chemical Reaction Engineering 1.1 The importance of chemical reaction Chemical Physical Raw Physical treatment treatment treatment Products materials steps steps steps Recycle Figure 1.1 Typical chemical process. 6
6 Chapter 1 Overview of Chemical Reaction Engineering • 1.1 The importance of chemical reaction
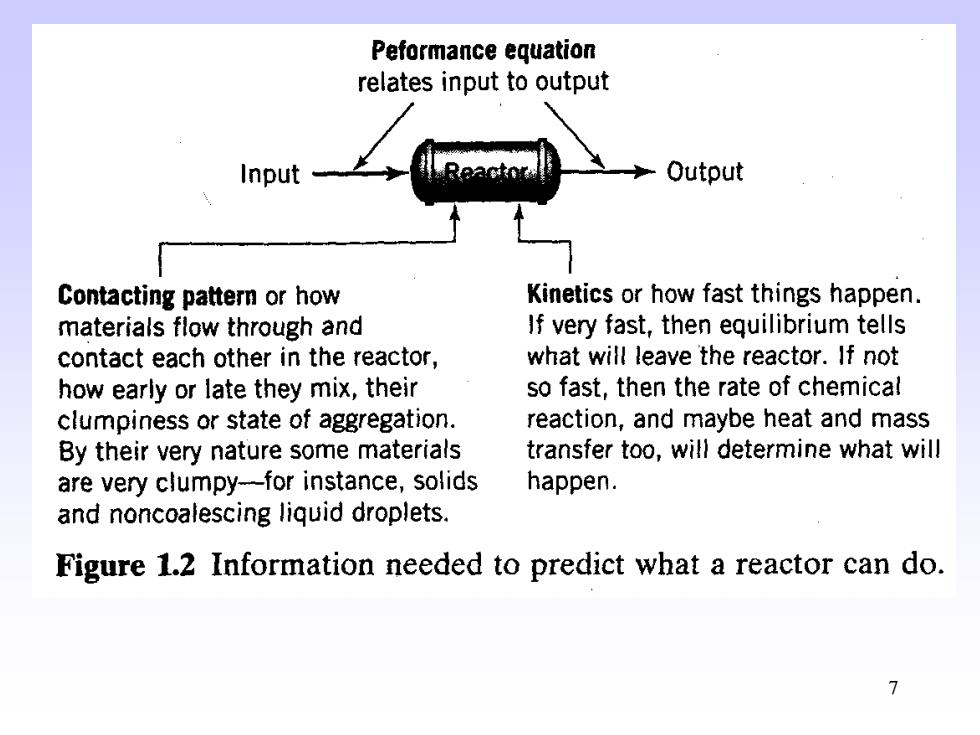
Peformance equation relates input to output Input- Output Contacting patter or how Kinetics or how fast things happen. materials flow through and If very fast,then equilibrium tells contact each other in the reactor, what will leave the reactor.If not how early or late they mix,their so fast,then the rate of chemical clumpiness or state of aggregation. reaction,and maybe heat and mass By their very nature some materials transfer too,will determine what will are very clumpy-for instance,solids happen. and noncoalescing liquid droplets. Figure 1.2 Information needed to predict what a reactor can do. 7
7
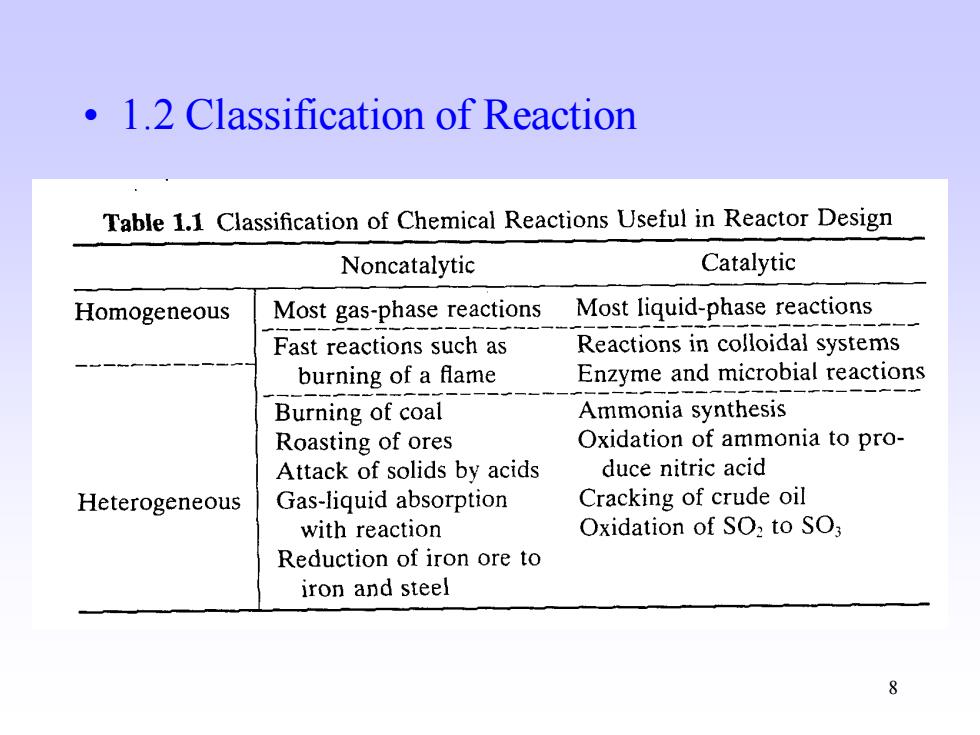
1.2 Classification of Reaction Table 1.1 Classification of Chemical Reactions Useful in Reactor Design Noncatalytic Catalytic Homogeneous Most gas-phase reactions Most liquid-phase reactions Fast reactions such as Reactions in colloidal systems burning of a flame Enzyme and microbial reactions Burning of coal Ammonia synthesis Roasting of ores Oxidation of ammonia to pro- Attack of solids by acids duce nitric acid Heterogeneous Gas-liquid absorption Cracking of crude oil with reaction Oxidation of SO2 to SO; Reduction of iron ore to iron and steel 8
8 • 1.2 Classification of Reaction
1.3 Variables Affecting the Rate of Reaction In homogeneous systems,Temperature, Pressure and Composition In heterogeneous systems,besides T,P &C, mass heat transfer some times play important roles 9
9 • 1.3 Variables Affecting the Rate of Reaction • In homogeneous systems, Temperature, Pressure and Composition • In heterogeneous systems, besides T, P &C, mass & heat transfer some times play important roles