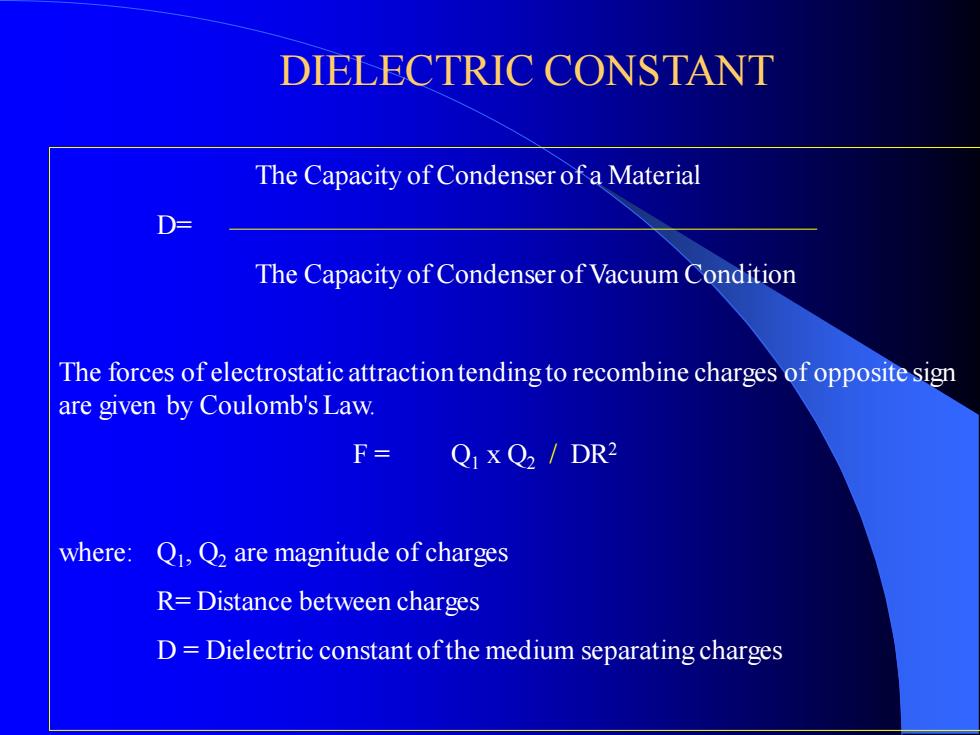
DIELECTRIC CONSTANT The Capacity of Condenser of a Material D= The Capacity of Condenser of Vacuum Condition The forces of electrostatic attraction tending to recombine charges of opposite sign are given by Coulomb's Law. F = Q1 x Q2 / DR2 where: Q1 , Q2 are magnitude of charges R= Distance between charges D = Dielectric constant of the medium separating charges
DIELECTRIC CONSTANT The Capacity of Condenser of a Material D= The Capacity of Condenser of Vacuum Condition The forces of electrostatic attraction tending to recombine charges of opposite sign are given by Coulomb's Law. F = Q1 x Q2 / DR2 where: Q1 , Q2 are magnitude of charges R= Distance between charges D = Dielectric constant of the medium separating charges

KINDS OF WATER - DEGREE OF WATER BINDNESS Monolayer Water is bound in food - restricted in its movement due to charges, hydrogen bond, physical entrapment. Hard to remove from food. Never be able to remove water completely. Multilayer Water - additional layer of water around food particle. Not as hard to remove as the monolayer. Mobile or Free Water - consisted with ideal solution
KINDS OF WATER - DEGREE OF WATER BINDNESS Monolayer Water is bound in food - restricted in its movement due to charges, hydrogen bond, physical entrapment. Hard to remove from food. Never be able to remove water completely. Multilayer Water - additional layer of water around food particle. Not as hard to remove as the monolayer. Mobile or Free Water - consisted with ideal solution