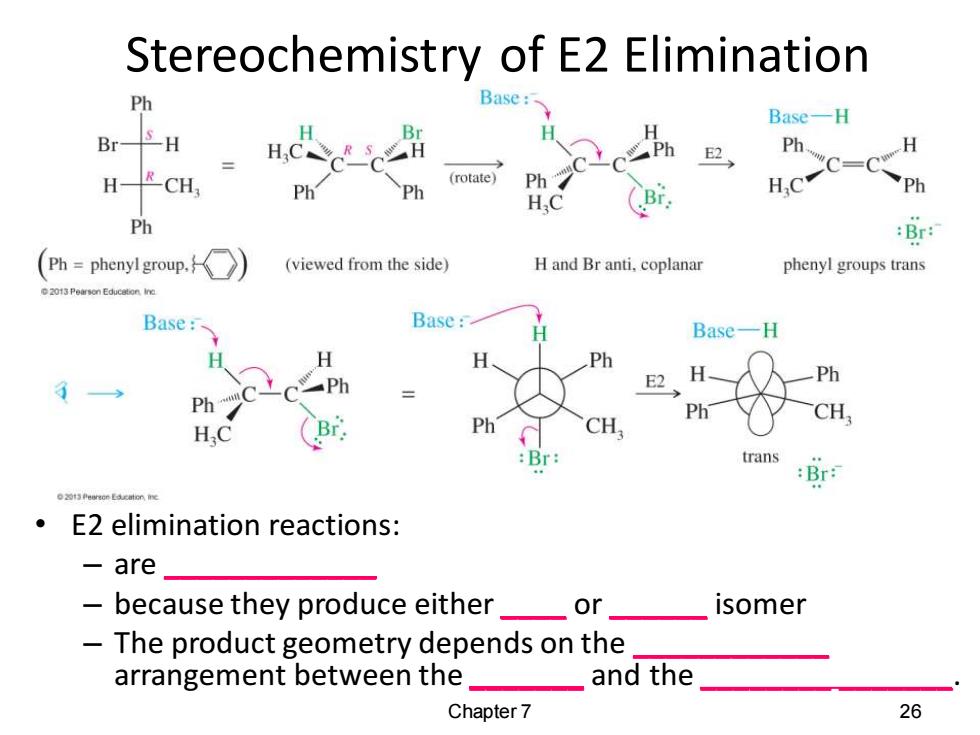
Stereochemistry of E2 Elimination Ph Base: Base-H Br-5H E2 Ph. H C=C H-RCH (rotate) Ph H.C ph H.C Ph :Br: Ph=phenyl group. (viewed from the side) H and Br anti.coplanar phenyl groups trans Base: Base: Base-H H H Ph Ph E2 Ph Ph Ph Ph CH. CH (Br :Br: trans :Br: E2 elimination reactions: -are because they produce either or isomer The product geometry depends on the arrangement between the and the Chapter 7 26
Stereochemistry of E2 Elimination • E2 elimination reactions: – are _____________ – because they produce either ____ or ______ isomer – The product geometry depends on the ____________ arrangement between the _______ and the ________ _______. Chapter 7 26
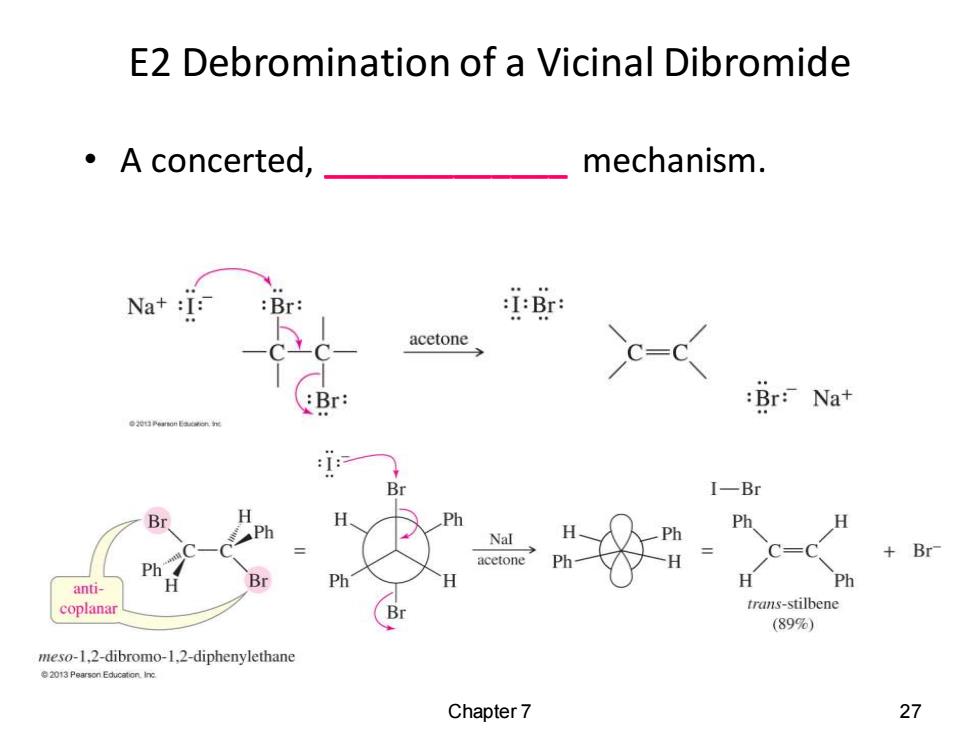
E2 Debromination of a Vicinal Dibromide ·A concerted, mechanism. Na+:I: :Br: :I:Br: acetone :Br: Br:Nat Br I-Br Br h Ph H Ph Nal +Br acetone C=C anti- Br Ph H Ph coplanar trans-stilbene (89) meso-1,2-dibromo-1.2-diphenylethane 2013 Pearson Educaton.in: Chapter 7 27
E2 Debromination of a Vicinal Dibromide • A concerted, _____________ mechanism. Chapter 7 27

E1 Elimination Mechanism:Dehydration of Alcohols -C- acidic catalyst,heat C-C+H.O H OH Step 1:Protonation of the hydroxyl group(fast equilibrium) Step 2:lonization to a carbocation(slow;rate limiting). H H:OH HSO Step 3:Deprotonation to give the alkene(fast) -ci +hò: + H,0+ Chapter 7 28
Chapter 7 28 E1 Elimination Mechanism: Dehydration of Alcohols Step 1: Protonation of the hydroxyl group (fast equilibrium). Step 2: Ionization to a carbocation (slow; rate limiting). Step 3: Deprotonation to give the alkene (fast)

Markovnikov's Rule CH CH3 CH3一CCH一CH add H'to secondary carbon CH,-C-CH-CH, →HB H Br tertiary carbocation CH; CH;-C-CH-CH3 add H to tertiary carbon CH3-C-CH-CH3 HBr H Br secondary carbocation The proton adds to the carbon with more hydrogens The acid proton will bond to carbon 3 in order to produce the most _possible. This is an example of Chapter8 29
Markovnikov’s Rule The acid proton will bond to carbon 3 in order to produce the most _______ ____________ possible. Chapter 8 29 This is an example of _____________ The proton adds to the carbon with more hydrogens

Anti-Markovnikov Product Free-Radical Addition of HBr Initiation: The peroxide bond breaks homolytically to form the first radical: R-O0-RmR-0:+0-R 4H°=+150kJ(+36kca) The peroxide effect is strongly endothermic with HCI or HI Hydrogen is abstracted from HBr to form the Chapter8 30
Free-Radical Addition of HBr • The peroxide bond breaks homolytically to form the first radical: • Hydrogen is abstracted from HBr to form the ________ ________ . Chapter 8 30 Initiation: Anti-Markovnikov Product The peroxide effect is strongly endothermic with HCl or HI