
Chapter 25 Protein trafficking 清苇大当
Chapter 25 Protein trafficking

25.1 Introduction 25.2 Oligosaccharides are added to proteins in the ER and Golgi 25.3 The Golgi stacks are polarized 25.4 Coated vesicles transport both exported and imported proteins 25.5 Different types of coated vesicles exist in each pathway 25.6 Cisternal progression occurs more slowly than vesicle movement 25.7 Vesicles can bud and fuse with membranes 25.8 SNAREs control targeting 25.9 The synapse is a model system for exocytosis 25.10 Protein localization depends on specific signals 25.11 ER proteins are retrieved from the Golgi 25.12 Brefeldin A reveals retrograde transport 25.13 Receptors recycle via endocytosis 25.14 Internalization signals are short and contain tyrosine 清苇大当
25.1 Introduction 25.2 Oligosaccharides are added to proteins in the ER and Golgi 25.3 The Golgi stacks are polarized 25.4 Coated vesicles transport both exported and imported proteins 25.5 Different types of coated vesicles exist in each pathway 25.6 Cisternal progression occurs more slowly than vesicle movement 25.7 Vesicles can bud and fuse with membranes 25.8 SNAREs control targeting 25.9 The synapse is a model system for exocytosis 25.10 Protein localization depends on specific signals 25.11 ER proteins are retrieved from the Golgi 25.12 Brefeldin A reveals retrograde transport 25.13 Receptors recycle via endocytosis 25.14 Internalization signals are short and contain tyrosine

25.1 Introduction Sorting signal is a motif in a protein (either a short sequence of amino acids or a covalent modification)that is required for it to be incorporated into vesicles that carry it to a specific destination. 清菜大当
Sorting signal is a motif in a protein (either a short sequence of amino acids or a covalent modification) that is required for it to be incorporated into vesicles that carry it to a specific destination. 25.1 Introduction
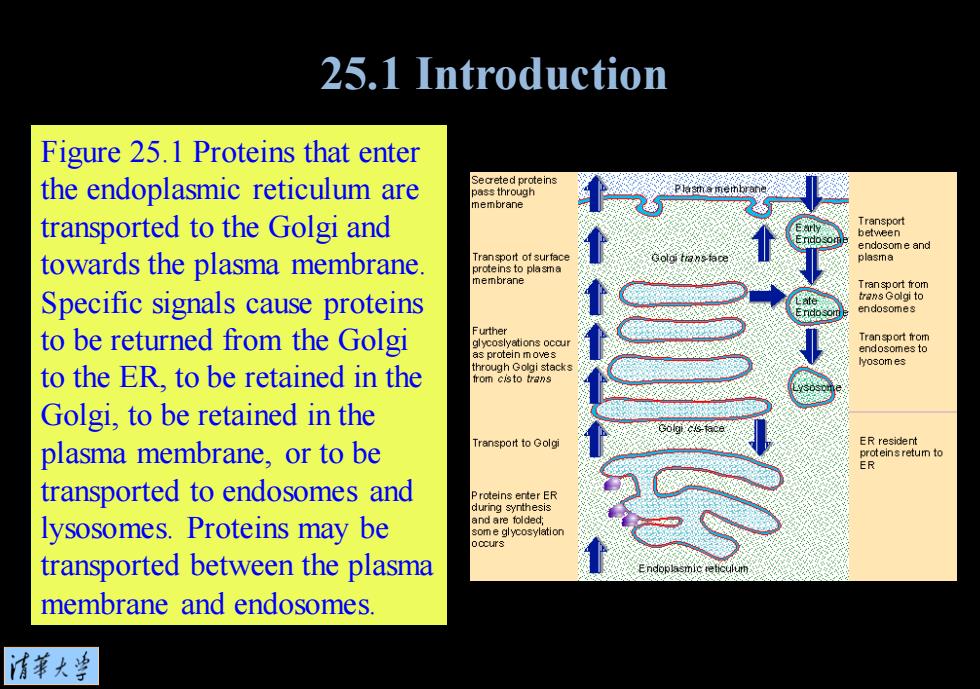
25.1 Introduction Figure 25.1 Proteins that enter the endoplasmic reticulum are Secreted proteins oass through nembrane transported to the Golgi and Transport between endosome and towards the plasma membrane. Transport of surface plasma proteins to plasma membrane Tran sport from Specific signals cause proteins trans Golgi to endosomes to be returned from the Golgi urther ations ocau Tran sport from endosomes to yosom es to the ER,to be retained in the through Golgi stac Golgi,to be retained in the ER resident plasma membrane,or to be ansport to Golgi proteinsretum to ER transported to endosomes and during s lysosomes.Proteins may be transported between the plasma membrane and endosomes. 清菜大兰
Figure 25.1 Proteins that enter the endoplasmic reticulum are transported to the Golgi and towards the plasma membrane. Specific signals cause proteins to be returned from the Golgi to the ER, to be retained in the Golgi, to be retained in the plasma membrane, or to be transported to endosomes and lysosomes. Proteins may be transported between the plasma membrane and endosomes. 25.1 Introduction
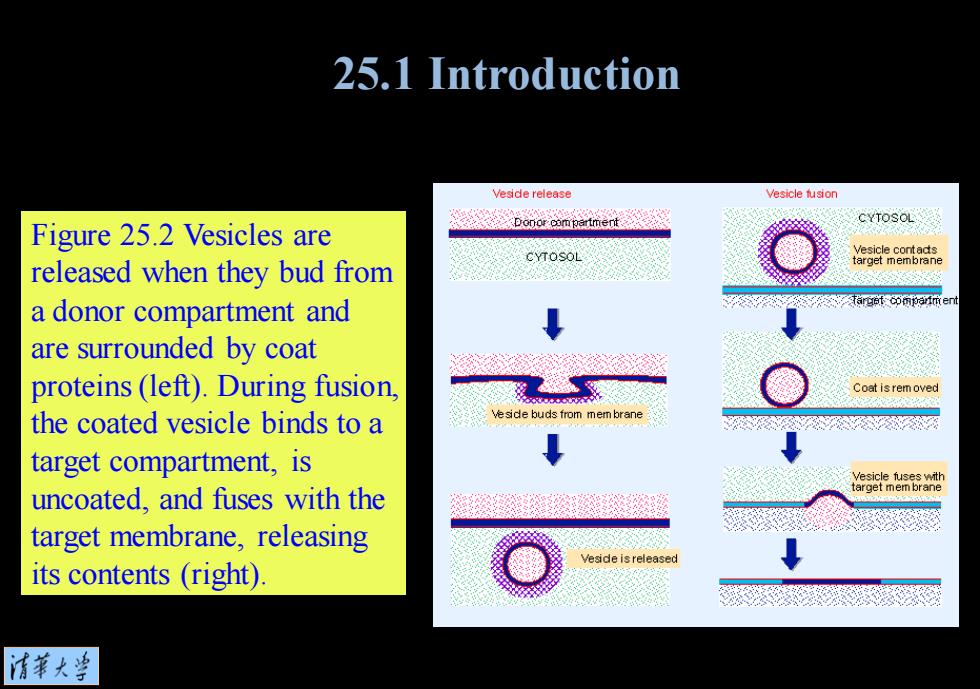
25.1 Introduction Veside release Vesicle tusion CYTOSOL Figure 25.2 Vesicles are CYTOSOL Vesicle contads released when they bud from arget membrane a donor compartment and are surrounded by coat proteins(left).During fusion, Coat is rem oved the coated vesicle binds to a esde buds trom mem brane target compartment,is uncoated,and fuses with the target membrane,releasing Veside is released its contents(right) 清菜大当
Figure 25.2 Vesicles are released when they bud from a donor compartment and are surrounded by coat proteins (left). During fusion, the coated vesicle binds to a target compartment, is uncoated, and fuses with the target membrane, releasing its contents (right). 25.1 Introduction