
Other Inhalation:provides the rapid delivery across the surface area of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract Intranasal:desmopressin in the treatment of diabetes insipidus. Intrathecal/intraventricular:to introduce drugs directly into the CSF. Topical:the application is used when a local effect of the drug is desired
Other ◼ Inhalation: provides the rapid delivery across the surface area of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract. ◼ Intranasal: desmopressin in the treatment of diabetes insipidus. ◼ Intrathecal/intraventricular: to introduce drugs directly into the CSF. ◼ Topical: the application is used when a local effect of the drug is desired
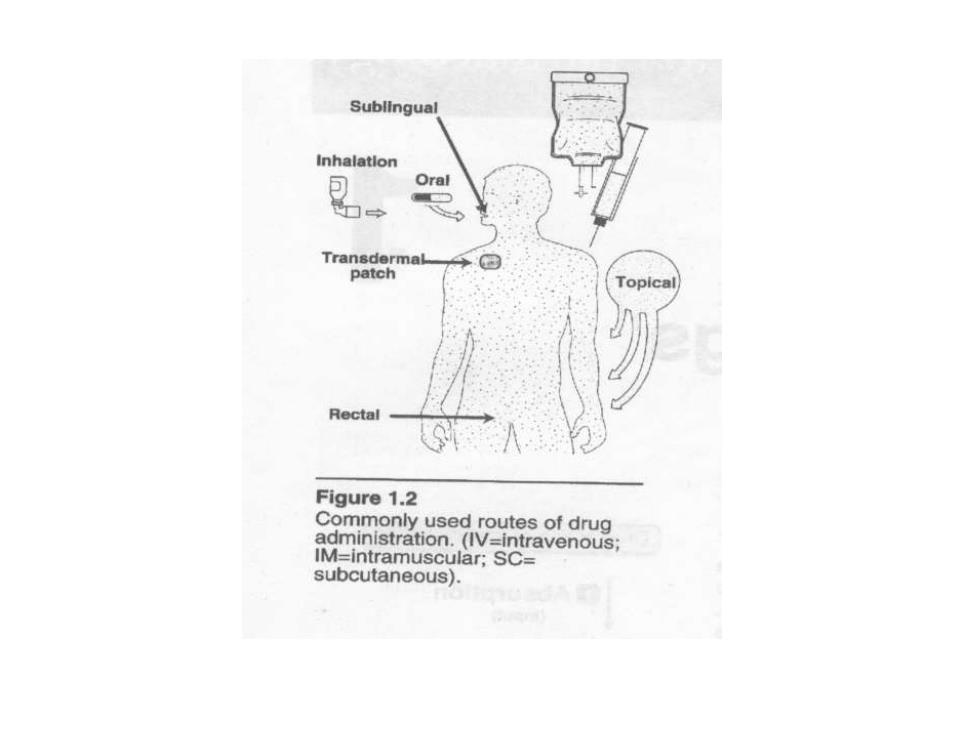
Sublingual Inhalation Oral patch Topica Rectal Figure 1.2 Commonly used routes of drug administration.(IV=intravenous; IM=intramuscular;SC= subcutaneous)

Absorption of drugs Absorption is the transfer of a drug from its site of administration to the blood stream. The rate and efficiency of absorption depend on the route of administration
Absorption of drugs ◼ Absorption is the transfer of a drug from its site of administration to the blood stream. The rate and efficiency of absorption depend on the route of administration

Transport of drug from the GI tract Passive diffusion:moves from a region of high concentration to one of lower concentration. Active transport:involves specific carrier proteins.Energy-dependent.Against a concentration gradient
Transport of drug from the GI tract ◼ Passive diffusion: moves from a region of high concentration to one of lower concentration. ◼ Active transport: involves specific carrier proteins. Energy-dependent. Against a concentration gradient

Effect of pH on drug absorption Weak acids or weak bases HAH++A+ BH B+H+ the effective concentration of the permeable form of each drug at its absorption site is determined by the relative concentrations of the charged and uncharged forms
Effect of pH on drug absorption ◼ Weak acids or weak bases HA H++A + BH B+H+ the effective concentration of the permeable form of each drug at its absorption site is determined by the relative concentrations of the charged and uncharged forms