
Inactive cassettes do not synthesize RNA 17.3 Yeast can switch silent and active loci for mating type Ya HMRa Figure 17.6 Silent cassettes Active cassettes synthesize mating-type-specific products have the same sequences as the corresponding active Ya MATa cassettes,except for the d2 mRNA a1 mRNA absence of the extreme Ya MATa flanking sequences in HMRa. Only the Y region changes a1 mRNA between a and a types 500 1000 1500 2000 bp 清菜大兰
Figure 17.6 Silent cassettes have the same sequences as the corresponding active cassettes, except for the absence of the extreme flanking sequences in HMRa. Only the Y region changes between a and a types. 17.3 Yeast can switch silent and active loci for mating type
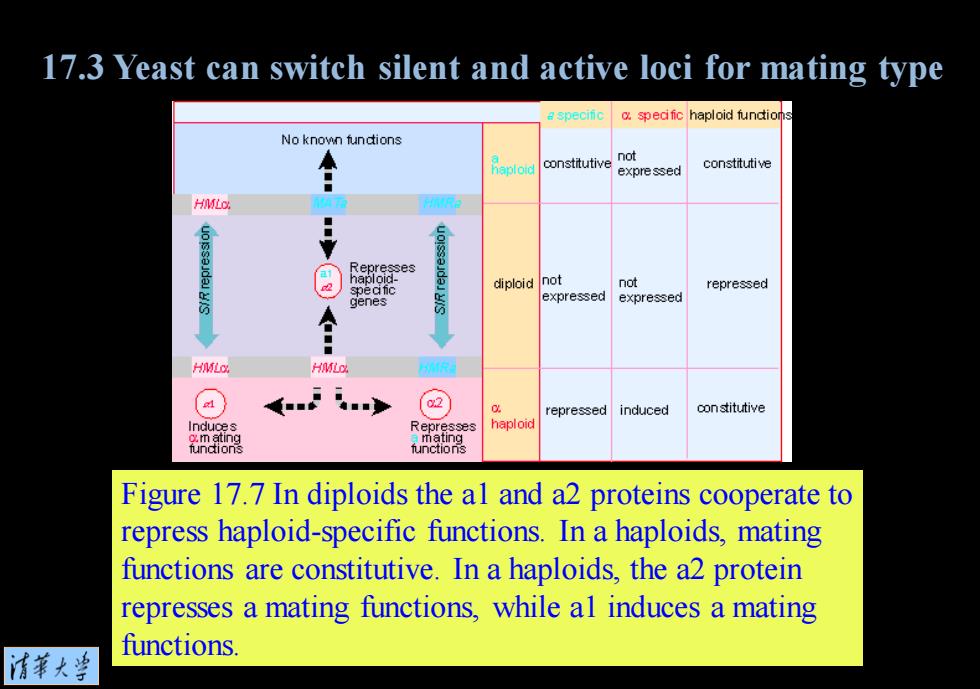
17.3 Yeast can switch silent and active loci for mating type a specific spedfic haploid fundion No known fundions constitutive not expressed constitutive HMLo Represses haploid not speafic diploid not repressed genes expressed expressed 日 H 02 repressed induced constitutive Represses haploid Figure 17.7 In diploids the al and a2 proteins cooperate to repress haploid-specific functions.In a haploids,mating functions are constitutive.In a haploids,the a2 protein represses a mating functions,while al induces a mating functions 情菜大当
Figure 17.7 In diploids the a1 and a2 proteins cooperate to repress haploid-specific functions. In a haploids, mating functions are constitutive. In a haploids, the a2 protein represses a mating functions, while a1 induces a mating functions. 17.3 Yeast can switch silent and active loci for mating type
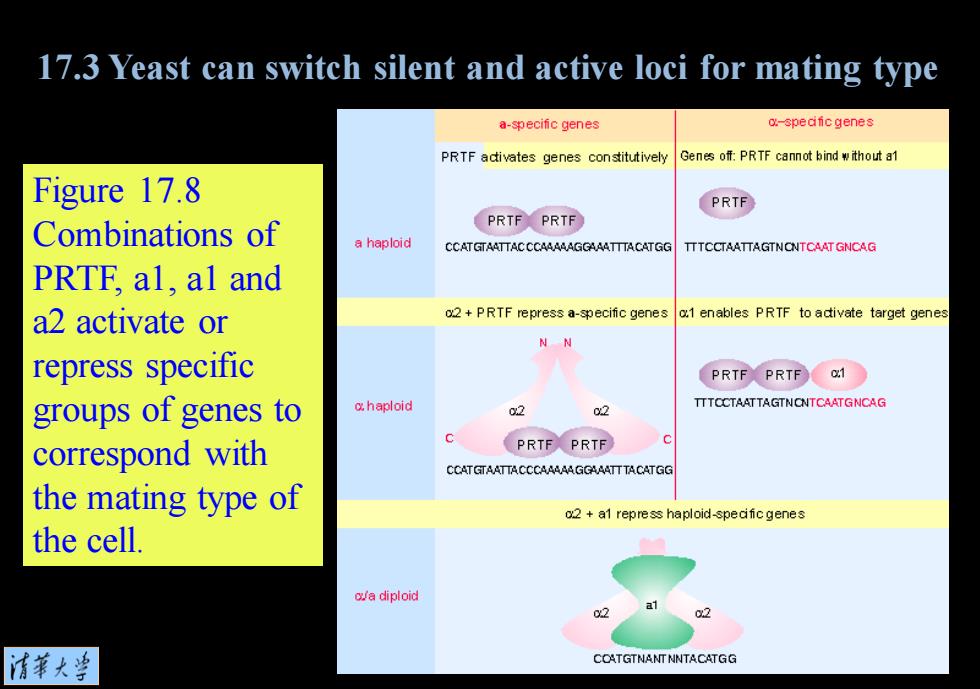
17.3 Yeast can switch silent and active loci for mating type a-specific genes o-spedfic genes PRTF adivates genes constitutively Genes off:PRTF cannot bind without a1 Figure 17.8 PRTF Combinations of PRTF PRTF a haploid CCATGTAATTACCCAAAAAGGAAATTTACATGG TTTCCTAATTAGTNCNTCAAT GNCAG PRTF,al,al and a2 activate or 02+PRTF repress a-specific genes o.1 enables PRTF to adivate target genes repress specific PRTF PRTF 01 groups of genes to o.haploid TTTOCTAATTAGTNCNTCAATGNCAG 02 02 correspond with PRTF PRTF CCATGTAATTACCCAAAAAGGAAATTTACATGG the mating type of o2 a1 repress haploid-spedfic genes the cell. oa diploid 02 清菜大当 COATGTNANT NNTACATGG
Figure 17.8 Combinations of PRTF, a1, a1 and a2 activate or repress specific groups of genes to correspond with the mating type of the cell. 17.3 Yeast can switch silent and active loci for mating type

Initiation complex contains sigma and covers 75-80 bp 9.4 Sigma factor -50-40-30-20-101+10+20+30 controls binding to DNA I nitial ebongation oomplex forms at 10 bases loses sigma,and loses cmtadsin-35 to 65 region -50-40-30-20-101+10+20+30 Figure 9.10 RNA polymerase initially contacts the region from-55 to +20.When sigma dissociates,the core enzyme contracts to -30;when the General elongation complex en☑yme moves a few base foms at 15-20 bases and covers 30-40 bp pairs,it becomes more -50-40-30-20-101+10+20+30 compactly organized into the general elongation complex. 清菜大当
Figure 9.10 RNA polymerase initially contacts the region from -55 to +20. When sigma dissociates,the core enzyme contracts to -30; when the enzyme moves a few base pairs, it becomes more compactly organized into the general elongation complex. 9.4 Sigma factor controls binding to DNA

17.4 Silent cassettes at HML and HMR are repressed Inactive cassettes do not synthesize RNA HMLo Figure 17.6 Silent cassettes have the same Ya HMRa sequences as the Active cassettes synthesize corresponding active mating-type-specific products cassettes,except for the Y区 MATa absence of the extreme flanking sequences in 02 mRNA a1 mRNA HMRa.Only the Y Ya MATa region changes between a1 mRNA a and a types. 清菜大兰 500 1000 1500 2000 bp
Figure 17.6 Silent cassettes have the same sequences as the corresponding active cassettes, except for the absence of the extreme flanking sequences in HMRa. Only the Y region changes between a and a types. 17.4 Silent cassettes at HML and HMR are repressed