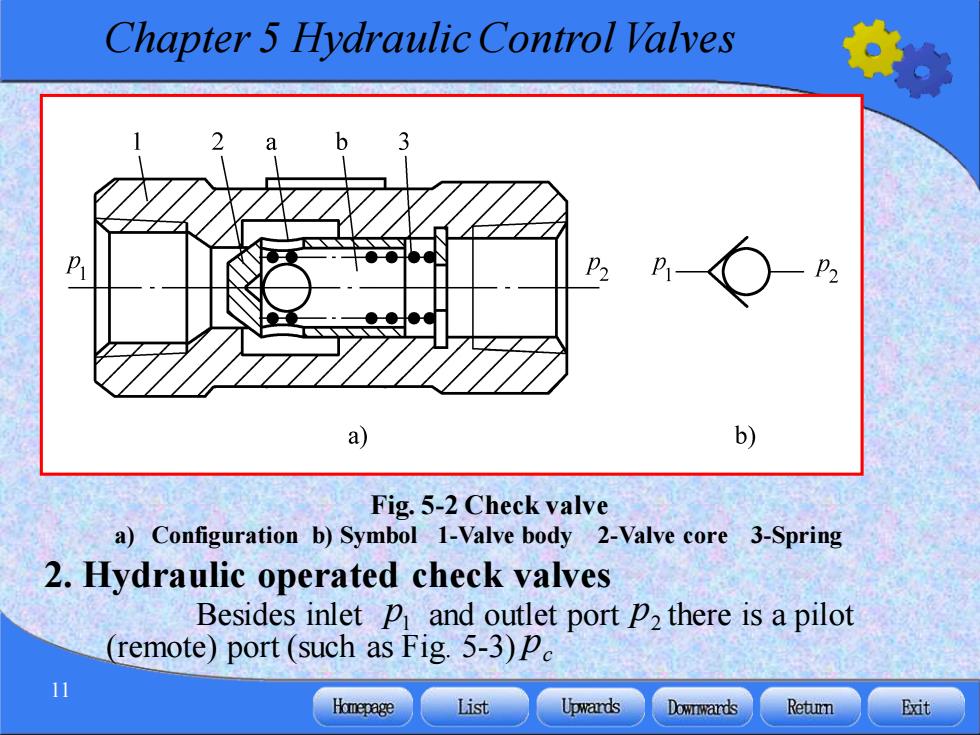
Chapter 5 Hydraulic Control Valves p a b) Fig.5-2 Check valve a)Configuration b)Symbol 1-Valve body 2-Valve core 3-Spring 2.Hydraulic operated check valves Besides inlet p and outlet port p2 there is a pilot (remote)port (such as Fig.5-3)p 11 Homepage List Upwards Downward达s Retumn Exit
Chapter 5 Hydraulic Control Valves 11 Fig. 5-2 Check valve a) Configuration b) Symbol 1-Valve body 2-Valve core 3-Spring 2. Hydraulic operated check valves 1 p 2 p c p Besides inlet and outlet port there is a pilot (remote) port (such as Fig. 5-3)

Chapter 5 Hydraulic Control Valves 南 10 a) b) Fig.5-3 Hydraulic-operated a)General type check valve b)Hydraulic operated check valve 1,6-Spring 2,8-Valve core 3,9-Handspike 4,10-Control piston 5-Small discharged core 7-Spring seat 12 Homepage List Upwards Downward止 Return Exit
Chapter 5 Hydraulic Control Valves 12 、 Fig. 5-3 Hydraulic-operated a) General type check valve b) Hydraulic operated check valve 1,6- Spring 2,8- Valve core 3,9-Handspike 4,10-Control piston 5-Small discharged core 7-Spring seat

Chapter 5 Hydraulic Control Valves 阀体 芯 弹簧 进油口 出油口 内泄式液控单向 外批式液控单向 Play Play DVD Play DVD DVD Note that the port should be connected to the reservoir when it is not working,otherwise it cannot be returned 13 Homepage List Upwards Downwards Retun Exit
Chapter 5 Hydraulic Control Valves 13 Note that the port should be connected to the reservoir when it is not working, otherwise it cannot be returned

Chapter 5 Hydraulic Control Valves 5.2.2 Directional control valves 1.Functions: According to the core motions relative body,a directional control valve in a hydraulic system is usually used to control the oil paths that can be connected,or the oil flow direction that can be changed,which allows the actuator to be started,stopped or the oil flow direction to be shifted. 2.Classification (1)By configuration:rotary,sliding or ball; (2)By ports:two ports,three ports,four ports and so on: (3)By relative operating position of spool in the valve body. There are two,three,and four positions; Homepage List Upwards Downward止 Retu Exit
Chapter 5 Hydraulic Control Valves 14 5.2.2 Directional control valves 1. Functions: According to the core motions relative body, a directional control valve in a hydraulic system is usually used to control the oil paths that can be connected, or the oil flow direction that can be changed, which allows the actuator to be started, stopped or the oil flow direction to be shifted. 2. Classification (1) By configuration: rotary, sliding or ball; (2) By ports: two ports, three ports, four ports and so on; (3) By relative operating position of spool in the valve body. There are two, three, and four positions;

Chapter 5 Hydraulic Control Valves (4)By the operating means:These valve cores may be operated by a difference of oil pressure on the spool,or manually. mechanically,electrically,or by a combination of these means. 3.The construction of spool or directional control valve The common configurations of spool or direction valves are shown in Tab.5-2.Their differences lie in the ways and positions they possess.Two or three-position valves mean that their valve cores have two or three different working positions; similarly,two,three or four way valves indicate that there are two,three,or four oil paths on the valve body which are separated from each other and connected with their independent oil lines.The function of the direction valves depend upon their ways and working positions. Homepage List Upwards Downward达 Return Exit
Chapter 5 Hydraulic Control Valves 15 3. The construction of spool or directional control valve The common configurations of spool or direction valves are shown in Tab.5-2. Their differences lie in the ways and positions they possess. Two or three-position valves mean that their valve cores have two or three different working positions; similarly, two, three or four way valves indicate that there are two, three, or four oil paths on the valve body which are separated from each other and connected with their independent oil lines. The function of the direction valves depend upon their ways and working positions. (4) By the operating means: These valve cores may be operated by a difference of oil pressure on the spool, or manually, mechanically, electrically, or by a combination of these means