
CNGNGE JOHN MCMURRY CHAPTER 2 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications
CHAPTER 2 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases

2-1 Polar Covalent Bonds: Electronegativity Chemical bonds lonic bonds Bond in sodium chloride is ionic -Sodium transfers an electron to chlorine to give Na+and Cl- lons held together by electrostatic attractions between unlike charges Nonpolar Covalent bonds Two electrons are shared equally by the two bonding atoms Carbon-carbon bond in ethane Symmetrical electron distribution in the bond Most bonds are neither fully ionic or covalent
Chemical bonds ▪ Ionic bonds ▪ Bond in sodium chloride is ionic ▪ Sodium transfers an electron to chlorine to give Na+ and Cl- ▪ Ions held together by electrostatic attractions between unlike charges ▪ Nonpolar Covalent bonds ▪ Two electrons are shared equally by the two bonding atoms ▪ Carbon-carbon bond in ethane ▪ Symmetrical electron distribution in the bond Most bonds are neither fully ionic or covalent 2-1 Polar Covalent Bonds: Electronegativity
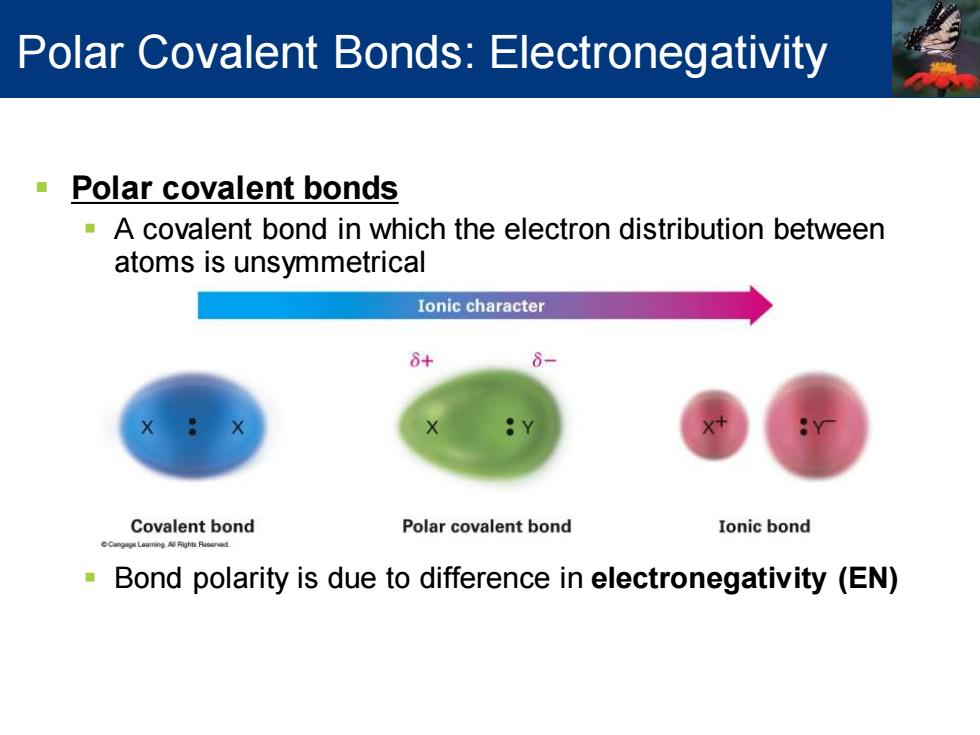
Polar Covalent Bonds:Electronegativity Polar covalent bonds A covalent bond in which the electron distribution between atoms is unsymmetrical Ionic character 8+ Covalent bond Polar covalent bond Ionic bond Bond polarity is due to difference in electronegativity (EN)
▪ Polar covalent bonds ▪ A covalent bond in which the electron distribution between atoms is unsymmetrical ▪ Bond polarity is due to difference in electronegativity (EN) Polar Covalent Bonds: Electronegativity
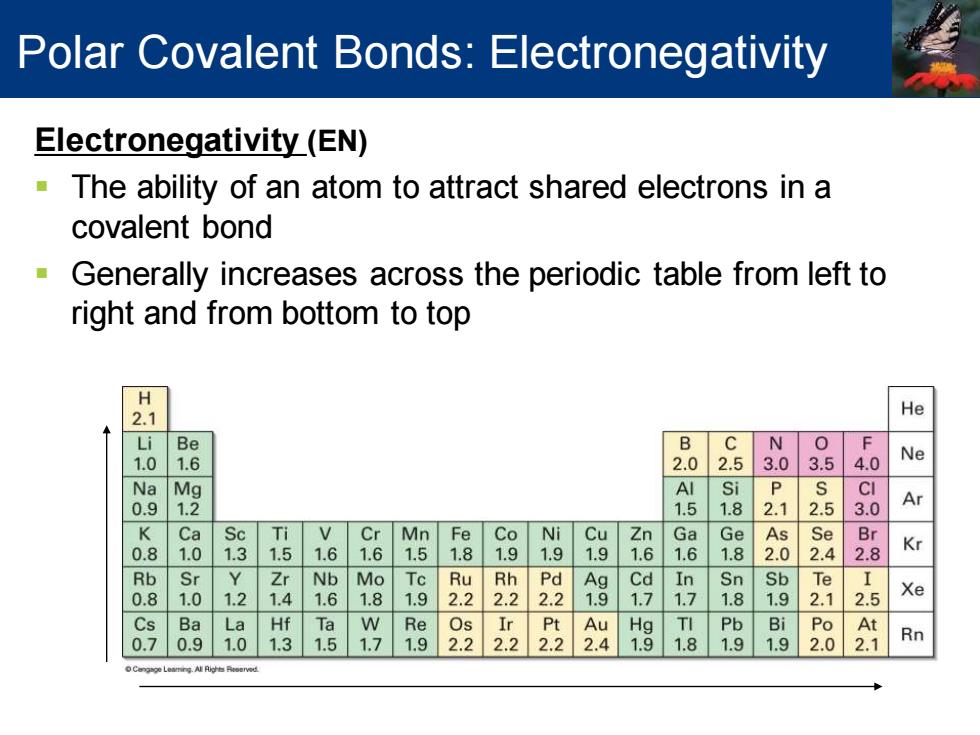
Polar Covalent Bonds:Electronegativity Electronegativity(EN) The ability of an atom to attract shared electrons in a covalent bond Generally increases across the periodic table from left to right and from bottom to top 2.1 He i Be B C N 1. 6 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 Ne N Mg Al i P CI 0. 2 1.5 1. 2.5 Ar K Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br . 0 1.3 1.5 1.6 1.6 5 1.8 9 1.9 9 6 1.6 1.8 2.0 2.4 2.8 Kr Rb Sr Zr Nb Mo Ru 22 22 铝 Cd In Sn Sb Te 8 1 1.2 4 6 8 1.9 2 7 7 8 9 2.1 2.5 Xe Cs Ba La Hf Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg TI Pb Bi Po At 0.7 .9 1.0 1.3 1.5 1.7 1.9 2.2 2.2 2.22.4 1.9 1.81.9 1.9 2.0 2.1 Rn
Electronegativity (EN) ▪ The ability of an atom to attract shared electrons in a covalent bond ▪ Generally increases across the periodic table from left to right and from bottom to top Polar Covalent Bonds: Electronegativity

Electronegativity and Bond Types Bonds between atoms whose electronegativities differ by less than 0.5 are nonpolar covalent Bonds between atoms whose electronegativities differ by 0.5 to 2.0 are polar covalent Bonds between atoms whose electronegativities differ by more than 2.0 are largely ionic Carbon hydrogen bonds are nonpolar.Bonds between carbon (EN 2.5)and more electronegative elements,such as oxygen (EN 3.5)and nitrogen (EN 3.0)are polar covalent bonds with the bonding electrons drawn towards the more electronegative atoms
▪ Bonds between atoms whose electronegativities differ by less than 0.5 are nonpolar covalent ▪ Bonds between atoms whose electronegativities differ by 0.5 to 2.0 are polar covalent ▪ Bonds between atoms whose electronegativities differ by more than 2.0 are largely ionic Carbon hydrogen bonds are nonpolar. Bonds between carbon (EN = 2.5) and more electronegative elements, such as oxygen (EN = 3.5) and nitrogen (EN = 3.0) are polar covalent bonds with the bonding electrons drawn towards the more electronegative atoms Electronegativity and Bond Types