
CNGNGE JOHN MCMURRY CHAPTER 3 Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry EDITION Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications
CHAPTER 3 Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry
3-1 Functional Groups Functional group A group of atoms within a molecule that has a characteristic chemical behavior These structural features allow compounds to be classified into families
Functional group ▪ A group of atoms within a molecule that has a characteristic chemical behavior ▪ These structural features allow compounds to be classified into families 3-1 Functional Groups
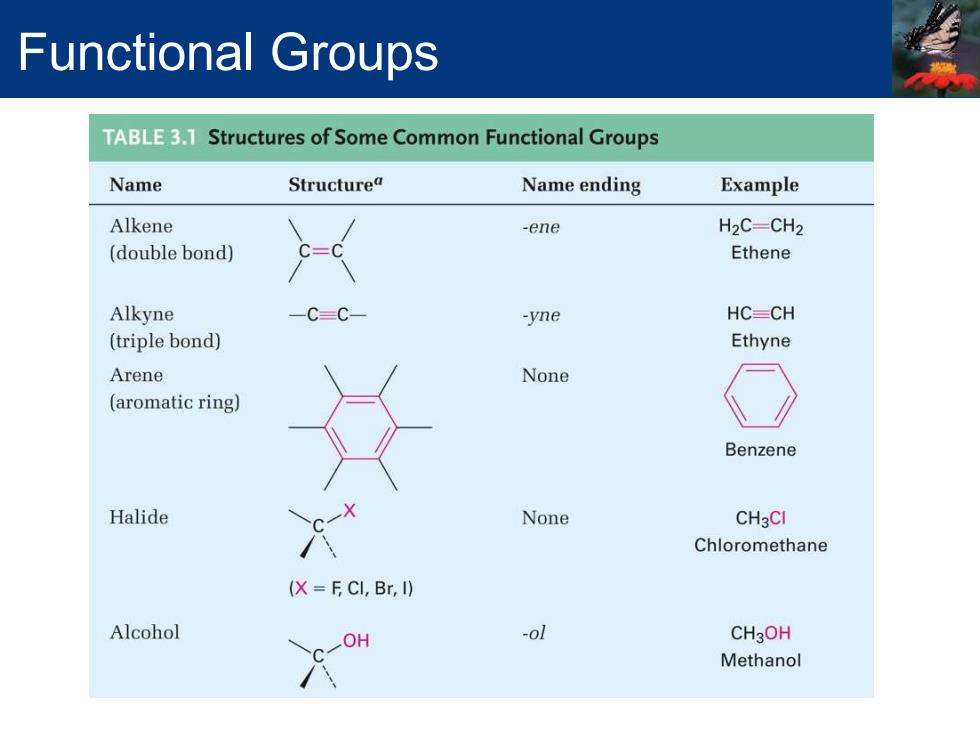
Functional Groups TABLE3.1 Structures of Some Common Functional Groups Name Structurea Name ending Example Alkene -ene H2C-CH2 (double bond) Ethene Alkyne C=C- -yne HC=CH (triple bond) Ethyne Arene None (aromatic ring) Benzene Halide None CH3CI Chloromethane (X F CI,Br,I) Alcohol OH -ol CH3OH Methanol
Functional Groups
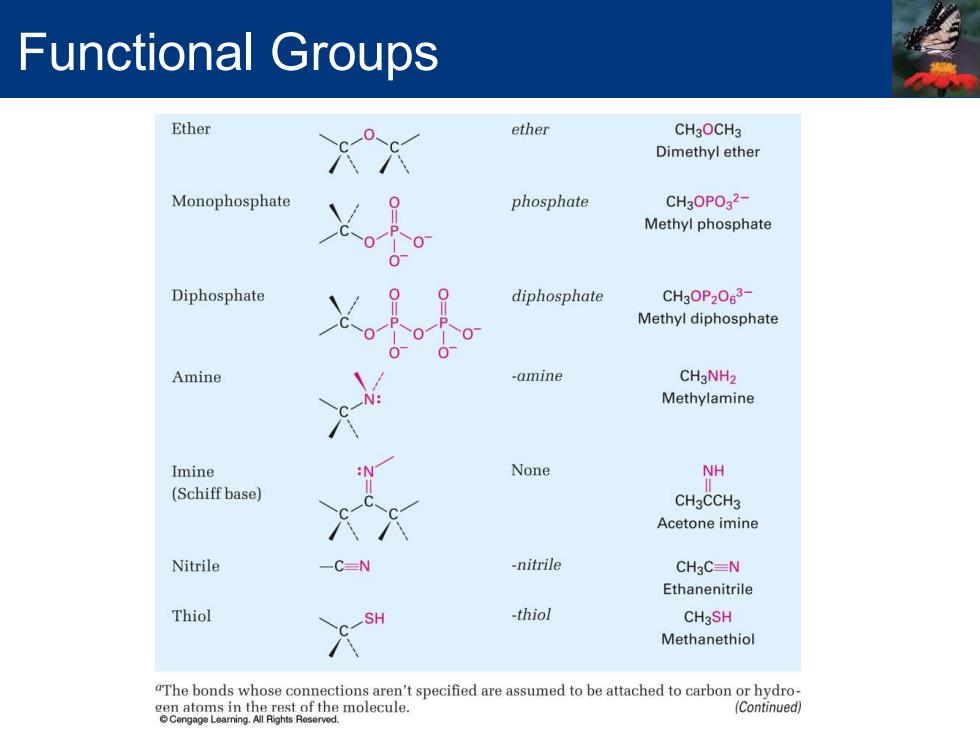
Functional Groups Ether ether CH30CH3 Dimethyl ether Monophosphate phosphate CH3OPO32- Methyl phosphate Diphosphate diphosphate CH3OP2063- Methyl diphosphate Amine -amine CH3NH2 Methylamine Imine None NH (Schiff base) CH3CCH3 Acetone imine Nitrile -C=N -nitrile CH3C=N Ethanenitrile Thiol SH thiol CH3SH Methanethiol "The bonds whose connections aren't specified are assumed to be attached to carbon or hydro- molecule. (Continued)
Functional Groups
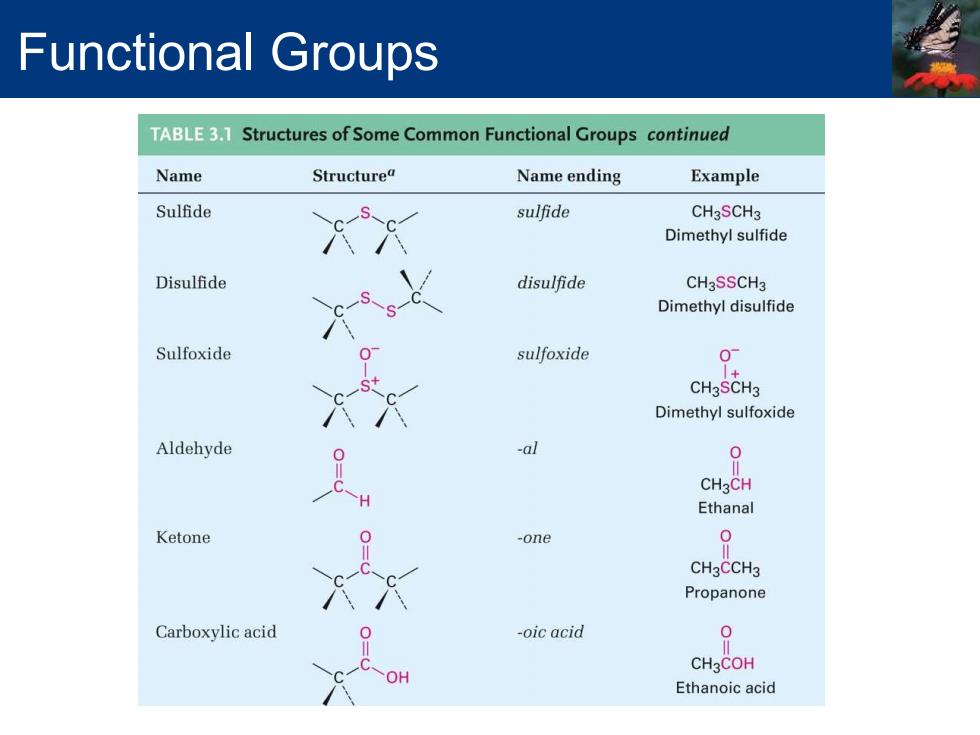
Functional Groups TABLE3.1 Structures of Some Common Functional Groups continued Name Structurea Name ending Example Sulfide sulfide CH3SCH3 Dimethyl sulfide Disulfide disulfide CHaSSCHa Dimethyl disulfide Sulfoxide sulfoxide 0 CH3SCH3 Dimethyl sulfoxide Aldehyde -al CH3CH Ethanal Ketone -one 0 CH3CCH3 Propanone Carboxylic acid -oic acid 0 CH3COH OH Ethanoic acid
Functional Groups