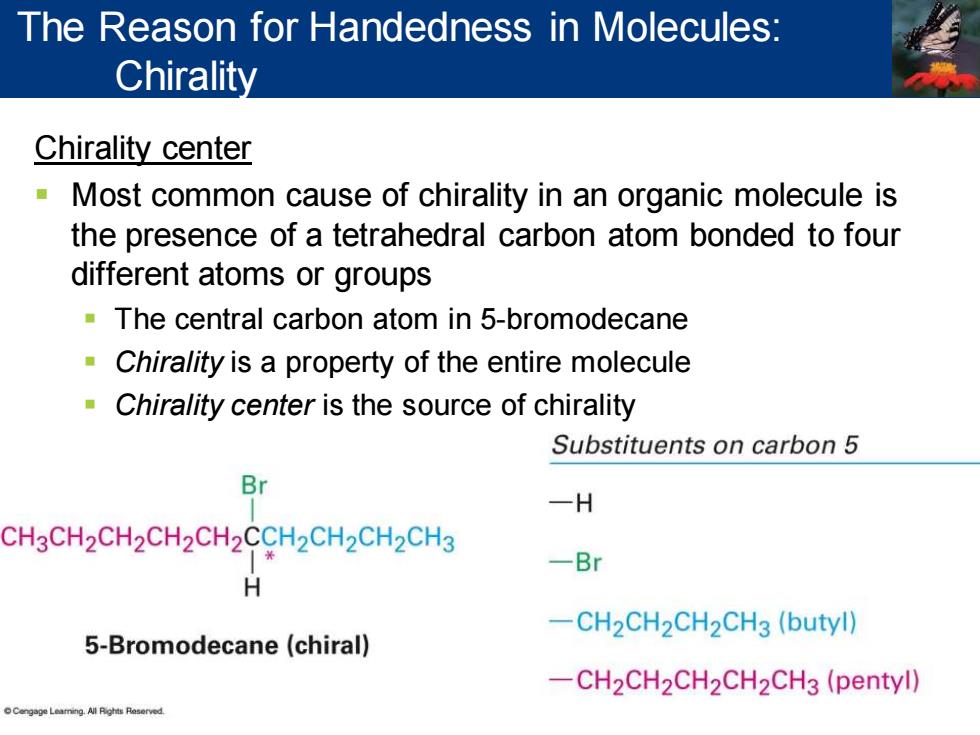
The Reason for Handedness in Molecules: Chirality Chirality center Most common cause of chirality in an organic molecule is the presence of a tetrahedral carbon atom bonded to four different atoms or groups The central carbon atom in 5-bromodecane Chirality is a property of the entire molecule Chirality center is the source of chirality Substituents on carbon 5 Br -H CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CCH2CH2CH2CH3 -Br H -CH2CH2CH2CH3(butyl) 5-Bromodecane (chiral) -CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3(pentyl) Cengsge Leaming.All Rights Reserved
Chirality center ▪ Most common cause of chirality in an organic molecule is the presence of a tetrahedral carbon atom bonded to four different atoms or groups ▪ The central carbon atom in 5-bromodecane ▪ Chirality is a property of the entire molecule ▪ Chirality center is the source of chirality The Reason for Handedness in Molecules: Chirality
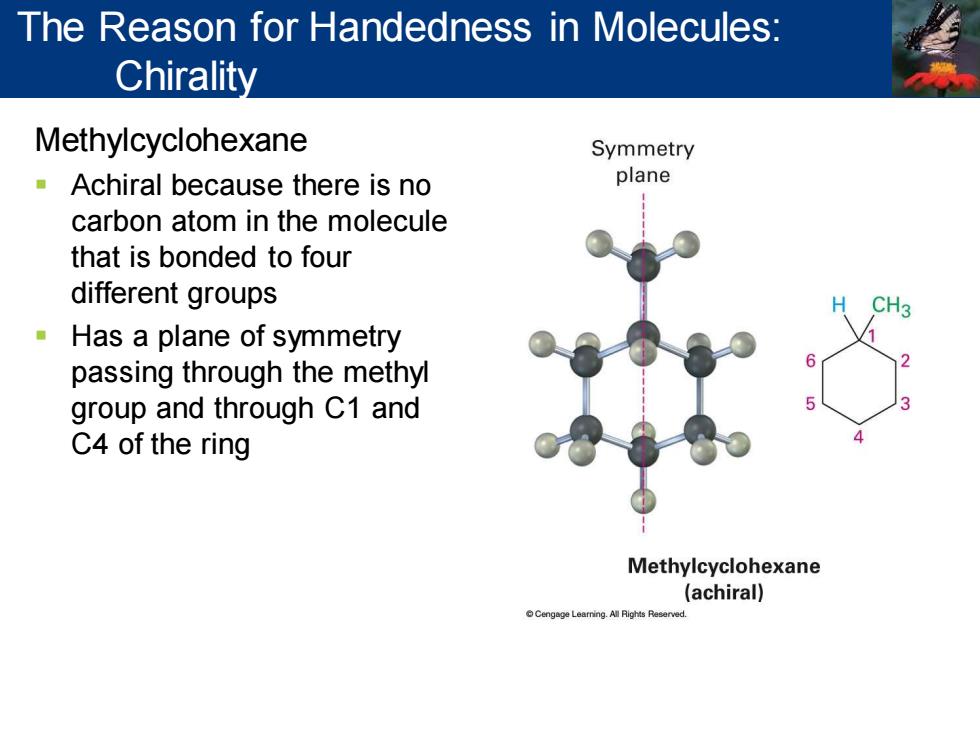
The Reason for Handedness in Molecules: Chirality Methylcyclohexane Symmetry Achiral because there is no plane carbon atom in the molecule that is bonded to four different groups Has a plane of symmetry passing through the methyl group and through C1 and C4 of the ring Methylcyclohexane (achiral) Cengege Learning.All Rights Reserved
Methylcyclohexane ▪ Achiral because there is no carbon atom in the molecule that is bonded to four different groups ▪ Has a plane of symmetry passing through the methyl group and through C1 and C4 of the ring The Reason for Handedness in Molecules: Chirality

The Reason for Handedness in Molecules: Chirality 2-Methylcyclohexanone Chiral because C2 is bonded to four different groups:a- CH3 group,an-H atom,a -COCH2-ring bond (C1)and a-CH2CH2-ring bond (C3) Has no plane of symmetry 2-Methylcyclohexanone (chiral)
2-Methylcyclohexanone ▪ Chiral because C2 is bonded to four different groups: a – CH3 group, an –H atom, a –COCH2– ring bond (C1) and a –CH2CH2– ring bond (C3) ▪ Has no plane of symmetry The Reason for Handedness in Molecules: Chirality

The Reason for Handedness in Molecules: Chirality Note:Carbons in-CH2,-CH3,C=O,C=C,and C=C groups cannot be chirality centers denotes a chirality center CH3 CH3 CH2 H3 H3C CH3 CH2 Carvone (spearmint oil) Nootkatone (grapefruit oil)
▪ Note: Carbons in –CH2 , –CH3 , C=O, C=C, and C≡C groups cannot be chirality centers ▪ * denotes a chirality center The Reason for Handedness in Molecules: Chirality

Worked Example 5.1 Drawing the Three Dimensional Structure of a Chiral Molecule Draw the structure of a chiral alcohol
Draw the structure of a chiral alcohol. Worked Example 5.1 Drawing the Three Dimensional Structure of a Chiral Molecule