
Chapter 3 Chemical kinetics 3.1 Brief introduction of chemical reaction rates 3.2 Brief introduction of effect of concentration of reactants on reaction rate-the rate expression 3.3 Brief introduction of effect of temperature on reaction rate-Arrhenius equation 3.4 Brief introduction of theory of reaction rate and reaction mechanisms 3.5 Brief introduction of catalyst and catalysis
Chapter 3 Chemical kinetics 3.1 Brief introduction of chemical reaction rates 3.2 Brief introduction of effect of concentration of reactants on reaction rate —the rate expression 3.3 Brief introduction of effect of temperature on reaction rate—Arrhenius equation 3.4 Brief introduction of theory of reaction rate and reaction mechanisms 3.5 Brief introduction of catalyst and catalysis

3.1 Brief Introduction of chemical reaction rates 3.1.1 Average rates and instantaneous rates of chemical reactions
§3.1 Brief Introduction of chemical reaction rates 3.1.1 Average rates and instantaneous rates of chemical reactions
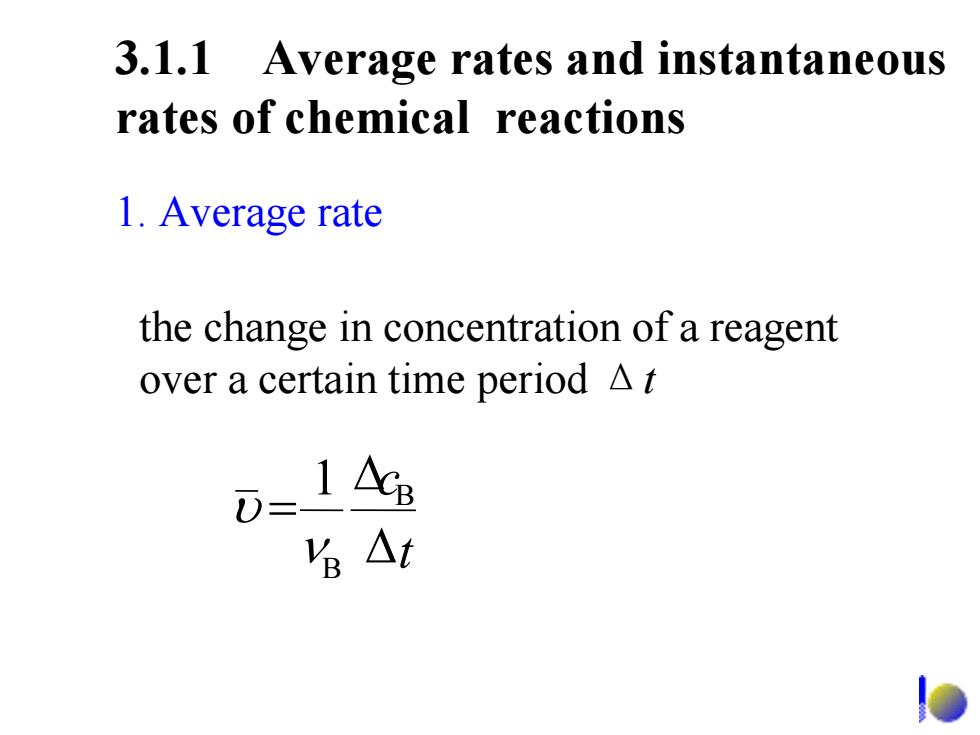
3.1.1 Average rates and instantaneous rates of chemical reactions 1.Average rate the change in concentration of a reagent over a certain time period A t 1 AcB 名△t
3.1.1 Average rates and instantaneous rates of chemical reactions 1. Average rate the change in concentration of a reagent over a certain time period Δ t 1 B B Δ Δ = t c ν υ
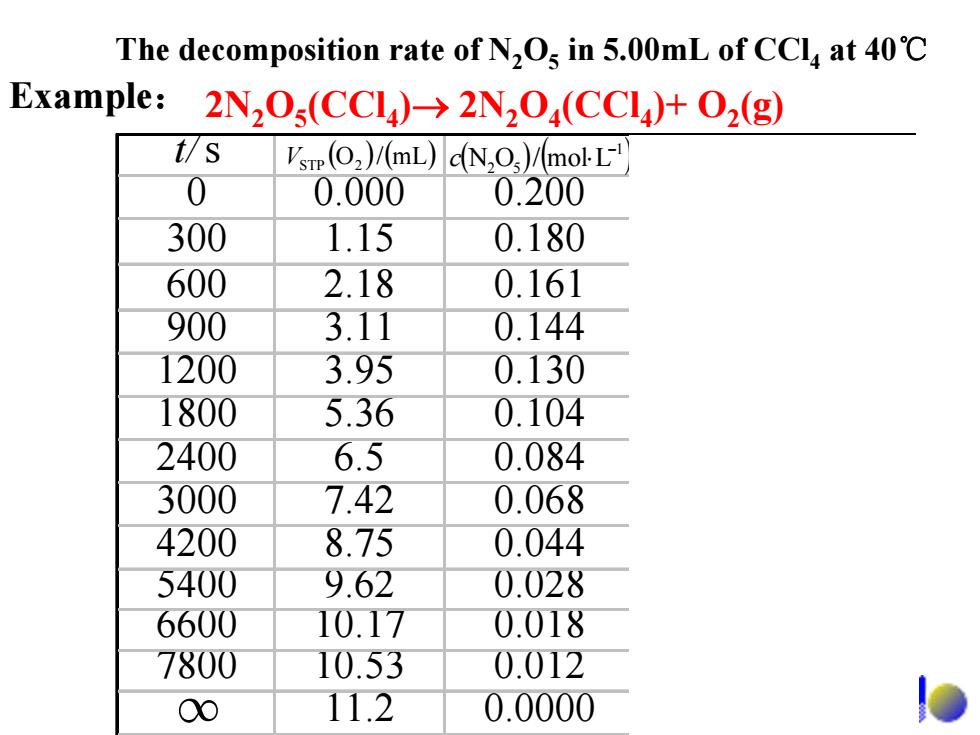
The decomposition rate of N,Os in 5.00mL of CCla at 40C Example:2N,O(CCI)>2N2O(CCI)+O2(g) t/S Vsrp(O2)/(mL)dN,O)/molL 0 0.000 0.200 300 1.15 0.180 600 2.18 0.161 900 3.11 0.144 1200 3.95 0.130 1800 5.36 0.104 2400 6.5 0.084 3000 7.42 0.068 4200 8.75 0.044 5400 9.62 0.028 6600 10.17 0.018 7800 10.53 0.012 00 11.2 0.0000
t/s 0 0.000 0.200 300 1.15 0.180 600 2.18 0.161 900 3.11 0.144 1200 3.95 0.130 1800 5.36 0.104 2400 6.5 0.084 3000 7.42 0.068 4200 8.75 0.044 5400 9.62 0.028 6600 10.17 0.018 7800 10.53 0.012 11.2 0.0000 ( ) (mL/O ) V 2STP ( ) ( )1 52 Lmol/ON − c ⋅ ( )11 sLmol/ −− υ ⋅⋅ 5 1029.7 − × 5 1046.6 − × 5 1080.5 − × 5 1021.5 − × 5 1069.4 − × 5 1079.3 − × 5 1004.3 − × 5 1003.1 − × 5 1044.2 − × 5 1059.1 − × ∞ The decomposition rate of N2O5 in 5.00mL of CCl4 at 40℃ 2N2O5(CCl4)→ 2N2O4(CCl4)+ O2 Example: (g)

2N205(CC14)2N204(CC14)+O2(g) t1=0s c1N205)=0.200molL1 t2=300s c2N20s)=0.180molL1 D=-(0.1800,200mol-L=33×109mol-L2-s 2×300s 2.Instantaneous rate The instantaneous rate of a reaction is the limit of the average reaction rate
t1= 0 s c1(N2O5) = 0.200 mol·L-1 t2=300 s c2(N2O5) = 0.180 mol·L-1 5 1-1- -1 sLmol103.3 s3002 Lmol ⋅⋅×= × (0.180− − 0.200) ⋅ = − υ 2. Instantaneous rate The instantaneous rate of a reaction is the limit of the average reaction rate. 2N2O4 (CCl4) + O2 2N (g) 2O5(CCl4)