Rotavirus Infectionin Children
Rotavirus Infection in Children 1

Overview of Rotavirus infectionThe most common cause of severe diarrhea among infantsand young childrenAccounts for up to 50%ofhospitalizations for severediarrheaOne of several viruses that cause infections often calledstomach flu, despite having no relation to influenza.It is a double-stranded RNAvirus in the family ReoviridaeAlmost every child in the world has been infected withrotavirus at least once by the age of five. Adults are rarelyaffectedAbout 600,000 children under five years of age die fromrotavirus infection each year in whole world.Almost two million more become severely ill
2 Overview of Rotavirus infection • The most common cause of severe diarrhea among infants and young children. • Accounts for up to 50% ofhospitalizations for severe diarrhea. • One of several viruses that cause infections often called stomach flu, despite having no relation to influenza. • It is a double-stranded RNA virus in the family Reoviridae. • Almost every child in the world has been infected with rotavirus at least once by the age of five. Adults are rarely affected. • About 600,000 children under five years of age die from rotavirus infection each year in wholeworld. • Almost two million more become severely ill

History of RotavirusFirst identified as cause ofdiarrhea in 1973 by RuthBishop.Thomas Flewettsuggested the namerotavirus after observingthat.WheelRata(Latin)(E ng lish)
History of Rotavirus • • First identified as cause of diarrhea in 1973 by Ruth Bishop. Thomas Flewett suggested the name rotavirus after observing that. Rata (Latin) 3 Wheel = (E nglish)
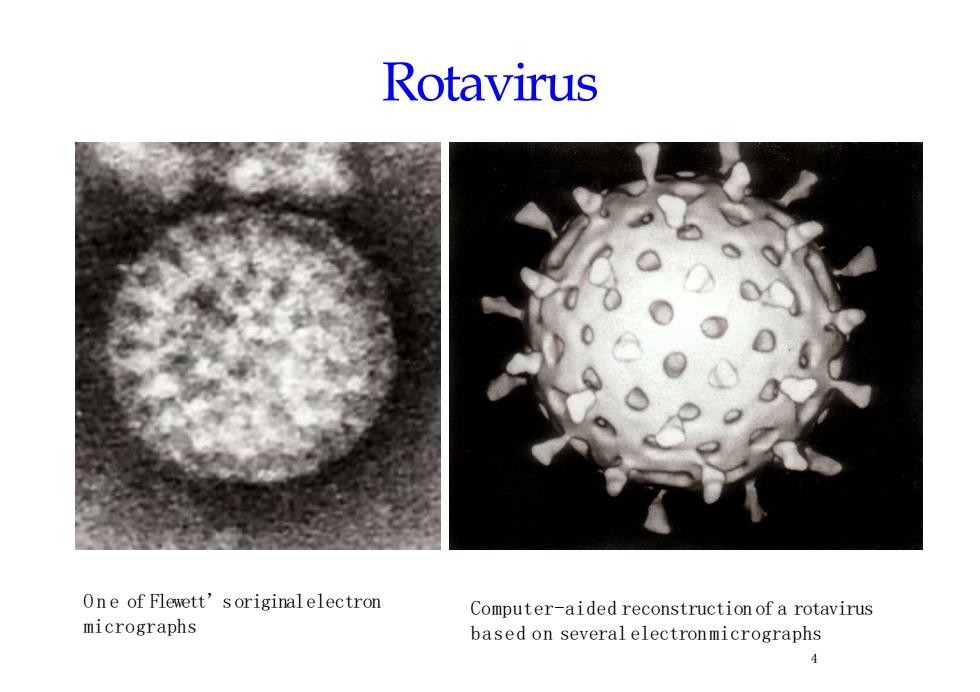
RotavirusOne of Flewett'soriginalelectronComputer-aidedreconstructionofarotavirusmicrographsbasedonseveralelectronmicrographs4
Rotavirus One of Flewett’soriginalelectron micrographs 4 Computer-aided reconstruction of a rotavirus based on several electronmicrographs
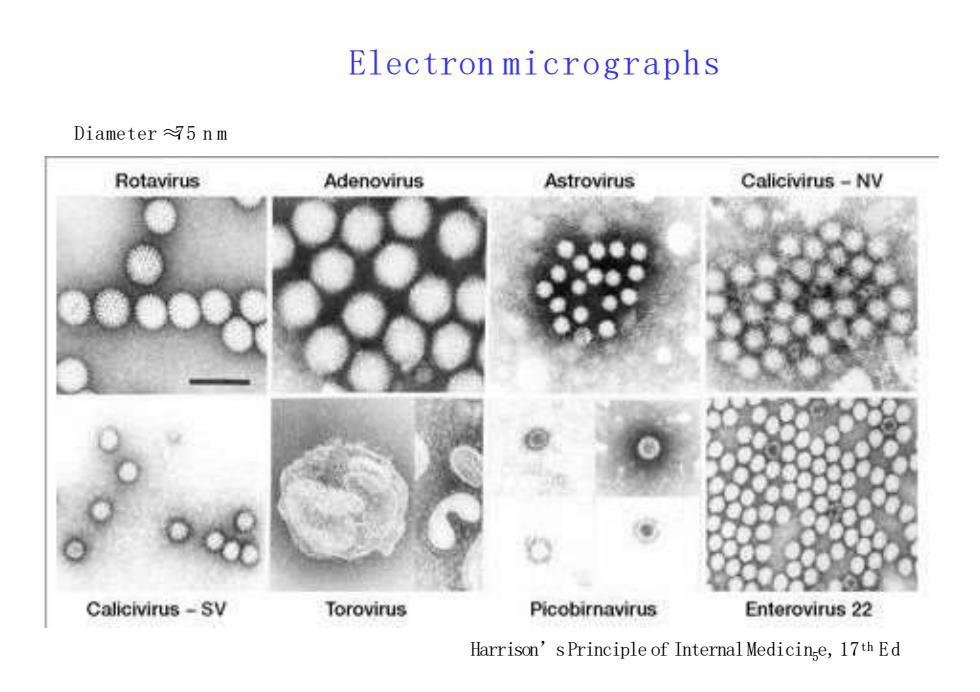
ElectronmicrographsDiameter75nmRotavirusAstrovirusCalicivirus-NVAdenovirusOCalicivirus-SvTorovirusPicobirnavirusEnterovirus22Harrison' s Principle of Internal Medicinge, 17th Ed
Electron micrographs Harrison’sPrinciple of InternalMedicin5 e,17th E d Diameter ≈75 n m