
1.4 Definition of Reaction Rate If the rate of change in number of moles of component i due to reaction is dN dt,the rate of reaction is defined as follows: Based on unit volum e of reacting fluid 1dN,_ mole i formed n=v dt (volume of fluid )(time) Based on unit mass of solid in fluid -solid system mole i formed w dt (mass of solid )(time) 10
10 • 1.4 Definition of Reaction Rate • If the rate of change in number of moles of component i due to reaction is dNi /dt, the rate of reaction is defined as follows: ( )( ) ( )( ) mass of solid i formed Based on unit mass of solid in fluid -solid system volume of fluid i formed Based on unit volum e of reacting fluid : time mole dt dN W 1 r time mole dt dN V 1 r i i i i = = = =

Based on unit interfacia I surface in two -liquid system or based on unit surface of solid in gas-solid systems I dN mole i formed (surface)(time) Based on unit volum e of solid in gas-solid systems I dNi mole i formed 'vdi (volume of solid )(time) Based on unit volum e of reactor,in diferent from the rate based on unit volum e of fluid, I dN; mole i formed V.dt (volume of reactor)(time) 11
11 ( )( ) ( )( ) ( )(time) mole dt dN V 1 r time mole dt dN V 1 r time mole dt dN S 1 r i r i i s i i i volume of reactor i formed rate based on unit volum e of fluid, Based on unit volum e of reactor, in diferent from the volume of solid i formed Based on unit volum e of solid in gas -solid systems : surface i formed or based on unit surface of solid in gas -solid systems : Based on unit interfacia lsurface in two - liquid system = = = = = =
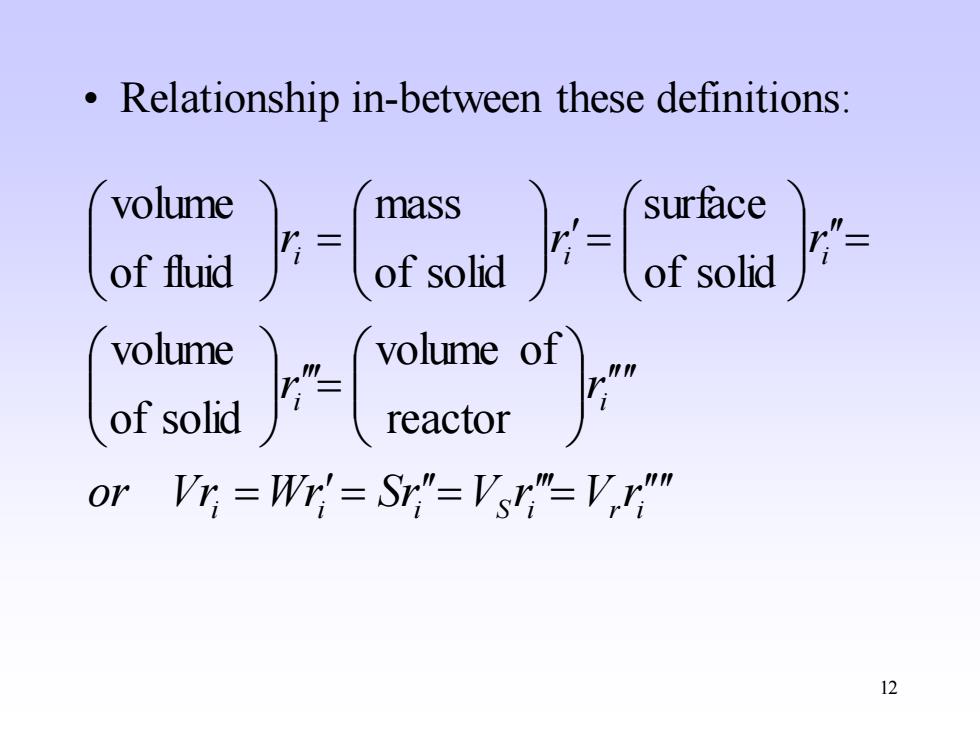
Relationship in-between these definitions: volume mass surface of fluid of solid volume volume of of solid reactor 0r V听=W=S"=V"=V" 12
12 • Relationship in-between these definitions: i i i S i r i i i i i i or Vr Wr Sr V r V r r r r r r = = = = = = = = reactor volume of of solid volume of solid surface of solid mass of fluid volume
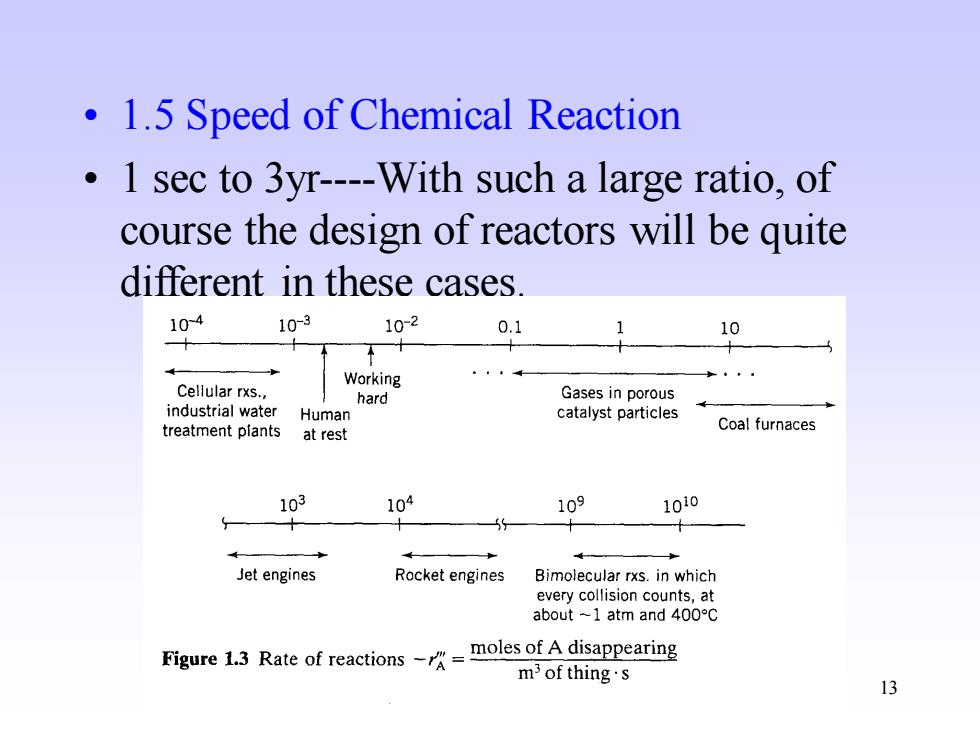
1.5 Speed of Chemical Reaction 1 sec to 3yr----With such a large ratio,of course the design of reactors will be quite different in these cases. 104 10-3 10-2 0.1 10 Working Cellular rxs., hard Gases in porous industrial water Human catalyst particles treatment plants Coal furnaces at rest 103 104 109 1010 X 5 Jet engines Rocket engines Bimolecular rxs.in which every collision counts,at about-1 atm and400°C Figure 1.3 Rate of reactions-moles ofAdisappearing m3 of thing's 13
13 • 1.5 Speed of Chemical Reaction • 1 sec to 3yr----With such a large ratio, of course the design of reactors will be quite different in these cases
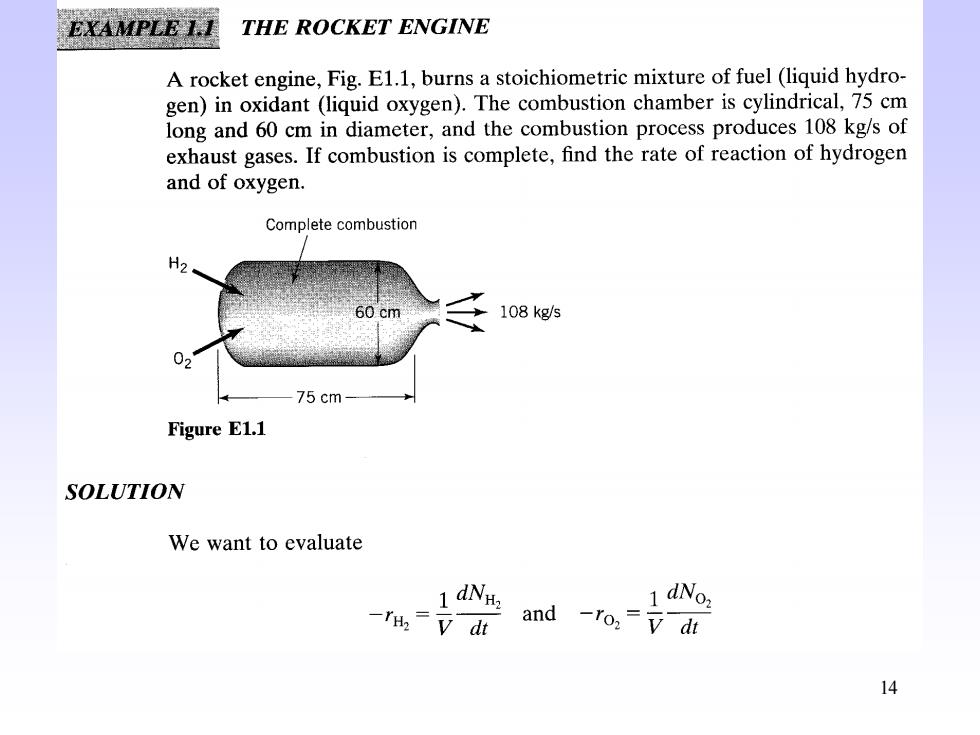
EXAMPLE 1.I THE ROCKET ENGINE A rocket engine,Fig.E1.1,burns a stoichiometric mixture of fuel (liquid hydro- gen)in oxidant (liquid oxygen).The combustion chamber is cylindrical,75 cm long and 60 cm in diameter,and the combustion process produces 108 kg/s of exhaust gases.If combustion is complete,find the rate of reaction of hydrogen and of oxygen. Complete combustion H2 60 cm 108 kg/s 02 75cm- Figure E1.1 SOLUTION We want to evaluate 1 dNH. -=v dt and -ro:=di 14
14