?Virulence ofGASHyaluronic AcidCapsulecapsule1protein antigenscarbohydratespeptidoglycan州cell coatcytoplasmcell wallSketchMapofStructureof StreptococciDIVISION OFINFECTIOUS DISEASE ANDGASTROENTEROLOGY
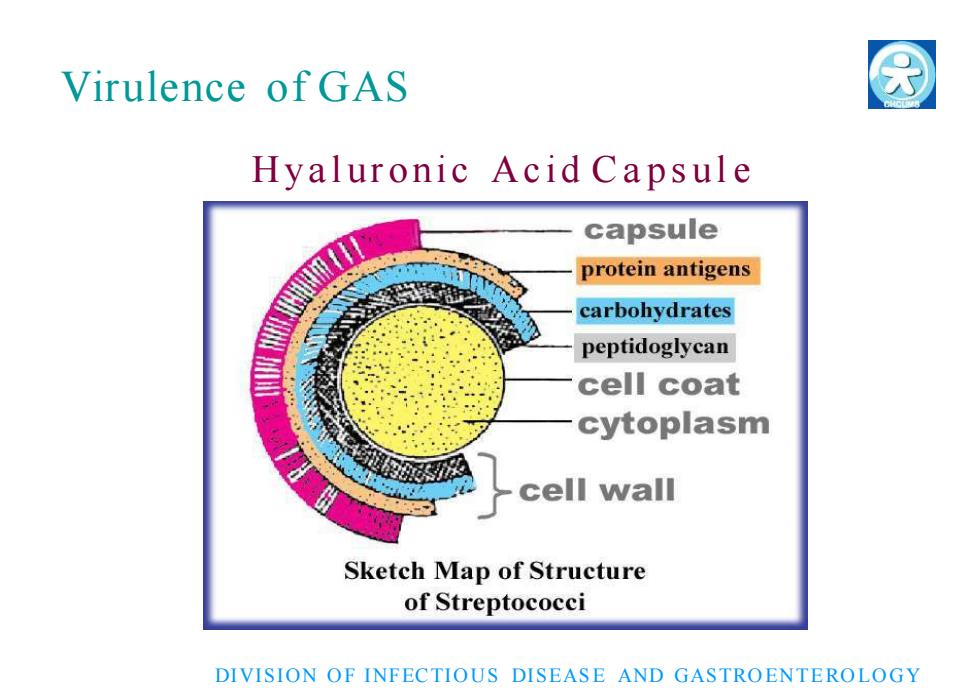
Virulence of GAS H ya l ur oni c Aci d C a p s u l e DIVISION O F INFECTIO US DISEAS E AND GASTRO ENT E RO LO GY

?Virulence ofGAsHyaluronic Acid CapsuleGAS escape from recognization bytheimmune systems (Antigenic disguise)It can protect GAS from phagocytosis by口host neutrophils or macrophagesDIVISION OFINFECTIOUS DISEASE AND GASTROENTEROLOGY
H ya l ur oni c Aci d C a p s u l e □ GAS e s ca p e from recognization by the immune s ys t e ms (Antigenic disguise) □ It can protect GAS from phagocytosis by host neutrophils or macropha ges DIVISION O F INFECTIO US DISEAS E AND GASTRO ENT E RO LO GY Virulence of GAS
?VirulenceofGASMproteincapsule0protein antigenscarbohydrates州peptidoglycancell coatcytoplasmcell wallSketchMapof Structureof StreptococciDIVISION OFINFECTIOUS DISEASE ANDGASTROENTEROLOGY
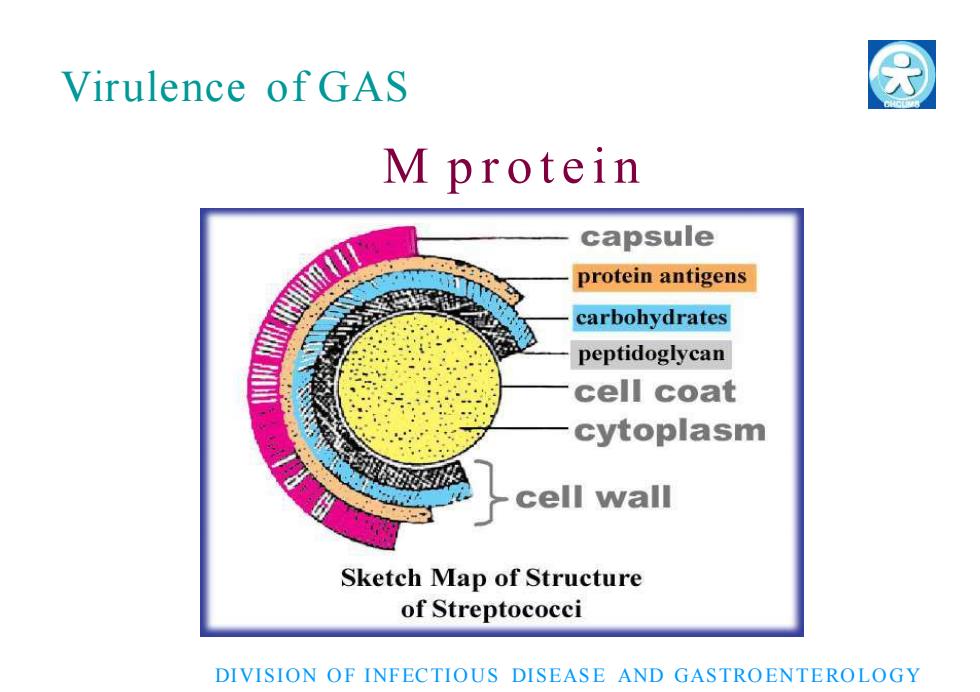
M p r o t e i n DIVISION O F INFECTIO US DISEAS E AND GASTRO ENT E RO LO GY Virulence of GAS
?Virulence ofGASMprotein Mprotein is the clearly majorvirulencefactor ofGAS Attachment to epithelial cells and resistanceto phagocytosis Antibody against Mprotein is theeffectiveprotective antibody Someof Mproteins contain antigenic epitopesrelated to heartmuscleDIVISION OFINFECTIOUS DISEASE ANDGASTROENTEROLOGY
M p r o t e i n □ M protein is the clearly major virulence factor of GAS □ Attachment to epithelial cells a n d res is ta n ce to p h a gocytosis □ Antibody against M protein is the effective protective antibody □ Some of M proteins contain antigenic epitopes related to heart mu scle DIVISION O F INFECTIO US DISEAS E AND GASTRO ENT E RO LO GY Virulence of GAS
?Virulence ofGASLipoteichoic acid (LTA)Promotes colonization by binding to fibronectinon the surface of epithelial cells and furtherfacilitates the virulence.Fibronectin-binding protein(Protein F)Mediates streptococcal adherence to the aminoterminus of fibronectin onmucosal surfacesDIVISION OFINFECTIOUS DISEASE AND GASTROENTEROLOGY
Lipoteichoic acid (LTA) Promotes colonization by binding to fibronectin on the surface of epithelial cells and further facilitates the virulence. Fibronectin-binding protein (Protein F) Mediates streptococcal adherence to the amino terminus of fibronectin on mucosal surfaces DIVISION O F INFECTIO US DISEAS E AND GASTRO ENT E RO LO GY Virulence of GAS