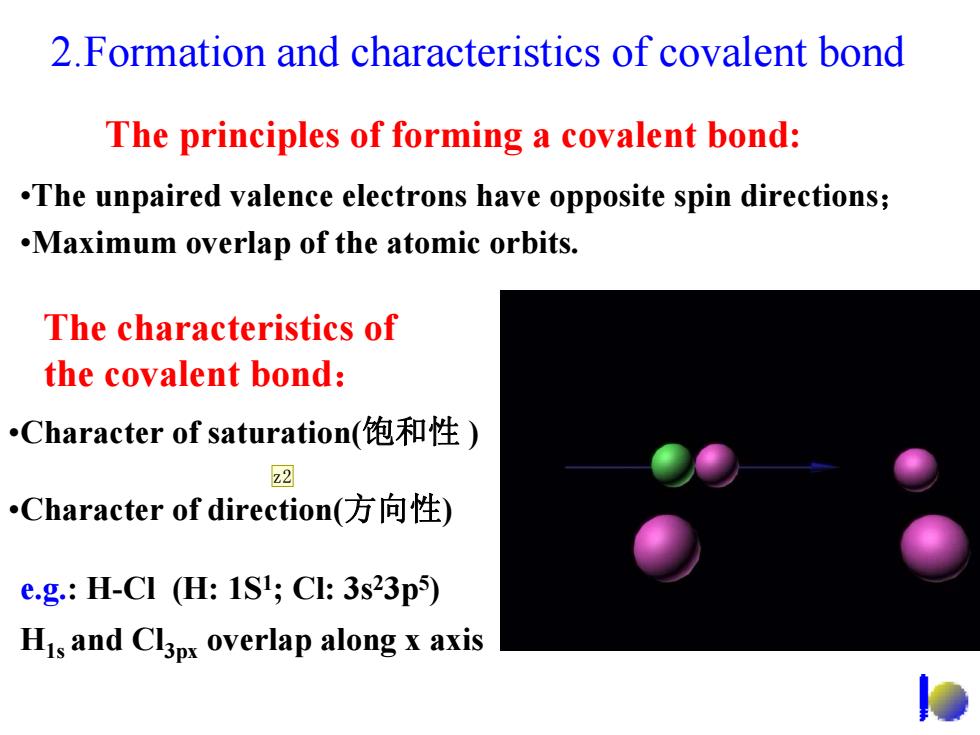
2.Formation and characteristics of covalent bond The principles of forming a covalent bond: .The unpaired valence electrons have opposite spin directions; .Maximum overlap of the atomic orbits. The characteristics of the covalent bond: Character of saturation(饱和性) 22 Character of direction(方向性) e.g.:H-CI (H:1S1;Cl:3s23p5) His and Cl3px overlap along x axis
2.Formation and characteristics of covalent bond The principles of forming a covalent bond: •The unpaired valence electrons have opposite spin directions; •Maximum overlap of the atomic orbits. The characteristics of the covalent bond : •Character of direction(方向性 ) •Character of saturation(饱和性 ) e.g.: H-Cl (H: 1S 1; Cl: 3s 23p 5 ) H1s and Cl3px overlap along x axis z2

幻灯片6 的 子间成键是两个原子的未成对电子的配对,每个原子的未成对电子数是一定的,可提供的成键轨道数也是一定的,所以,最多成键数也是一定 的 ang,.2007-11-16
幻灯片 6 z2 原子间成键是两个原子的未成对电子的配对,每个原子的未成对电子数是一定的,可提供的成键轨道数也是一定的,所以,最多成键数也是一定 的 zhang, 2007-11-16

9.1.2 The types of covalmd 1.o bonds: o bonds arise from the overlap of atomic orbits along the internuclear axis..(头碰头重叠). s·s轨道形成键 Symmetry of o bond:o symmetry,i.e., rotation of any angle around the x axis, both shape and symbols are unchanged 8-p,轨道形成。键 o bonds have much overlap of atomic orbits along the internuclear axis
1.σ bonds: σ bonds arise from the overlap of atomic orbits along the internuclear axis. (头碰头重叠). Symmetry of σ bond:σ symmetry, i.e., rotation of any angle around the x axis, both shape and symbols are unchanged σ bonds have much overlap of atomic orbits along the internuclear axis. 9.1.2 The types of covalent bond
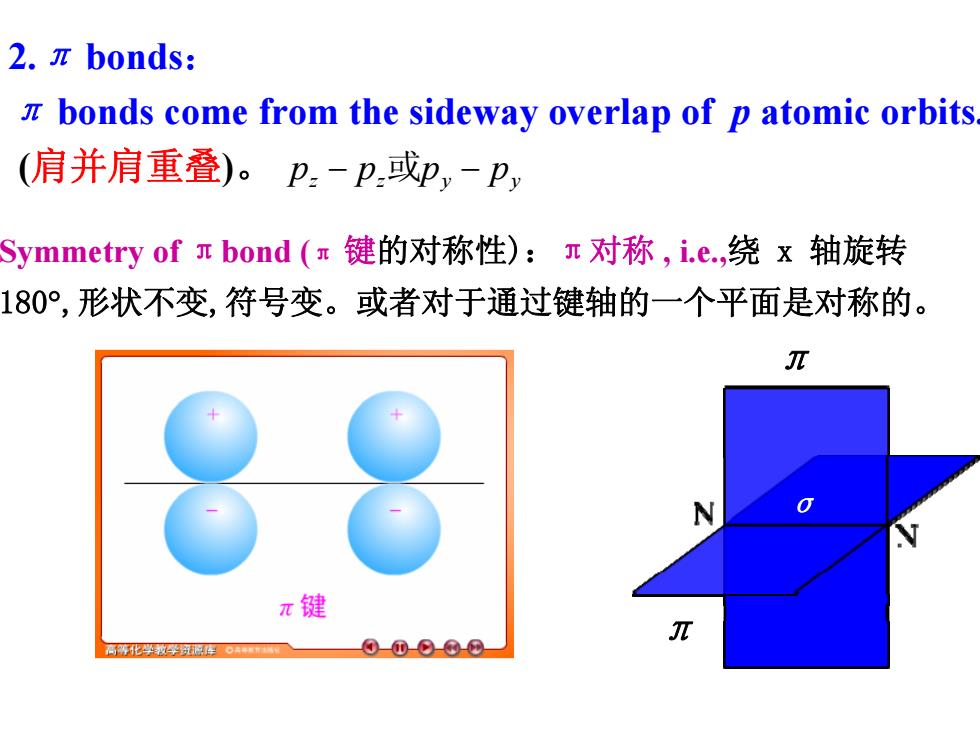
2.πbonds: z bonds come from the sideway overlap of p atomic orbits (肩并肩重叠)。p-p或p,-P, Symmetry of n bond(π键的对称性):r对称,i.e.,绕x轴旋转 180°,形状不变,符号变。或者对于通过键轴的一个平面是对称的。 π N π键 π 高鸦化学被学别形库。+ 0-①-9-©-@
2.π bonds: π bonds come from the sideway overlap of p atomic orbits. (肩并肩重叠)。 z z y y p − p 或p − p Symmetry of πbond (π 键的对称性):π对称 , i.e.,绕 x 轴旋转 180°,形状不变,符号变。或者对于通过键轴的一个平面是对称的。 σ π π

o bonds have much overlap of atomic orbits along the internuclear axis,while n bonds have less overlap, resulting in that o bonds are relatively stronger than x bonds
σ bonds have much overlap of atomic orbits along the internuclear axis, while π bonds have less overlap, resulting in that σ bonds are relatively stronger than π bonds