
GD Convergence Analysis
GD Convergence Analysis
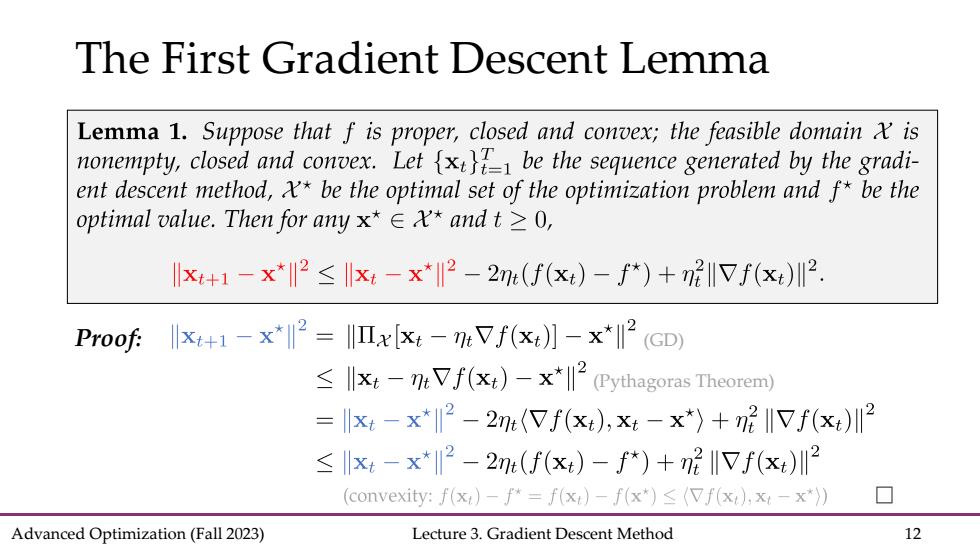
The First Gradient Descent Lemma Lemma 1.Suppose that f is proper,closed and convex;the feasible domain is nonempty,closed and convex.Letx be the sequence generated by the gradi- ent descent method,x*be the optimal set of the optimization problem and f*be the optimal value.Then for any x*∈X*andt≥0, lx+1-x*2≤x-x*2-2m(f(x)-f*)+m2IVf(x)川2. Proof:-x2=x[:-mVf(x)]-x*2 (CD) llxt-mVf(xt)-x*(Pythagoras Theorem) =xt-x*2-2m:(Vf(x),x-x*)+72I17f(x)川2 ≤xt-x*2-2(f(xt)-f*)+n2I1Vf(x)川2 (convexity:f(x:)-f*=f(x)-f(x*)(Vf(x),x:-x*)) Advanced Optimization(Fall 2023) Lecture 3.Gradient Descent Method 12
Advanced Optimization (Fall 2023) Lecture 3. Gradient Descent Method 12 The First Gradient Descent Lemma Proof: (Pythagoras Theorem) (GD)
Part 2.Polyak Step Size ·Polyak Step Size Convergence Convergence Rate Advanced Optimization(Fall 2023) Lecture 3.Gradient Descent Method 13
Advanced Optimization (Fall 2023) Lecture 3. Gradient Descent Method 13 Part 2. Polyak Step Size • Polyak Step Size • Convergence • Convergence Rate
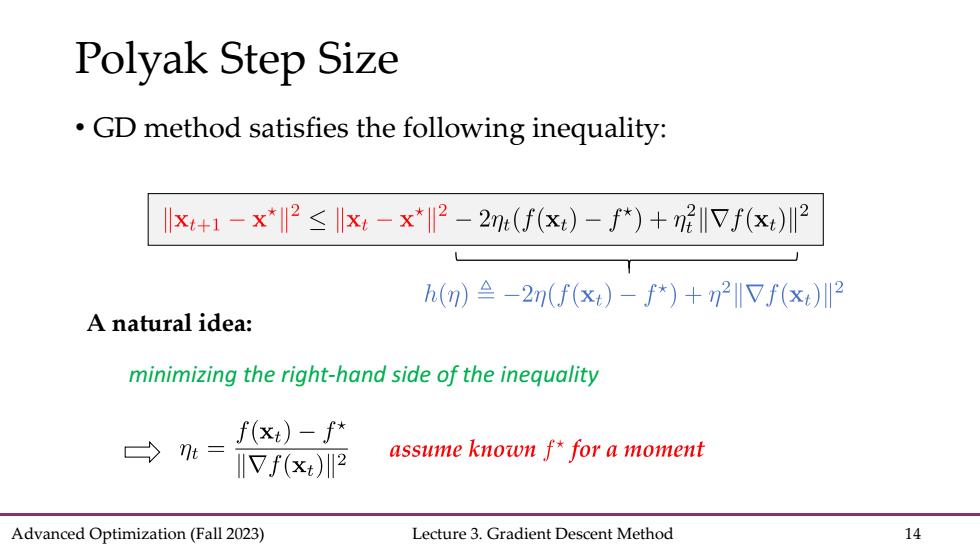
Polyak Step Size GD method satisfies the following inequality: x+1-x*2≤Ix-x*2-2n(f(x)-*)+72I7f(x)2 h()≌-2n(f(xt)-f*)+n2IVf(x)川2 A natural idea: minimizing the right-hand side of the inequality f(x)-f* t= IIVf(x)2 assume known f*for a moment Advanced Optimization(Fall 2023) Lecture 3.Gradient Descent Method 14
Advanced Optimization (Fall 2023) Lecture 3. Gradient Descent Method 14 Polyak Step Size • GD method satisfies the following inequality: A natural idea: minimizing the right-hand side of the inequality

Polyak Step Size x+1-x*2≤x4-x*-2m(f(xt)-f*)+n呢IVf(x)川2 f(xt)-f* = h(n)-2n(f(x:)-f*)+n2f(xt) IVf(2 Cornercase:when Vf(x:)=0 actually a good news owing to convexity,Vf(x)=0 implies optimality f(xi)-f* Vf(x)卡0 Polyak step size:n= llVf(x:), 1, Vf(x:)=0 Without loss of generality,we assume Vf(x)0 from now on. Advanced Optimization(Fall 2023) Lecture 3.Gradient Descent Method 15
Advanced Optimization (Fall 2023) Lecture 3. Gradient Descent Method 15 Polyak Step Size